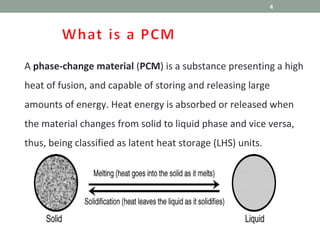
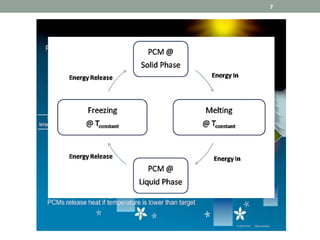
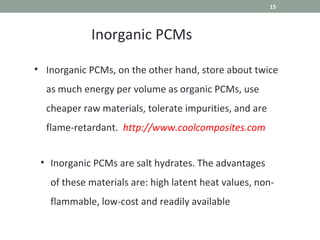
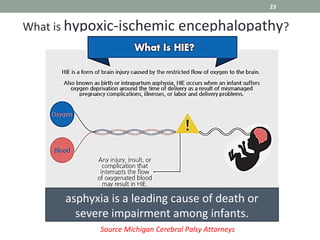
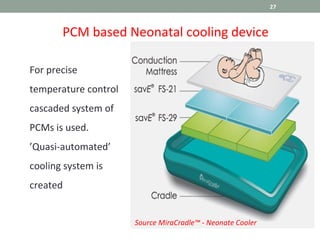
Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are substances capable of storing and releasing large amounts of energy through phase transitions, primarily used for thermal energy storage and cooling applications. In the medical field, PCMs have shown promise in neonatal cooling devices to treat birth asphyxia, offering significant advantages over traditional methods in terms of cost and maintenance. These devices utilize cascaded PCM systems for precise temperature control, effectively inducing and sustaining hypothermia to protect brain function in infants.