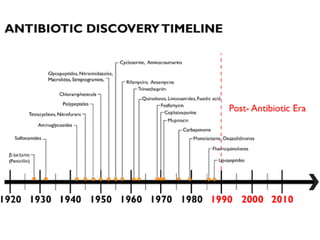
This document discusses the classification and mechanisms of action of antibiotics. It covers several key topics:
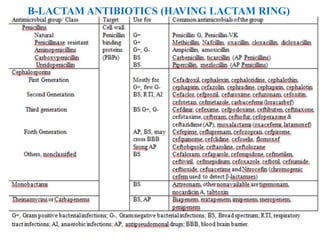
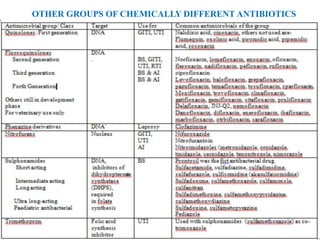
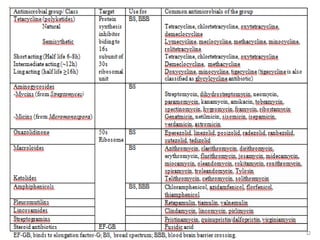
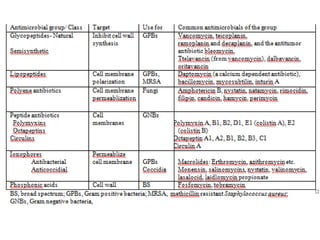
1. Antibiotics can be classified based on their chemical structure or mechanism of action. Major classes include beta-lactams, quinolones, sulfonamides, and glycopeptides.
2. Antibiotics have selective toxicity toward bacteria and not the host. Their therapeutic index and whether they are bactericidal or bacteriostatic are important properties.
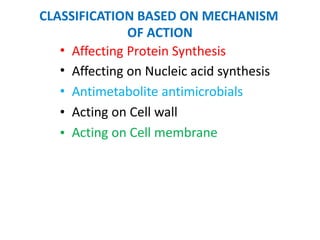
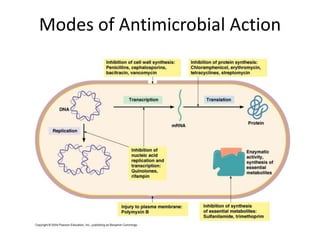
3. Antibiotics can inhibit protein synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, cell wall synthesis, or disrupt the bacterial cell membrane. They have different targets within each of these pathways.
4. Resistance can arise through mutation, acquisition of