The document provides information on various tenses in English including:
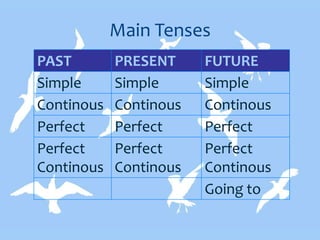
- Main tenses are simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous in past, present, and future.
- Simple present tense is used for habits, general truths, future meaning with timetables.
- Present continuous emphasizes ongoing or temporary actions.
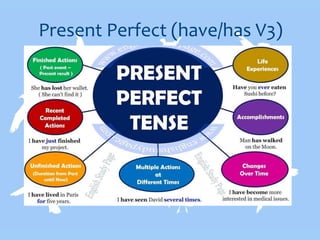
- Present perfect is used for unfinished or recent past actions with present results.
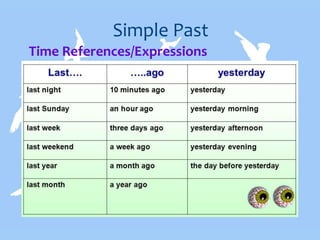
- Simple past tense expresses completed actions, narratives, and habitual past actions.
- Past continuous emphasizes parallel or interrupted past actions.
- Past perfect expresses actions completed before other past actions.