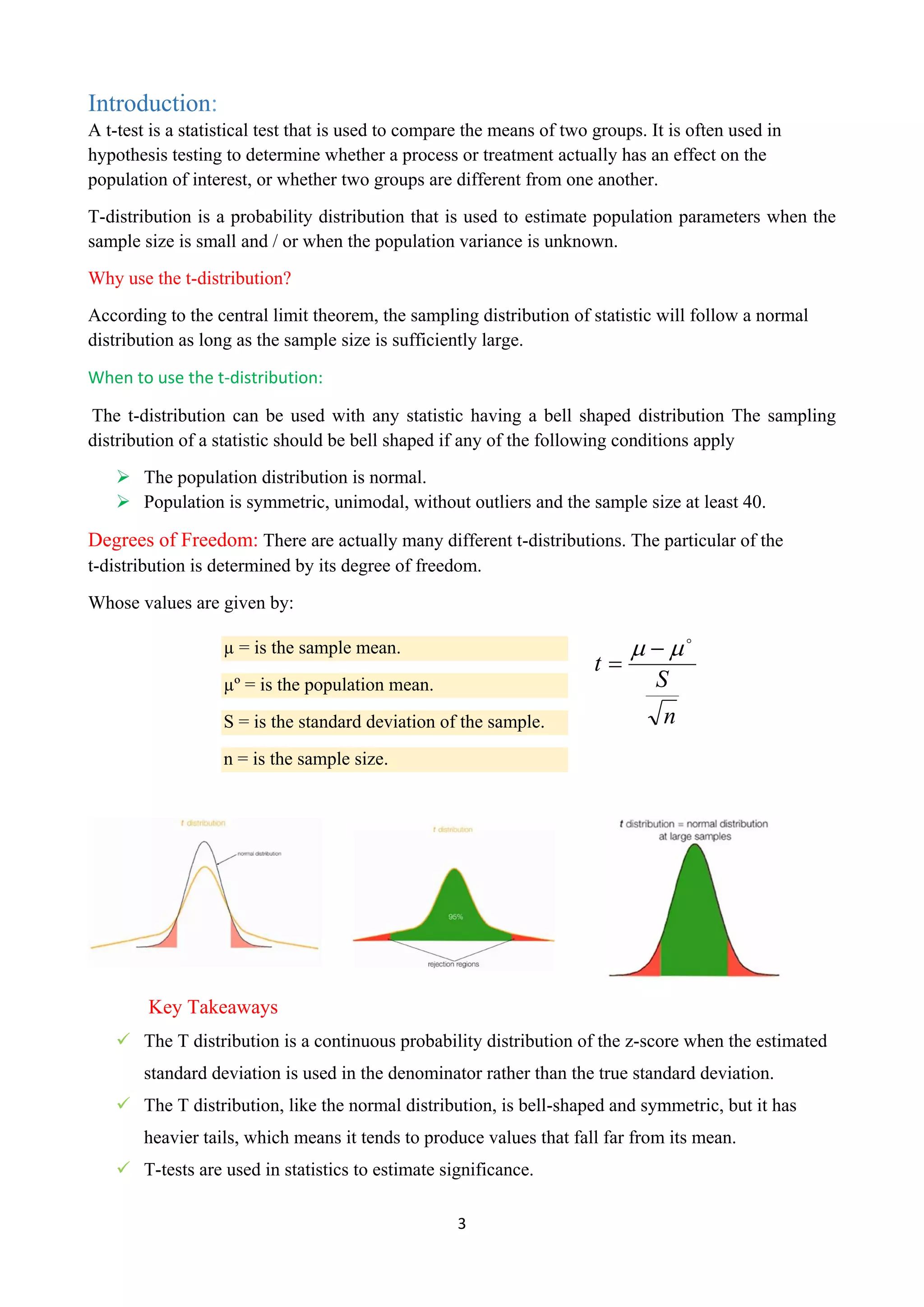
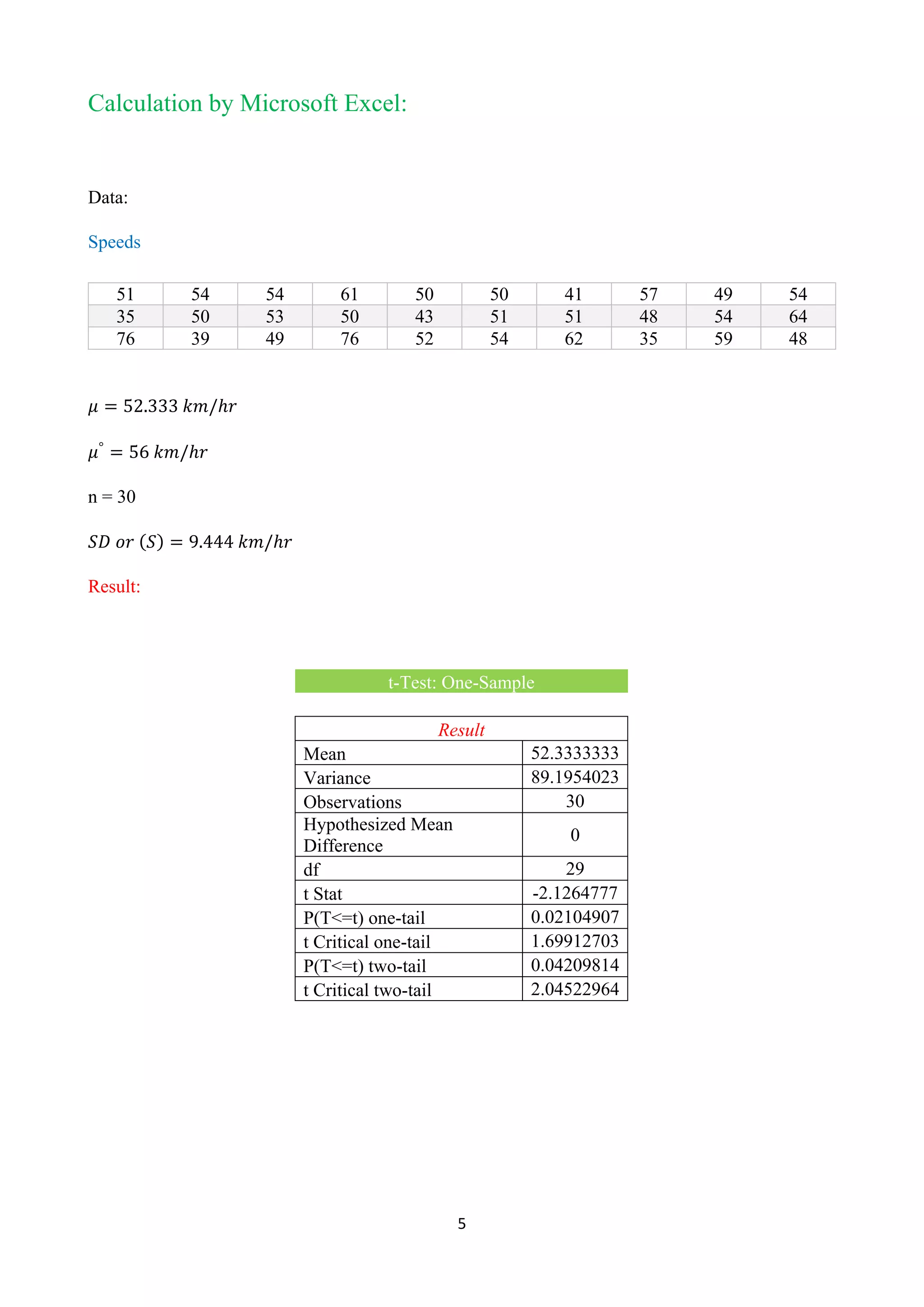
The document discusses the t-test, a statistical method used for comparing the means of two groups, particularly when the sample size is small and population variance is unknown. It explains the concept of t-distribution, degrees of freedom, and provides calculations for t-tests using both manual methods and Microsoft Excel. Key learning outcomes include determining hypotheses, summarizing data into test statistics, and deciding on statistical significance based on p-values.



![8
Discussion:
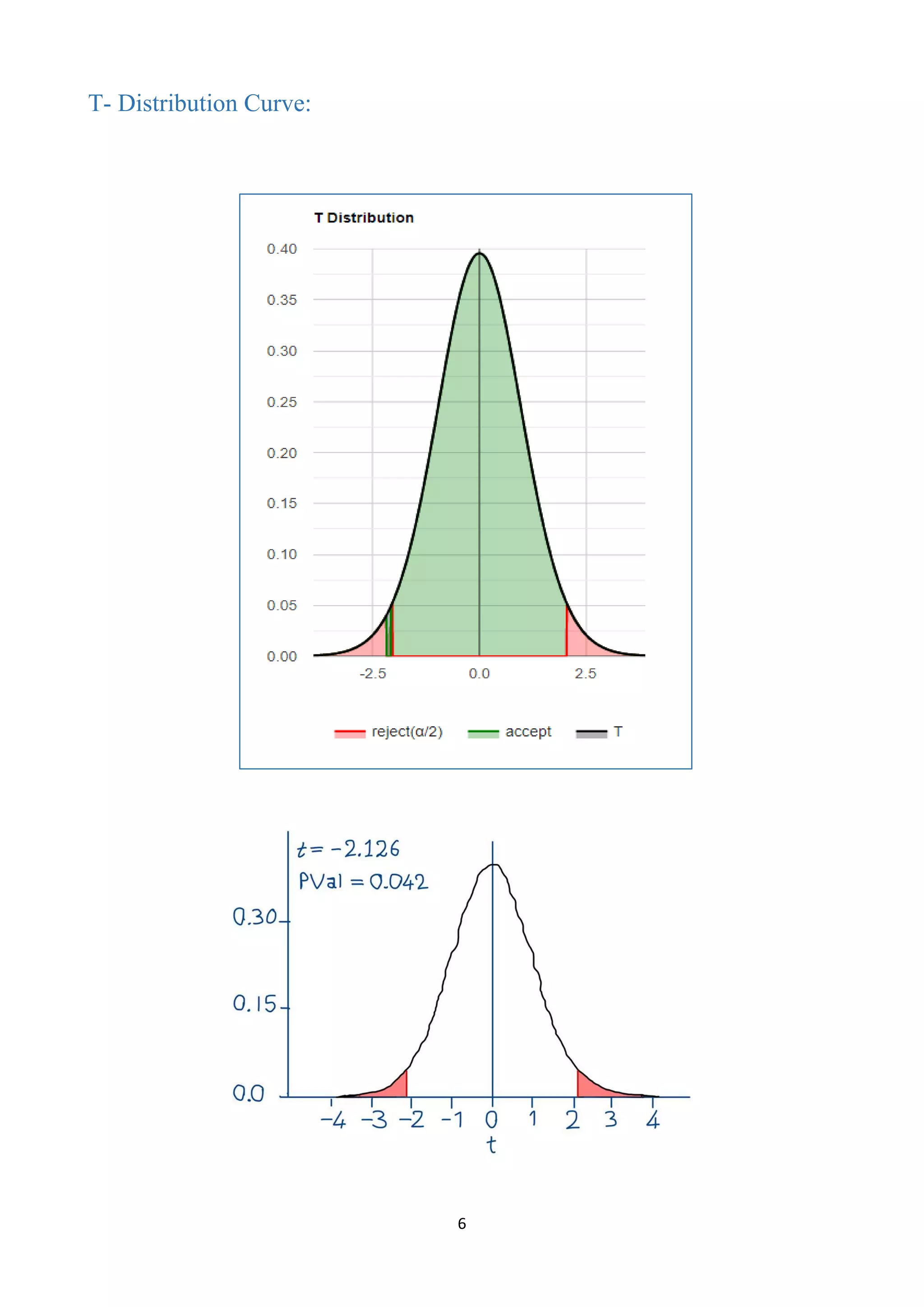
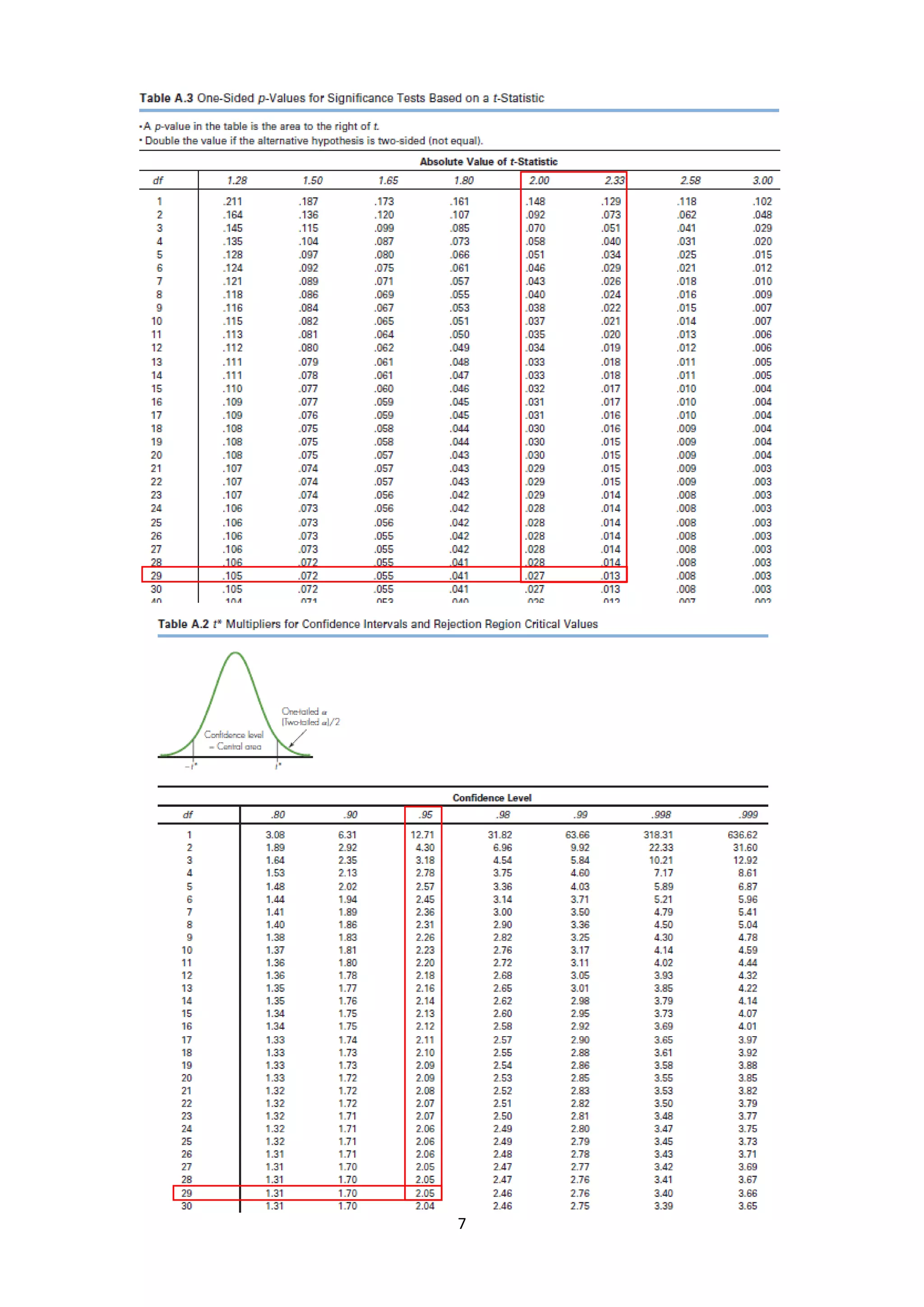
One sample t-test, using T distribution (DF=29) (two-tailed) (validation)
Since p-value < α, H0 is rejected.
The average of Speed's population is considered to be not equal to the μ0.
In other words, the difference between the average of the Speed and μ0 is big enough to be
statistically significant.
p-value equals 0.0420981, ( p( x ≤ T ) = 0.0210491 ). This means that the chance of type1 error
(rejecting a correct H0) is small: 0.04210 (4.21%).
The smaller the p-value the more it supports Ha.
The test statistic T equals -2.126478, is not in the 95% critical value accepted range: [-2.0452 :
2.0452].
x=52.33, is not in the 95% accepted range: [52.4700 : 59.5300].
The statistic S' equals 1.724 .
The observed standardized effect size is medium (0.39). That indicates that the magnitude of the
difference between the average and μ0 is medium.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bahzad-230110180348-617942c4-230111060239-57bdcf04/75/T-Distribution-Report-8-2048.jpg)


