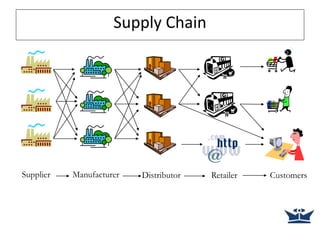
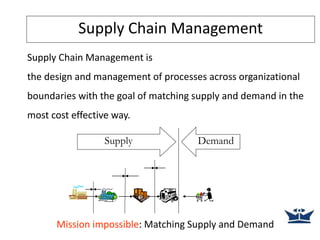
A supply chain is the network of organizations, people, activities, information and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. Supply chain management (SCM) coordinates these activities and seeks to match supply and demand as cost-effectively as possible. SCM has become increasingly important due to trends like shorter product life cycles, more product variety, and globalization. However, matching supply and demand is difficult due to uncertainties, changing customer demands, and conflicting objectives within and between organizations in the supply chain.