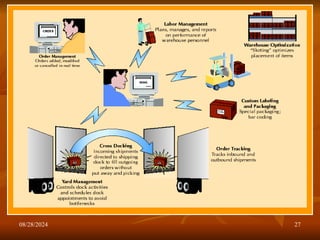
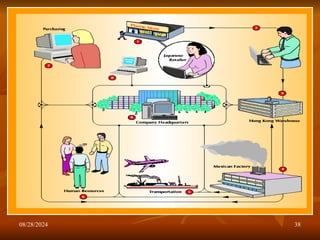
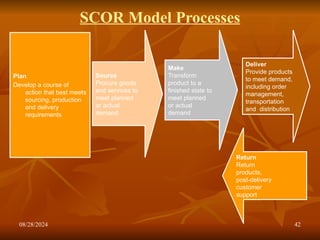
The document outlines the fundamentals of supply chain management (SCM), detailing its importance, definitions, processes, and decision phases. It highlights the roles of information technology and collaboration in enhancing supply chain efficiency while addressing challenges such as uncertainty and global trade complexities. Key performance indicators for measuring supply chain success are also discussed.