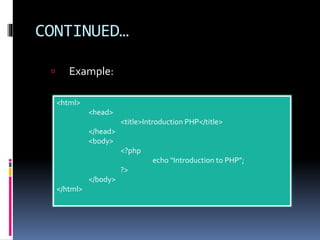
The document provides an introduction to writing and running PHP scripts, including embedding scripts in HTML and executing them via a web browser. It covers key concepts such as data types, variable declaration rules, constants, and various operators in PHP. The document serves as a foundational guide for understanding basic PHP programming principles.







![VARIABLES
Variables are declared memory that contains
data during execution.
Rules to declare variable_
Only $, [A-Z, a-z], [0-9] and underscore are
allowed.
Every name must preceded by the $ sign.
After the $ sign there must be an alphabet or
underscore.
E.g. $var_name, $varName, $abc123, $_1234 etc
are some valid declaration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2basicsofphp-170215181627/85/basics-of-php-9-320.jpg)