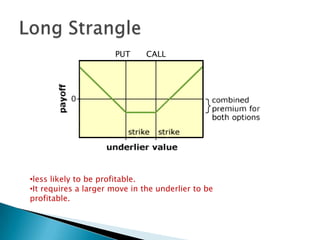
The document discusses various risk mitigation strategies using derivatives for different groups involved in the natural gas market, including producers, gas processors, pipelines, distributors, marketers, and end users. It outlines strategies like hedging with futures contracts, options spreads like straddles and strangles, and basis trades. The key groups' price risks and how various derivative structures can address them are summarized.