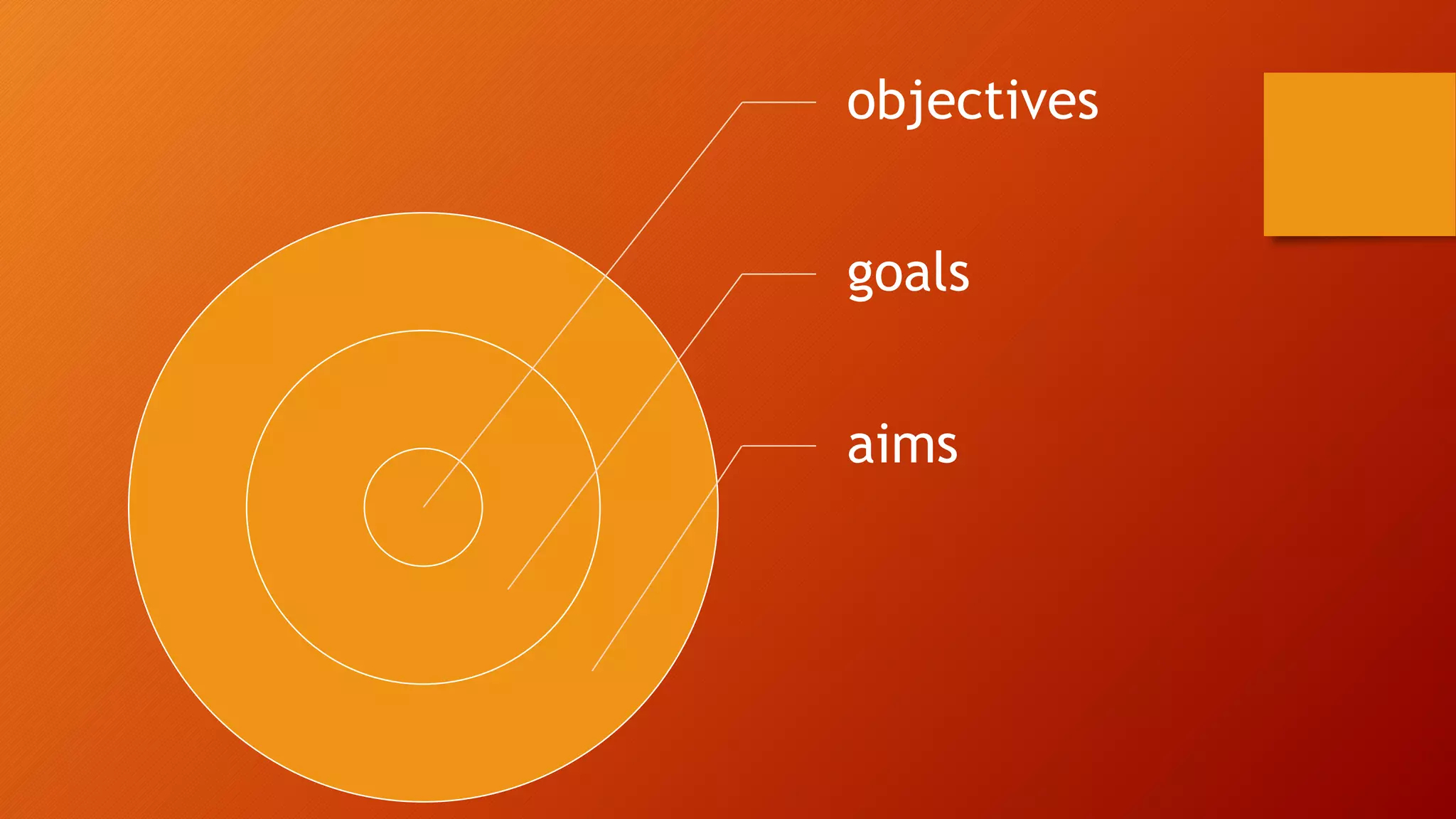
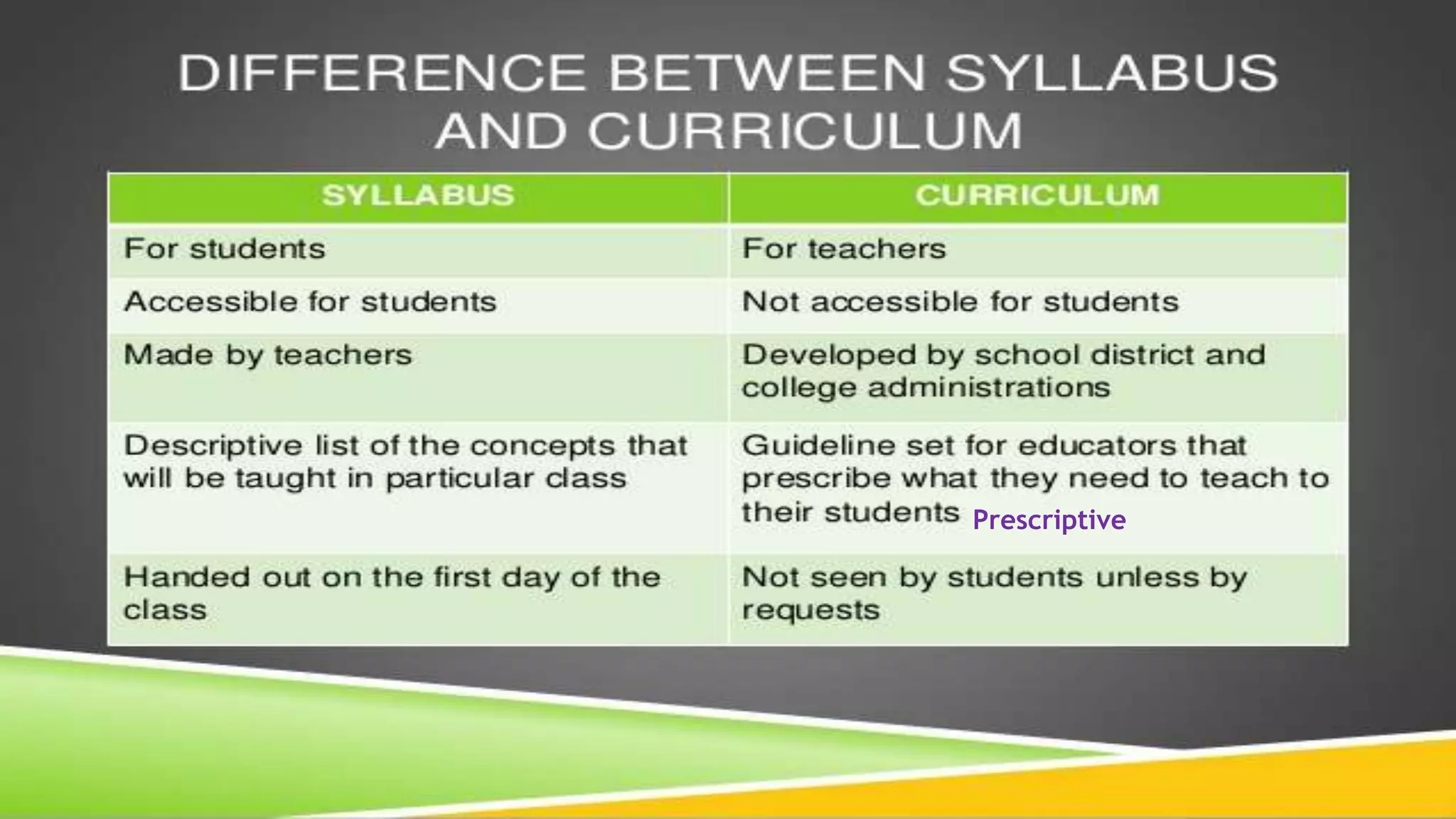
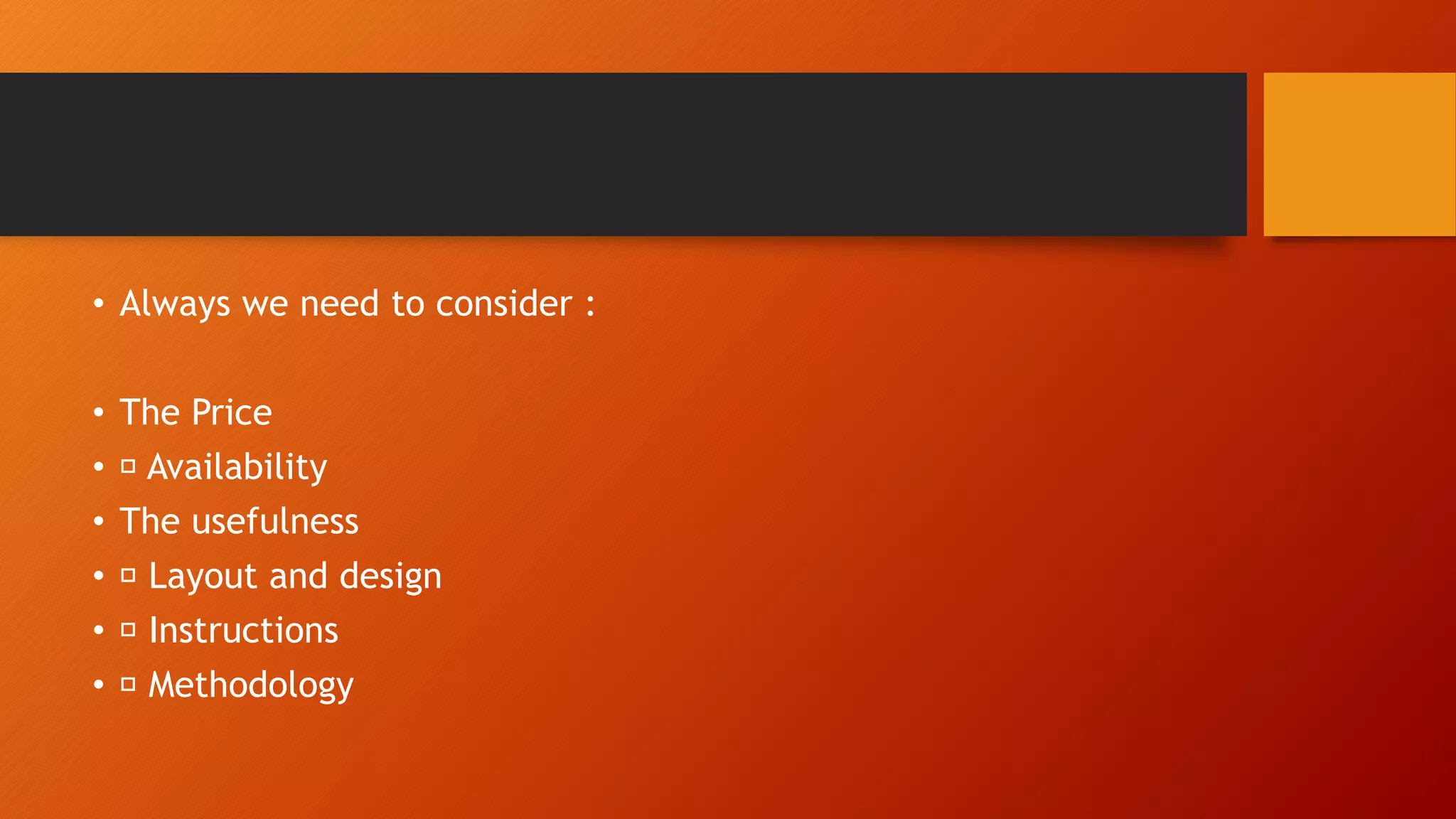
This document discusses curriculum and course design. It defines key terms like curriculum, program, syllabus, and course. It also outlines the main factors to consider in situation analysis for curriculum planning like educational setting, class characteristics, and course content. The document recommends performing a needs analysis and specifying goals, objectives, and aims. It provides examples of conceptualizing a course syllabus and assessing students. Key steps in revising a course are outlined as seeing the need for change, determining the extent of change, engaging in realistic change, and following principled teaching.