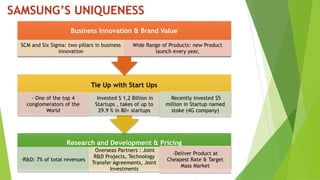
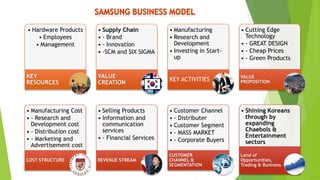
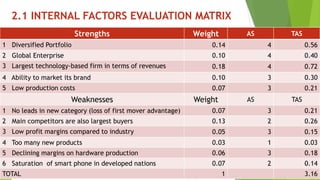
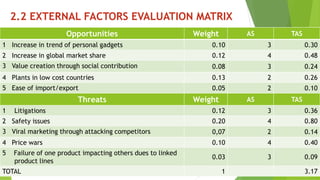
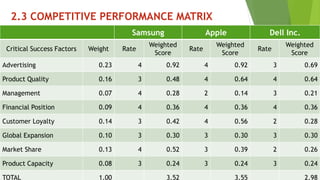
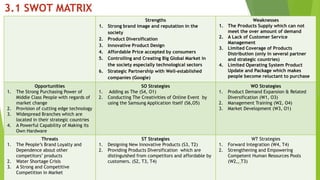
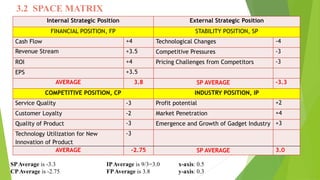
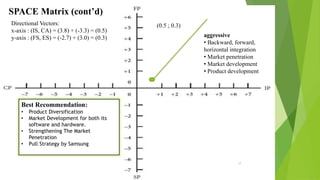
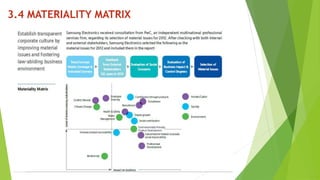
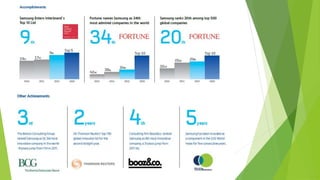
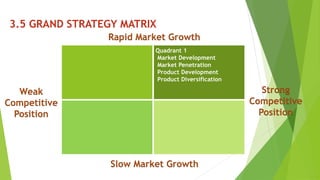
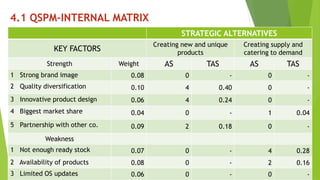
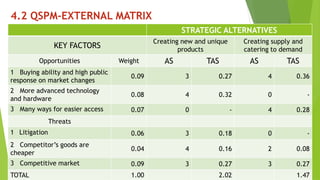
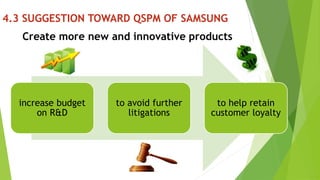
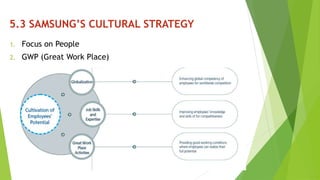
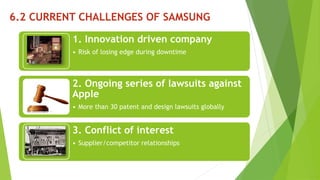
The document presents a strategic analysis of Samsung's global business performance, covering its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats through various strategic frameworks. It emphasizes Samsung's innovative capabilities, R&D investment, and market positioning while addressing challenges such as competition and litigation. Key recommendations include product diversification, market development, and reinforcing customer loyalty.