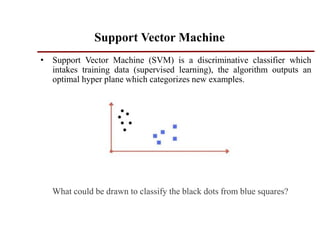
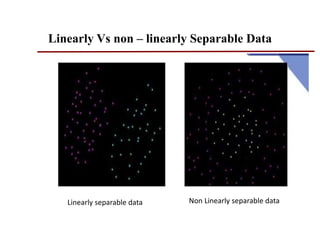
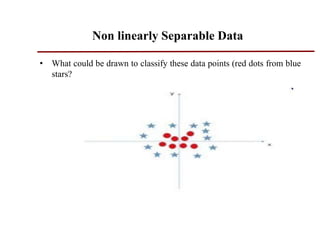
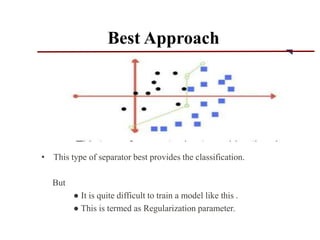
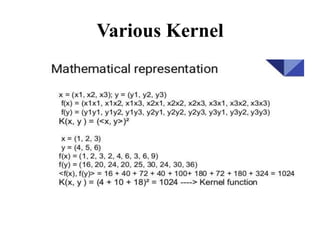
Support vector machines (SVMs) are classifiers that output an optimal separating hyperplane to categorize data points. SVMs can handle both linearly and non-linearly separable data using techniques like kernels, regularization, tuning the gamma and margin parameters. Key aspects of SVMs include maximizing the margin distance between the hyperplane and closest data points (support vectors), using kernels to transform data non-linearly, and adjusting regularization (C parameter) to control overfitting/underfitting.