This document provides information about Samsung, including:
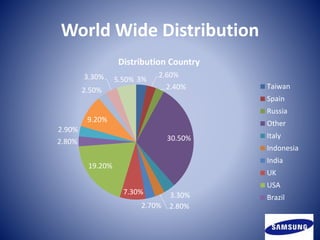
1. Samsung is a South Korean multinational electronics company founded in 1938 that operates in 80 countries with over 307,000 employees.
2. Samsung has a diversified product portfolio and invests heavily in research and development, with over 42,000 employees working in R&D.
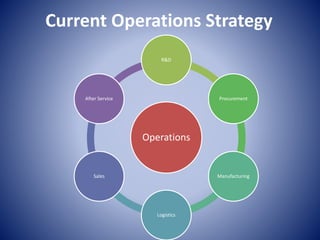
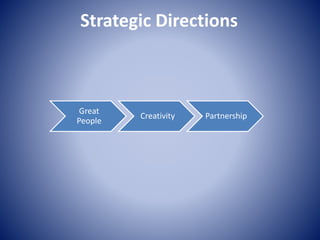
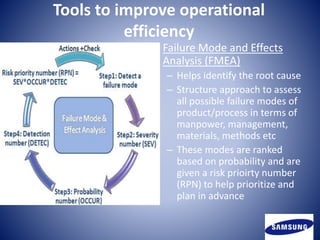
3. The document outlines Samsung's current operations strategy, which focuses on R&D, procurement, manufacturing, logistics, sales, and after service. It also provides recommendations to help Samsung improve, such as focusing on quality over variety.