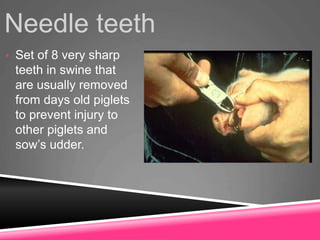
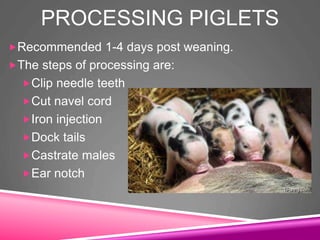
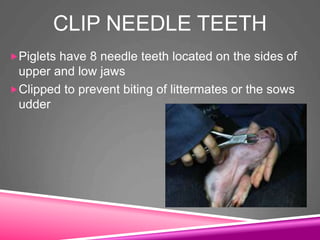
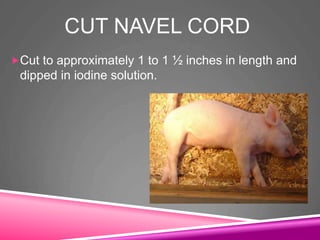
This document provides information on swine production. It discusses the objectives and terminology of swine farming, describes various pig breeds such as Berkshire and Yorkshire, and outlines management practices including feeding, farrowing, and processing piglets. Key topics covered include the social hierarchy of pigs, their behavior and intelligence, growth and reproductive development, and common diseases. The document concludes by outlining areas to evaluate pigs such as muscle, fat cover, soundness, and general appearance.