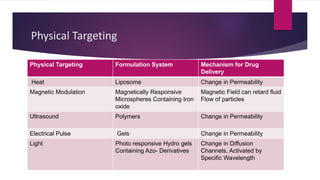
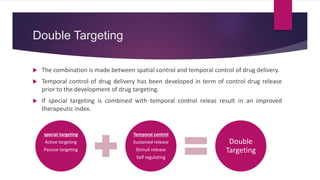
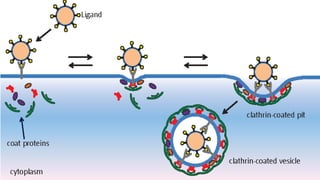
The document discusses targeted drug delivery systems. It describes how targeted delivery aims to selectively deliver drugs to specific targets like cells or organs while limiting exposure to non-target tissues to maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity. This is achieved through various carrier systems and targeting strategies, including passive targeting which utilizes natural biodistribution, and active targeting using ligands to bind carriers to receptors on target sites. The biological processes involved in targeted delivery include cellular uptake, transport across barriers like epithelia, extravasation from blood vessels, and lymphatic uptake.