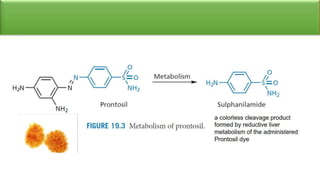
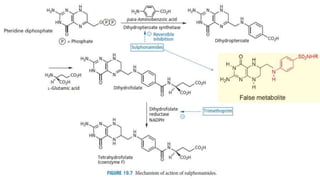
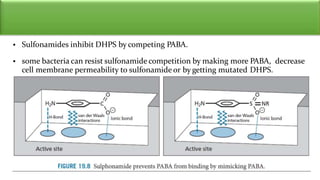
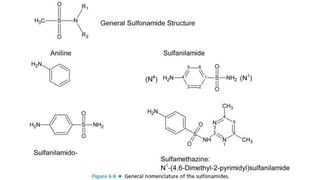
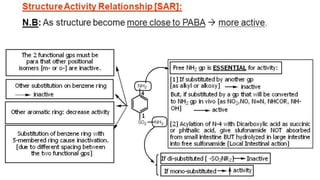
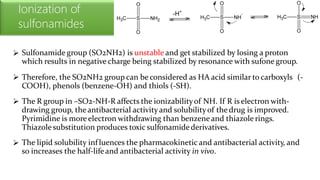
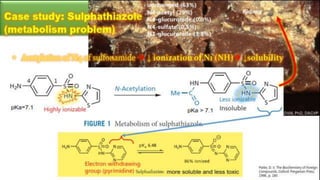
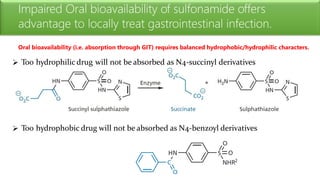
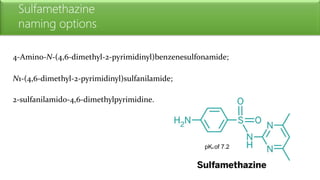
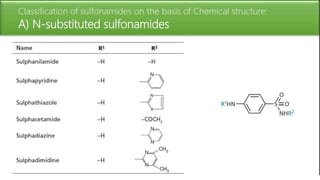
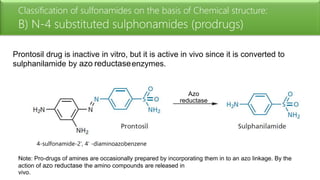
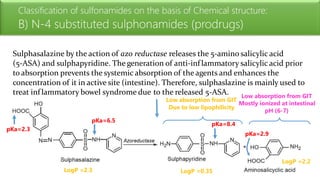
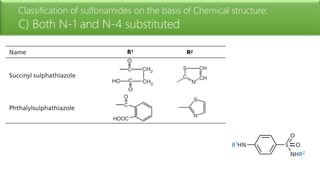
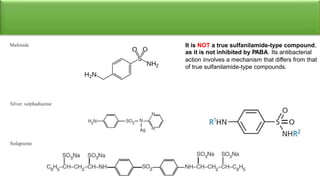
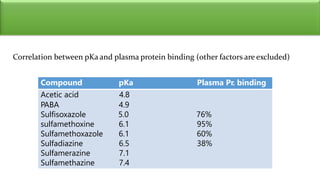
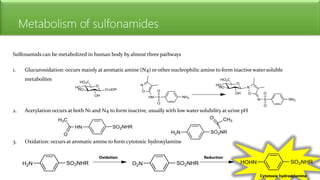
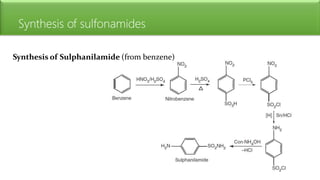
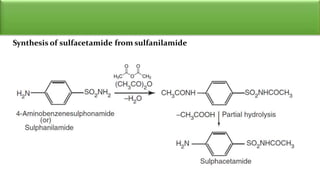
Sulfonamides are bacteriostatic drugs that inhibit the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase. They do this by competing with p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) for binding at the enzyme's active site. Some bacteria have developed resistance to sulfonamides by increasing PABA production, mutating the enzyme, or reducing drug permeability. Sulfonamides are classified based on their chemical structure, which affects their ionization, absorption, and resistance profiles. Modifications to the structure can improve solubility issues that originally limited their therapeutic use.