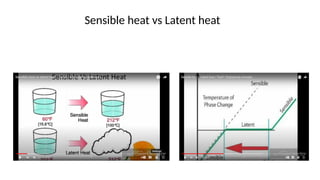
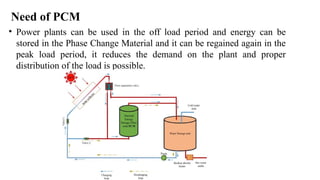
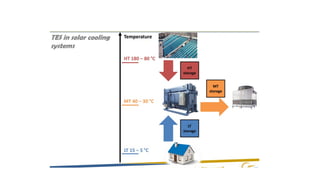
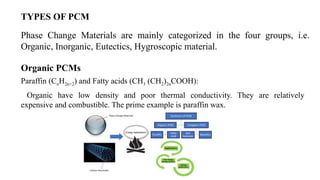
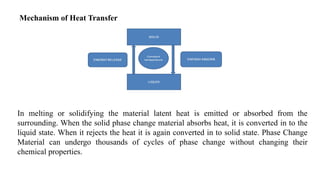
Phase change materials (PCMs) absorb and release significant energy during phase transitions, aiding in heat and cooling applications. They are categorized into organic, inorganic, eutectic, and hygroscopic types, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages regarding thermal properties and costs. PCMs are used in various applications including energy saving in buildings and telecommunications, improving hot water efficiency, and ensuring temperature control in transportation of sensitive goods.