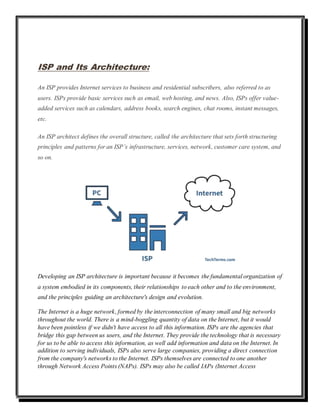
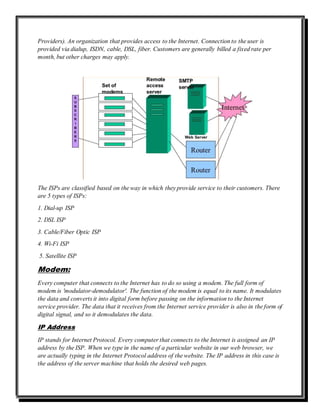
An ISP provides internet access and services to both residential and business subscribers. An ISP architect defines the overall structure and architecture of an ISP's infrastructure, network, services, and customer care system. There are different types of ISPs classified based on how they provide service, including dial-up, DSL, cable/fiber optic, Wi-Fi, and satellite. An ISP connects users to the internet through modems that modulate and demodulate data, and assigns IP addresses using DHCP to allow connection and identification of devices.