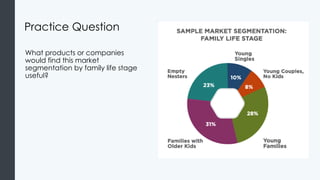
The document discusses segmentation and targeting in marketing, emphasizing the importance of dividing potential customers into groups to better understand and serve them. It outlines five criteria for a market, objectives of segmentation, and common market segmentation approaches, including demographic, psychographic, and behavioral criteria. The document also explores targeting strategies and how they influence the marketing mix, guiding marketers in selecting appropriate segments and effectively directing their efforts.