Phase change materials (PCMs) can store and release large amounts of heat energy as they change phase between solid and liquid states. There are three main types of thermal energy storage: sensible heat, latent heat, and thermochemical heat. Latent heat storage uses PCMs, which absorb or release heat during phase changes without changing temperature. Common PCMs include salt hydrates, paraffin waxes, and fatty acids. PCMs can be encapsulated in small spheres or other shapes to improve heat transfer properties and prevent leakage. Encapsulated PCMs have applications in building insulation, solar energy storage, textiles, and more.

![Phase Change Material
Phase change method[1]
1) Higher thermal storage capacity compared to sensible energy storage in water. This leads to
smaller required storage. Only a true advantage if only small useful temperature difference can
be achieved.
2) Relatively constant temperature during charging and discharging
3) Burner cycle for the backup generation unit and therefore their CO and HC emission can be
reduced.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-3-320.jpg)
![Phase Change Material
Properties of PCM[2]
1) Melting point should be in the desired temperature range.
2) High latent heat of fusion per unit volume to store more energy in a given volume.
3) High thermal conductivity to assist charging and discharging of energy.
4) Low changes in volume during phase change and low vapor pressure to avoid
containment problems.
5) Non-flammable and non-toxic.
6) Chemically stable.
7) Low cost and low containment cost.
8) Low vapor pressure (<1 bar) at the operational temperature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-4-320.jpg)
![Phase Change Material
Phase change material[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-5-320.jpg)
![Phase Change Material
Inorganic Material[3]
1) Salt Hydrate:
It may be regarded as alloy of inorganic salt and water forming a typical crystalline solid of general formula
AB.nH2O
AB.nH2O=AB.mH2O + (n-m)H2O
Example: Water of Crystallization
CuO + H2SO4 = CuSO4 + H2O
(CuSo4.5H2o) Hydrated salt
5.H2O= Water of Crystallization
A salt hydrate usually melts to either to a salt hydrate with fewer moles of water.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-6-320.jpg)

![Overview about Organic Materials
Organic Materials
• possess the ability to absorb and release the large quantity of latent
heat during phase change process over a certain temperature range
• are naturally existing petroleum bi-products such as naphtha,
gasoline, fuel oil, bitumen, and hexane [3].
• have their unique phase change temperature
• generally have the temperature range between -70 C to 250 C
• undergo solid-liquid, solid-solid phase transition during heating and
cooling processes [3]
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-9-320.jpg)
![Temperature effect [18]
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-10-320.jpg)
![Classification of Organic Materials [18]
(a) Paraffin Materials (b) Non-paraffin Materials
Paraffin wax Rubi-therm Dry granules
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-11-320.jpg)
![Paraffin Materials
• It consists of a mixture of mostly straight chain n- alkanes CH3–
(CH2)–CH3.
• The crystallization of a CH3 chain release a large amount of latent
heat.
• However, under cost consideration, only technical grade paraffin may
be used in latent heat storage systems.
Paraffin Freezing range(C) Heat of Fusion (KJ/KG)[3]
6106 42 – 44 189
5838 48 – 50 189
6035 58 – 60 189
6499 66 – 68 189
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-12-320.jpg)
![• The materials have phase change temperature below 15 C are used in
cooling cycles while the materials who have above 90 C phase change
temperature are used in absorption refrigeration cycles.
• Moreover, PCMs having in between 15 C to 90 C are used in heating
cycles.
• Paraffin is safe, reliable, non corrosive, and less expensive material.
• Some undesirable properties are [3] :
(i) Low thermal conductivity
(ii) Non compatible with plastic container
(iii) Flammable
• Above three effects can be partially eliminated by modifying the wax
and the storage system.
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-13-320.jpg)
![Non-Paraffin Materials
• They are different from the paraffin materials because all the
materials have unique properties.
• They should not be exposed to excessively high temperature.
• Properties [3] :-
(i) high heat of fusion
(ii) varying level of toxicity
(iii) instability at high temperature
(iv) mild corrosive
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-14-320.jpg)
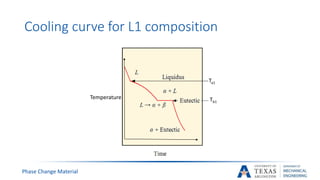
![Phase Change Material
Phase diagram of eutectic mixture[5] [6]
Ta1
L1 composition
Ta2
Ta3
Ta4
Proeutectic α
Liquid
Proeutectic α
Proeutectic α
eutectic β
eutectic α
Liquid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-15-320.jpg)
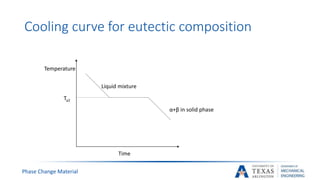
![Phase Change Material
Phase diagram of eutectic composition[5]
Ta2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-17-320.jpg)
![Phase Change Material
Eutectic materials[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-19-320.jpg)
![Phase Change Material
Eutectic mixture of Galactitol and Mannitol[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-20-320.jpg)
![Phase Change Material
Phase diagram of Galactitol and Mannitol [4]
Eutectic composition 30:70 G/M
Melting Temperature:153◦ C
Heat of fusion: 292 J.g-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-21-320.jpg)

![Applications of PCM[7]
• Latent heat battery
• Heating in buildings
• Solar water heater
• Cold storage and sports ware
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-23-320.jpg)
![Latent heat battery[7]
• Stores the heat from radiator of car.
• The stored heat is utilized to warm up the engine during cold start.
• It can store energy for 2 days.
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-24-320.jpg)
![Heating in building[8]
• Heating:
• PCM mats are used on the roof and walls of
the building.
• It absorbs the heat during sunshine hours and
melts.
• The liquid PCM freezes during night and
releases the heat in the building.
Phase Change Material
(Source:phasechangeenergy.com) [4.2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-25-320.jpg)
![Solar water heater[9]
• Water is heated during sunshine hours.
• Hot water transfers heat to the PCM.
• Hot water is replaced by cold water during
night which gets heat from the liquid PCM.
Phase Change Material
Solar water heater[4.5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-26-320.jpg)
![• Sports ware:[10]
• PCM maintains balance between heat generated from body
and heat released to the environment.
• It reduces thermal stress.
• Cold storage:[10]
• PCM can be used in refrigerator as a backup in case of power
failure.
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-27-320.jpg)
![Advantages of PCM:[12]
• Wide melting point range from -40 C to 151 C.
• Stable for more cycles.
• Service life is high.
• High latent heat.
• Non-toxic
• Cost depends on the purity of material( From 1.5$/lb to 24$/lb)
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-28-320.jpg)
![Disadvantages:[13]
• Flammable
• Low volumetric latent storage heat capacity
• Low heat transfer rate in solid state
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-29-320.jpg)

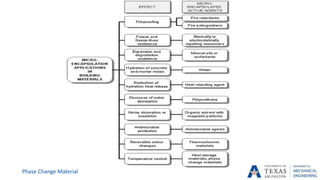
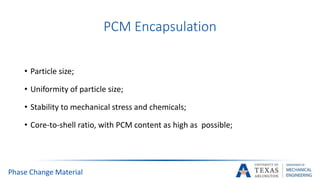
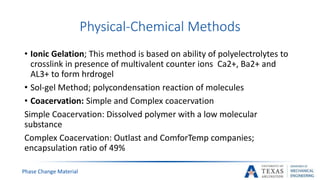
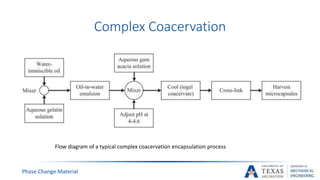
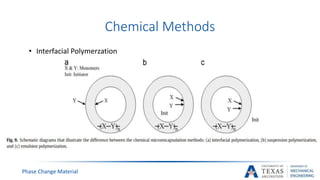
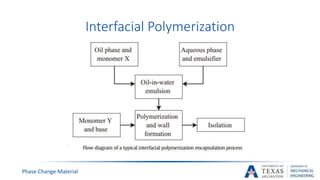
![PCM Encapsulation
Phase Change Material
[14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-31-320.jpg)

![Scaling Of Forces [15]
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-33-320.jpg)
![MPCM In Building [16]
PCM Encapsulation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-35-320.jpg)
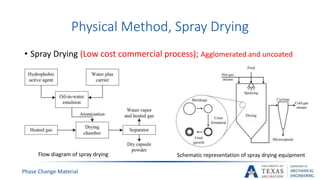
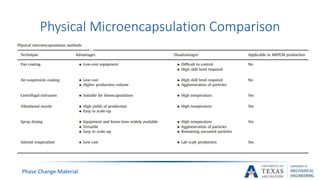
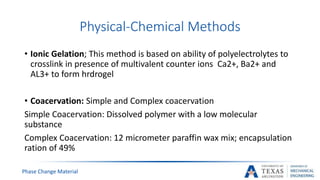
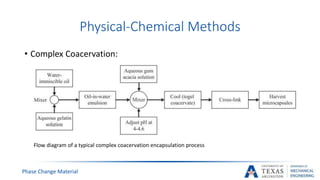
![PCM Encapsulation Manufacturing [17]
Pan coating
Air-Suspension
Centrifugal Extrusion
Vibrational Nozzle
Spray Dying
Solvent Evaporation
Physical
Methods
Ionic Gelation
Coacervation
Sol-GEl
Physic-
Chemical
methods
Ionic Polymerization
Suspension
Polymerization
Emulsion
Polymerization
Chemical
Methods
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-38-320.jpg)

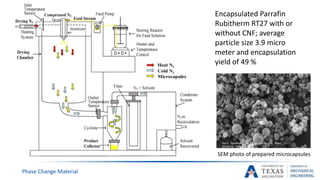

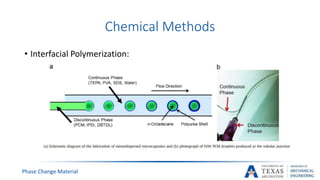
![Supercooling phenomenon [17]
• Supercooling is a state where liquids solidify below their normal
freezing point
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-51-320.jpg)

![References
[1] Gupta, E. & Reinhart, N. (n.d.). RGEES LLC innovating sustainable thermal
comfort. Retrieved from http://www.rgees.com/about.php
[2] Mishra, A., Shukla, A. & Sharma, A. (June 2015). Latent heat storage
through phase change material.
[3] Sharma, A., Tyagi, V. V., Chen, C. R., & Buddhi, D. (2009). Review on
thermal energy storage with phase change materials and
applications. Energy Renewable and Sustainable Reviews, 13(2), 318-
345. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2007.10.005
[4]Paul, A., Shi, L., & Bielawski, C. (2015). A eutectic mixture of galactitol and
mannitol as a phase change material for latent heat storage. Energy
Conversion and Management, 103, 139-146.
doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2015.06.013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-57-320.jpg)
![[5] Imre, B. (2007).Eutectic system phase diagram. Retrieved from
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eutectic_system#/media/File:Eute
ctic_system_phase_diagram.svg
[6] Best,B.,(n.d.). Lessons for Cryonics from Metallurgy and Ceramics
Retrived from http://www.benbest.com/cryonics/lessons.html
[7] Phase change material pcm manufacturers,applications and
uses, Retrieved from
http://www.teappcm.com/applications.htm
[8] Muruganantham. K. Applications of phase change material in
building: field data vs. energy plus simulation, (2010).
[9] Kitano, H., Sagara, K., Sharma, S.D, Phase change materials for
low temperature solar thermal applications,(2004),p.31-64.
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-58-320.jpg)
![[10] Arjun, D., Hayavadana,J., Thermal energy storage materials
(PCMs) for textile applications,Volume 8,Issue 4
[11] J. Prakash, H. P. Garg, G.Datta,A solar water heater with a
built-in latent heat storage, Energy conversion and
management 25 (1985) 51-56.
[12] Phase change materials, retrieved from
http://www.puretemp.com/stories/understanding-pcms
[13] Phase change materials,retrieved from
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phase-
change_material#Organic_PCMs
[14] Tyagi, V. V., et al. "Development of phase change materials
based microencapsulated technology for buildings: a
review." Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 15.2
(2011): 1373-1391.
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-59-320.jpg)
![[15] Fearing, Ronald S. "Survey of sticking effects for micro parts
handling."Intelligent Robots and Systems 95.'Human Robot
Interaction and Cooperative Robots', Proceedings. 1995 IEEE/RSJ
International Conference on. Vol. 2. IEEE, 1995.
[16] Jamekhorshid, A., S. M. Sadrameli, and M. Farid. "A review of
microencapsulation methods of phase change materials (PCMs) as a
thermal energy storage (TES) medium." Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews31 (2014): 531-542.
[17] Al-Shannaq, Refat, et al. "Supercooling elimination of phase change
materials (PCMs) microcapsules." Energy 87 (2015): 654-662.
[18] Sutterlin, W. R. (2011). Introduction to thermal energy storage. The
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Contract
Services. Retrieved from
http://www.pharmoutsourcing.com/Featured-Articles/37854-Phase-
Change-Materials-A-Brief-Comparison-of-Ice-Packs-Salts-
Paraffins-and- Vegetable-derived-Phase-Change-Materials/
Phase Change Material](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/655aff94-3c38-4d16-932e-6ba2144931fd-160207193218/85/Submitted-Presentation-60-320.jpg)