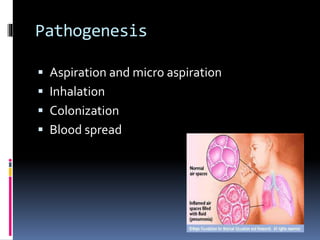
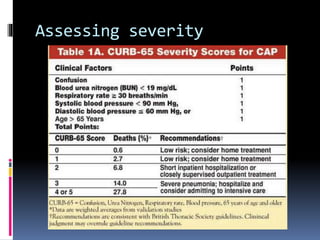
This document discusses pneumonia, including its definition, classifications, pathogenesis, predisposing factors, clinical features, investigations, differential diagnosis, and assessment of severity. Pneumonia is an acute infection of the lungs, usually bacterial, that causes inflammation and consolidation visible on imaging. It can be classified anatomically by location in the lungs or empirically based on where it was acquired. Risk factors include smoking, viral infections, alcohol use, medications, age, and underlying lung disease. Diagnosis involves identifying the infecting organism through sputum or blood tests as well as chest imaging.