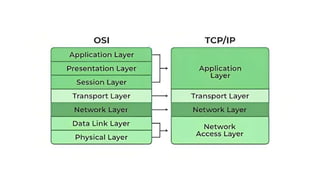
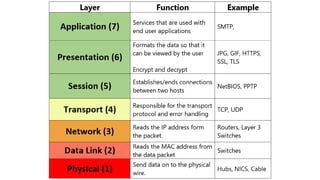
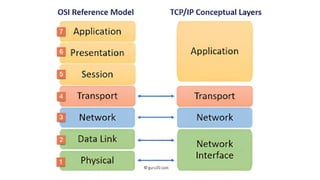
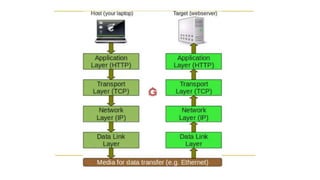
The document discusses the four layers of the TCP/IP model:
(1) Application layer which provides access to networked services and contains protocols like TCP and UDP;
(2) Transport layer which ensures reliable delivery using protocols like TCP and UDP;
(3) Internet layer which handles data routing using the IP protocol;
(4) Link layer which consists of device drivers and network interface cards to communicate over physical media like cables.