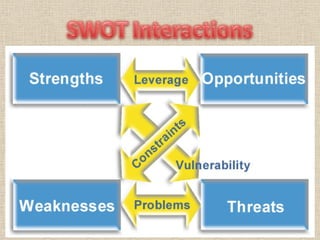
The document discusses SWOT analysis, which is a tool used to evaluate a firm's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It provides examples of various internal and external factors that could be considered for each category. These include resources, reputation, new technologies, shifts in customer tastes, and more. The document also explains how to construct a SWOT matrix and use the results to develop strategies through TOWS analysis, with the goal of pursuing opportunities that leverage strengths while overcoming weaknesses and reducing vulnerability to threats.