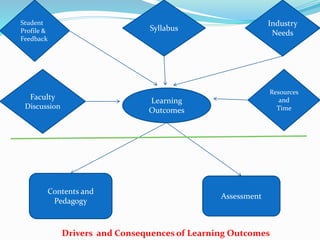
The document explains the distinction between a syllabus and a course outline, portraying the syllabus as a static guideline based on subject standards, while the course outline is dynamic, contextual, and reflects the instructor's approach. It highlights the importance of learning outcomes as central to course success and discusses various approaches to course design, emphasizing the need for alignment between learning outcomes, content, and assessment methods. Additionally, it identifies common problems in course design, including incoherence and misalignment between course components.