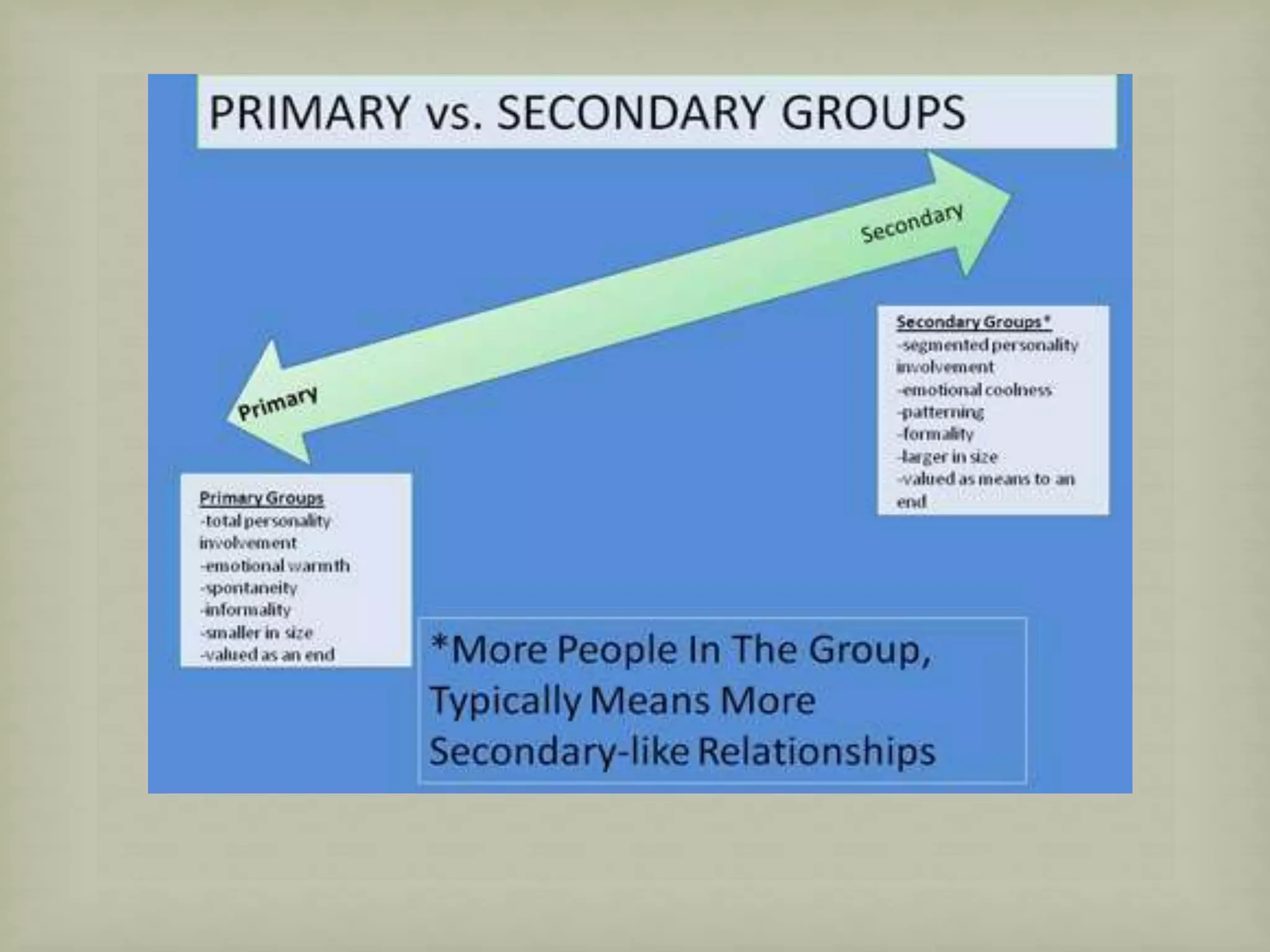
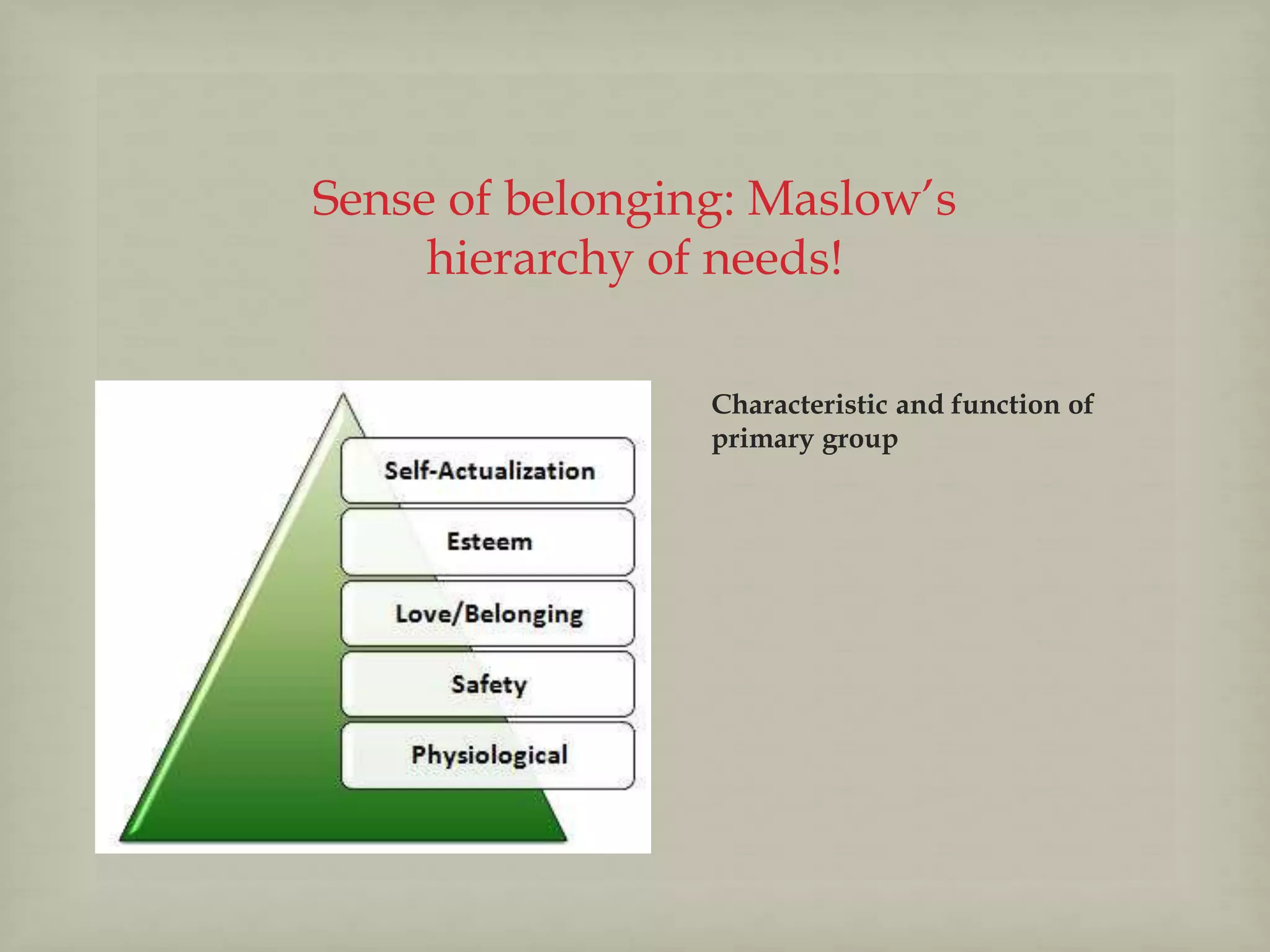
The document explores the concept of social groups, distinguishing them from non-groups such as aggregates and categories of people. It defines primary and secondary groups, highlighting their characteristics and functions, and discusses various types of social groups, including expressive and instrumental groups, as well as in-groups and out-groups. Key characteristics of social groups include shared goals, interactions, group norms, and varying degrees of openness and voluntary participation.