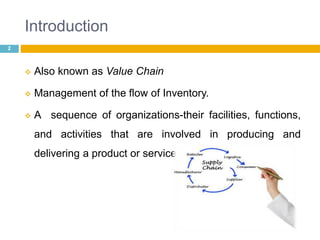
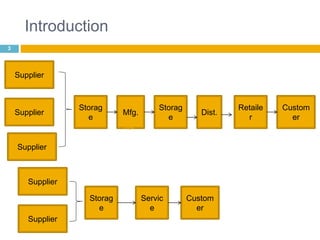
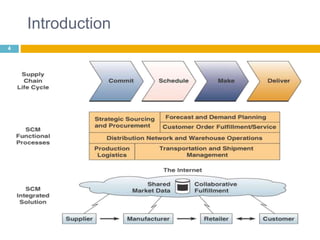
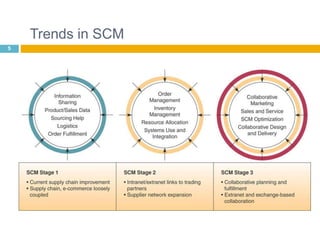
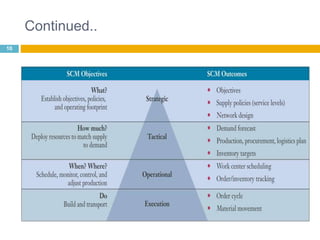
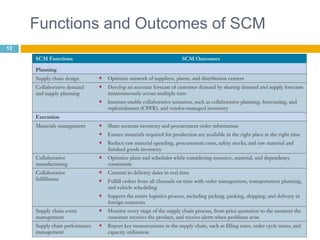
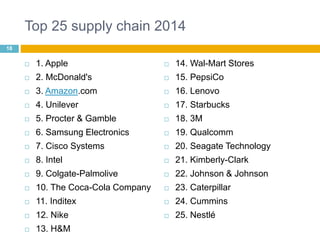
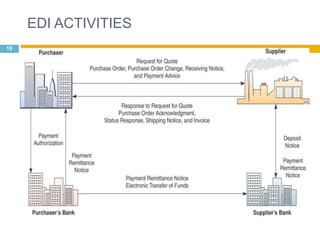
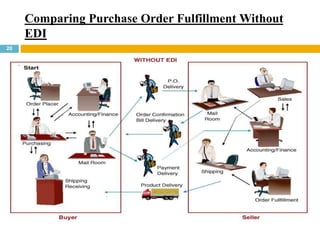
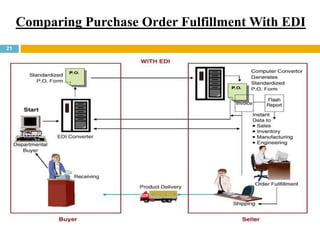
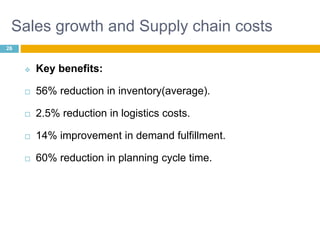
This document discusses supply chain management (SCM). It provides an introduction to SCM, including that it is also known as a value chain and involves the management of inventory flows across organizations. It discusses the importance of SCM in gaining efficiencies, reducing costs, and meeting competitive pressures. The objectives of SCM are also outlined, such as rapid demand fulfillment and giving customers what they want at low costs. Different SCM modules, functions, issues, software solutions, and EDI activities are described. It concludes with a case study of how Bharat Petroleum reduced logistics and distribution costs by 56% and inventory levels by 60% using SAP Supply Chain Management software.