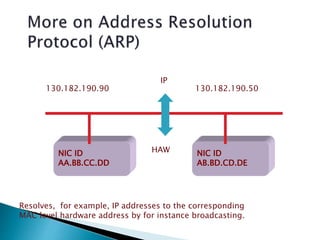
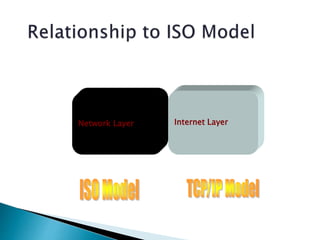
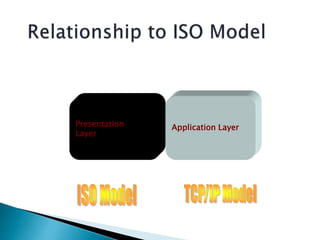
TCP/IP is a standardized protocol used widely on the Internet. It has four layers - transport, internet, data link, and physical. The transport layer includes TCP and UDP which handle packet sequencing, transmission, and delivery to the application layer. The internet layer includes IP, ARP, and ICMP which handle addressing, routing, and error reporting.