This document provides information about noun clauses and verb tenses in English. It discusses:
1) The common functions of noun clauses as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, and objects of prepositions. It also discusses alternative words that can be used in place of "that" in noun clauses.
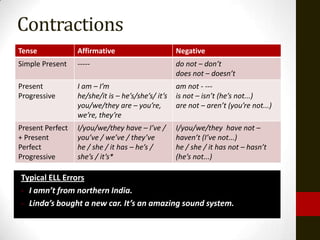
2) How verbs are backshifted in reported speech when the reporting verb is in the simple past tense. It also discusses verbs like "should", "ought to", and "might" that do not change in reported speech.
3) How the simple past, past perfect, and modal "would" are used to make wishes about the present, past, and future.
4) How the present