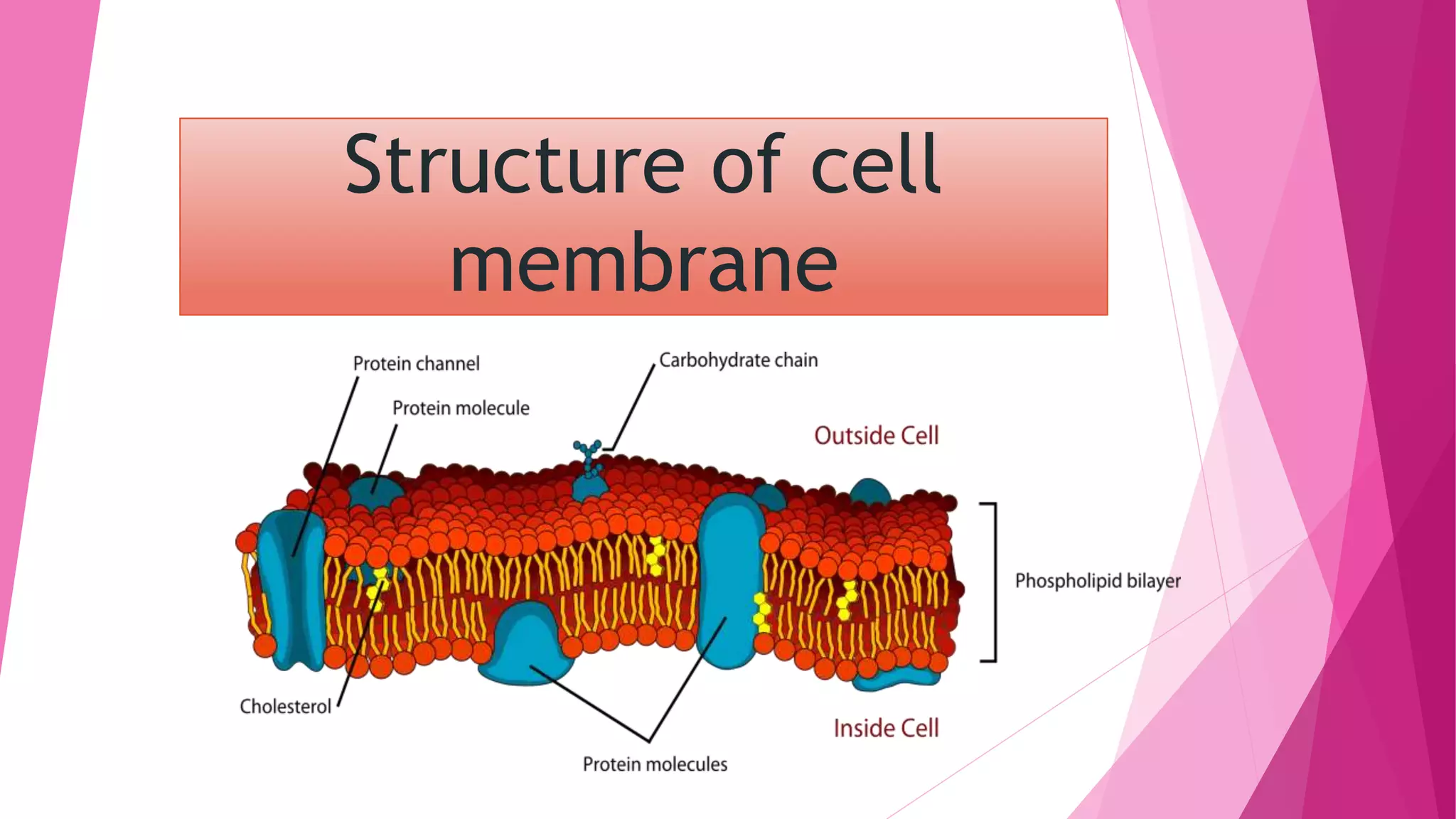
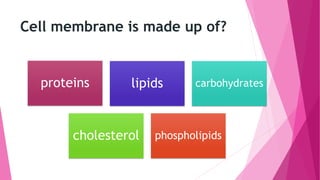
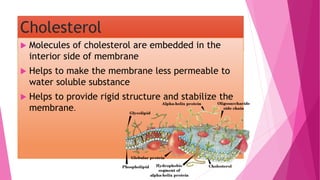
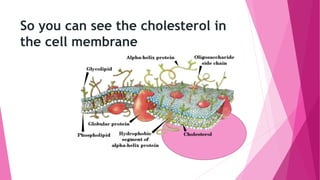
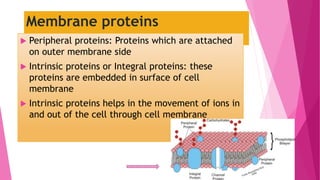
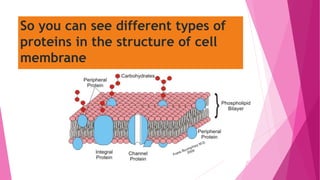
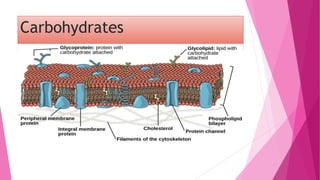
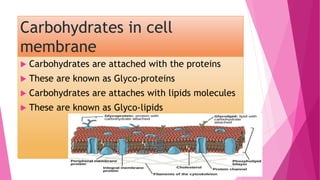
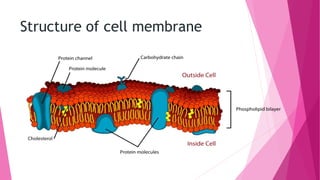
The fluid mosaic model developed by S. Jonathan and Garth Nicolson in 1972 describes the structure of the cell membrane. According to this model, the cell membrane is a double layer of phospholipids with proteins dispersed throughout. The phospholipids are amphipathic, with polar heads on the outer surface interacting with water and nonpolar tails in the interior. Cholesterol molecules are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, making the membrane less permeable. Membrane proteins can be peripheral, attached to the external surface, or intrinsic, embedded within the phospholipid bilayer. Carbohydrates are attached to proteins and lipids on the external cell surface forming the glycocalyx.