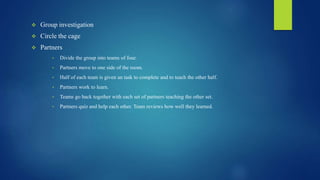
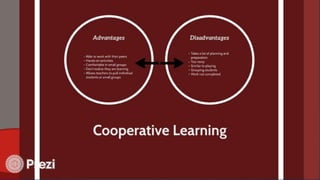
The document discusses Computer Assisted Language Learning (CALL) as an interactive teaching method utilizing technology to enhance language proficiency and communicative competence. It outlines its objectives, benefits, and characteristics, emphasizing learner-centered approaches such as communicative language teaching and task-based learning. The text also covers teaching roles, cooperation in learning, and various innovative strategies for effective language instruction.