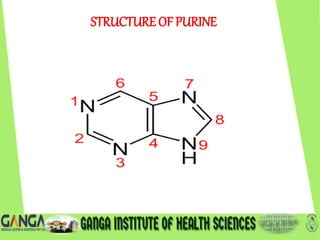
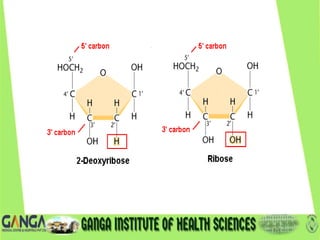
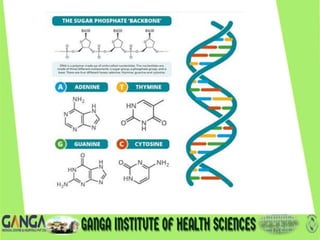
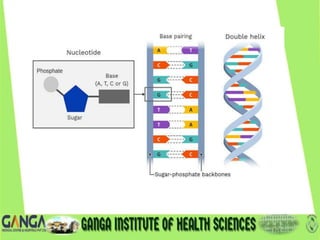
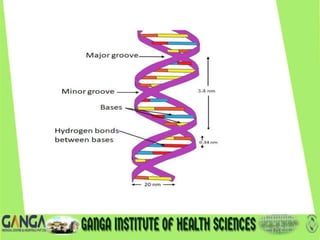
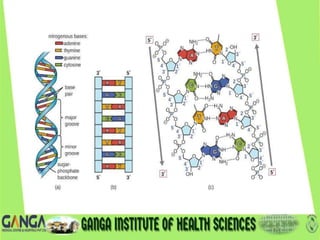
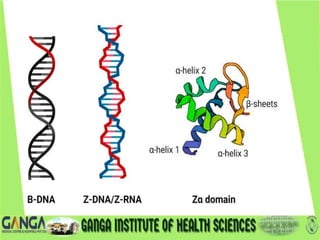
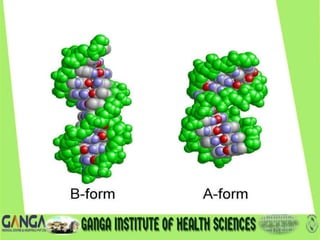
DNA is the hereditary material found in humans and most organisms. It is composed of nucleotides containing a nitrogenous base, sugar, and phosphate. The two main types of nitrogenous bases are purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil). DNA structure involves nucleotides linking to form a double helix with antiparallel strands bonded by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs. The three main DNA types are B-DNA, A-DNA, and Z-DNA, which differ in their helical structure, number of base pairs per turn, and handedness.