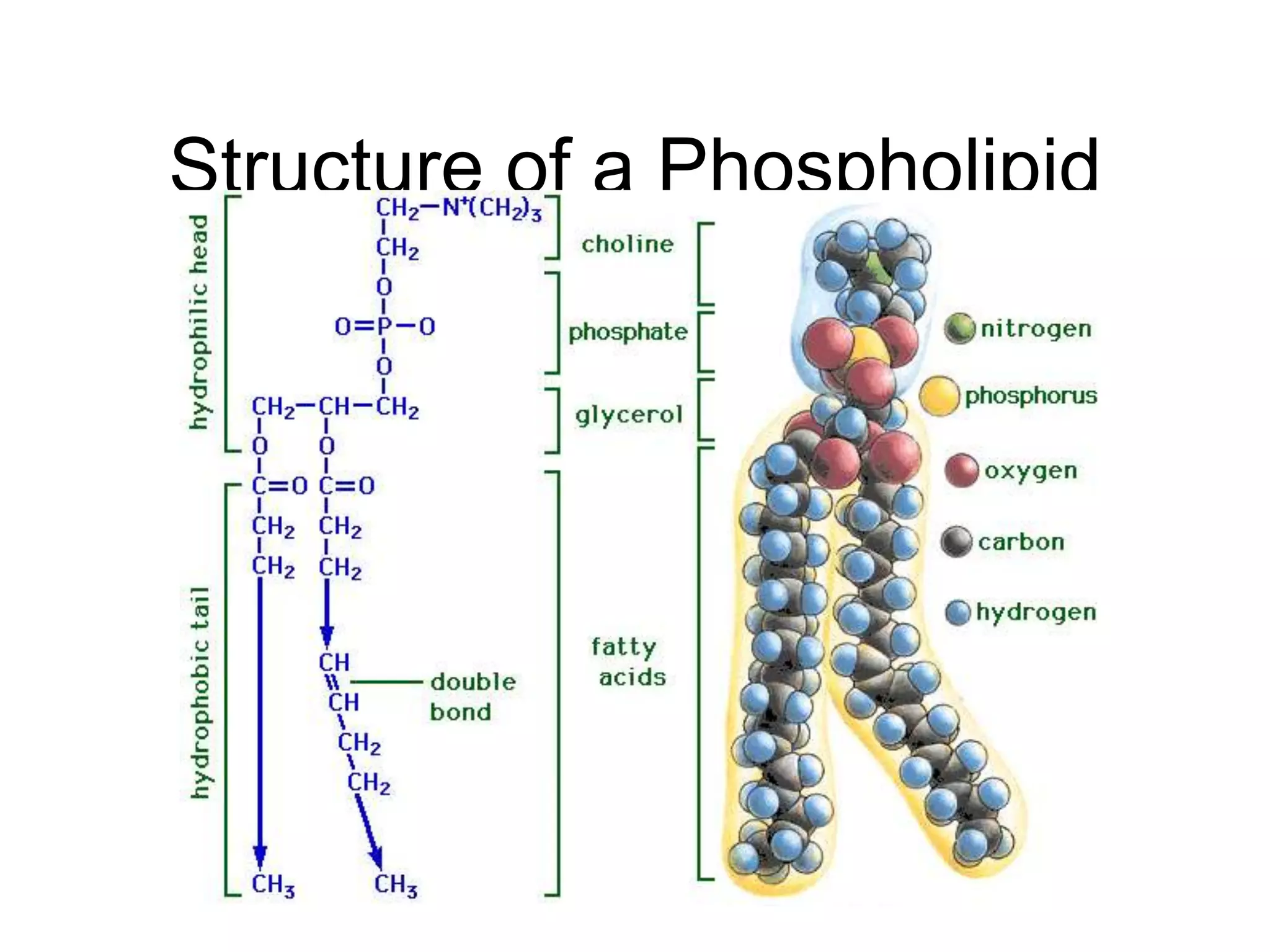
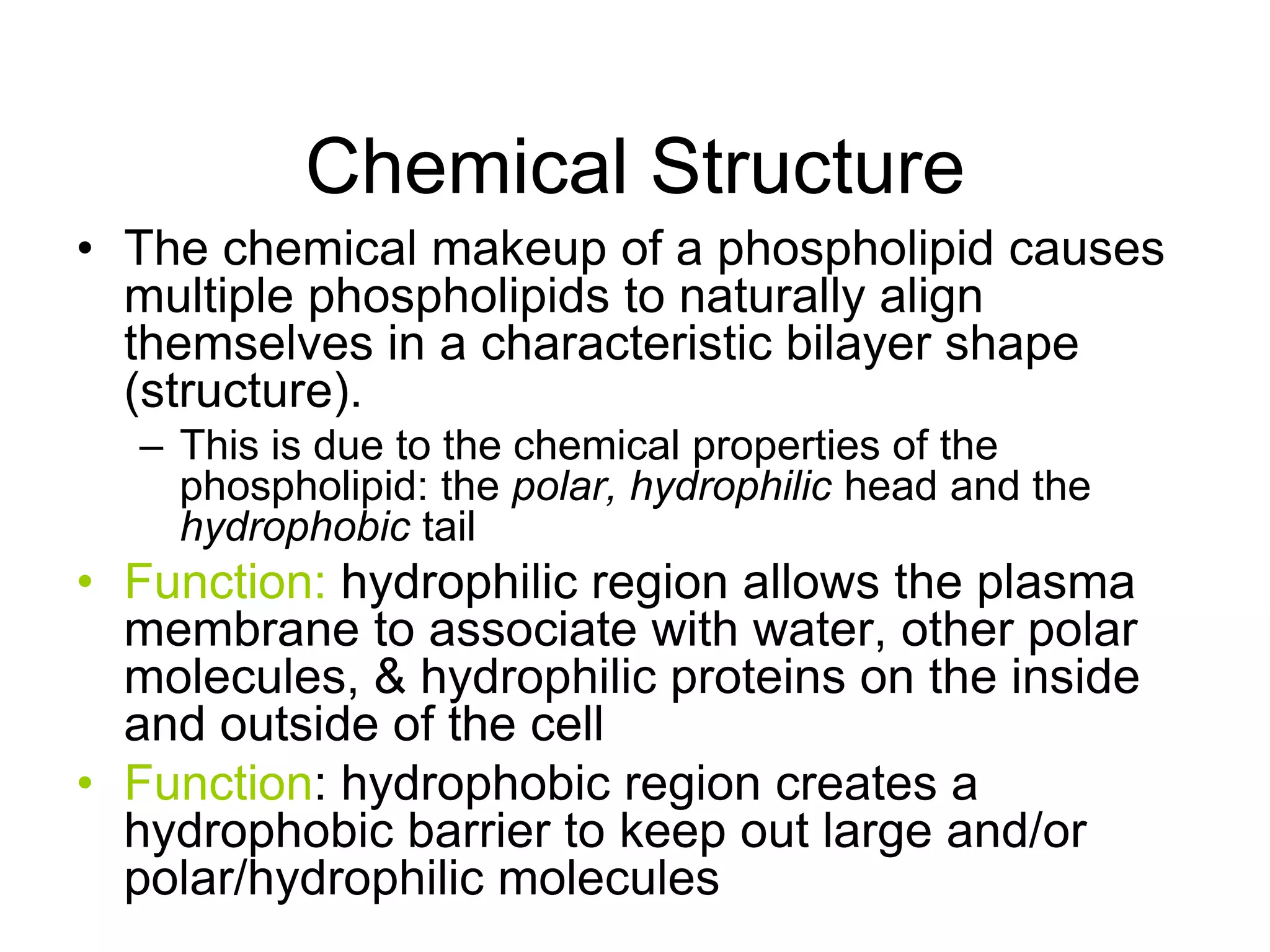
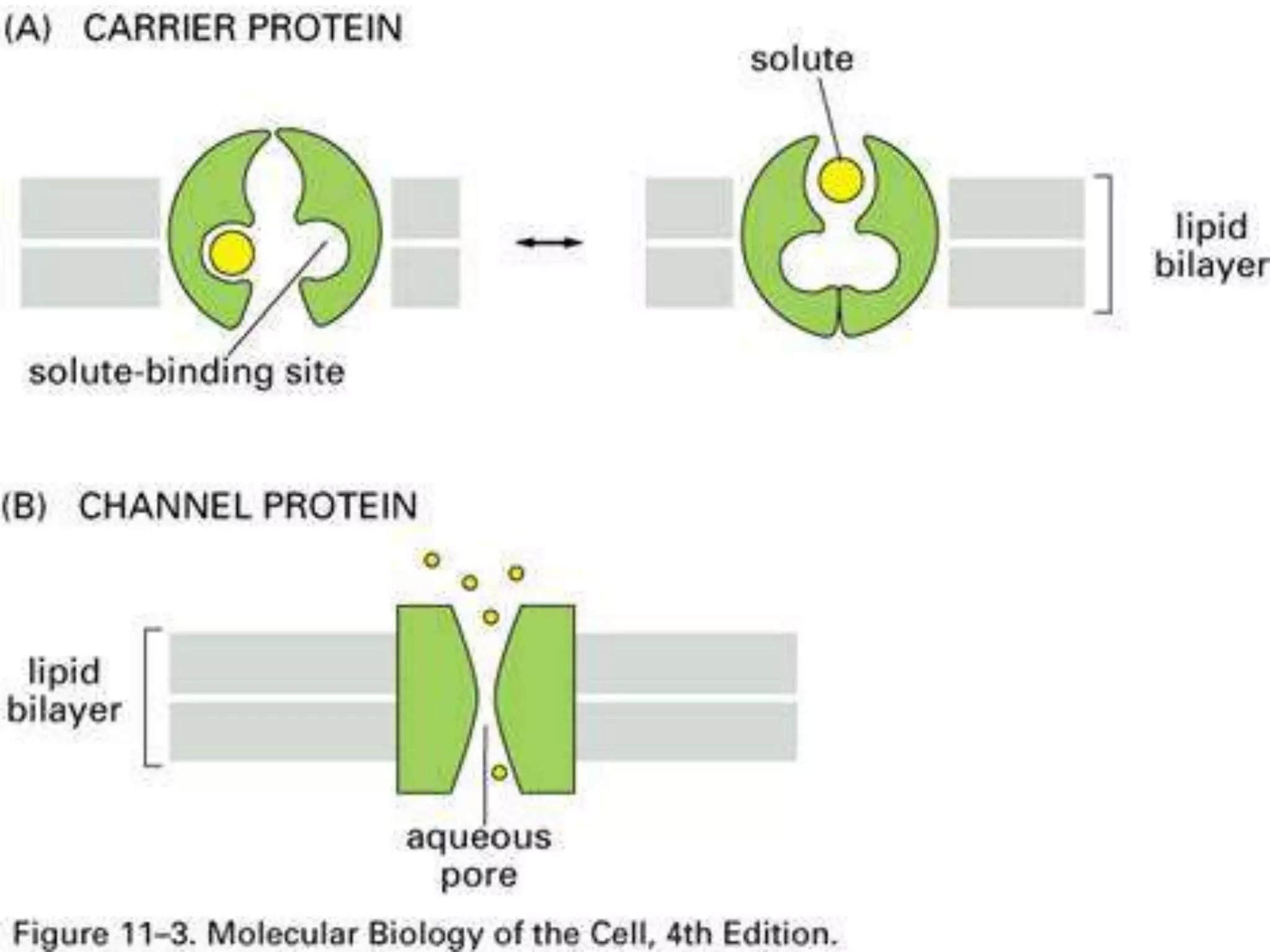
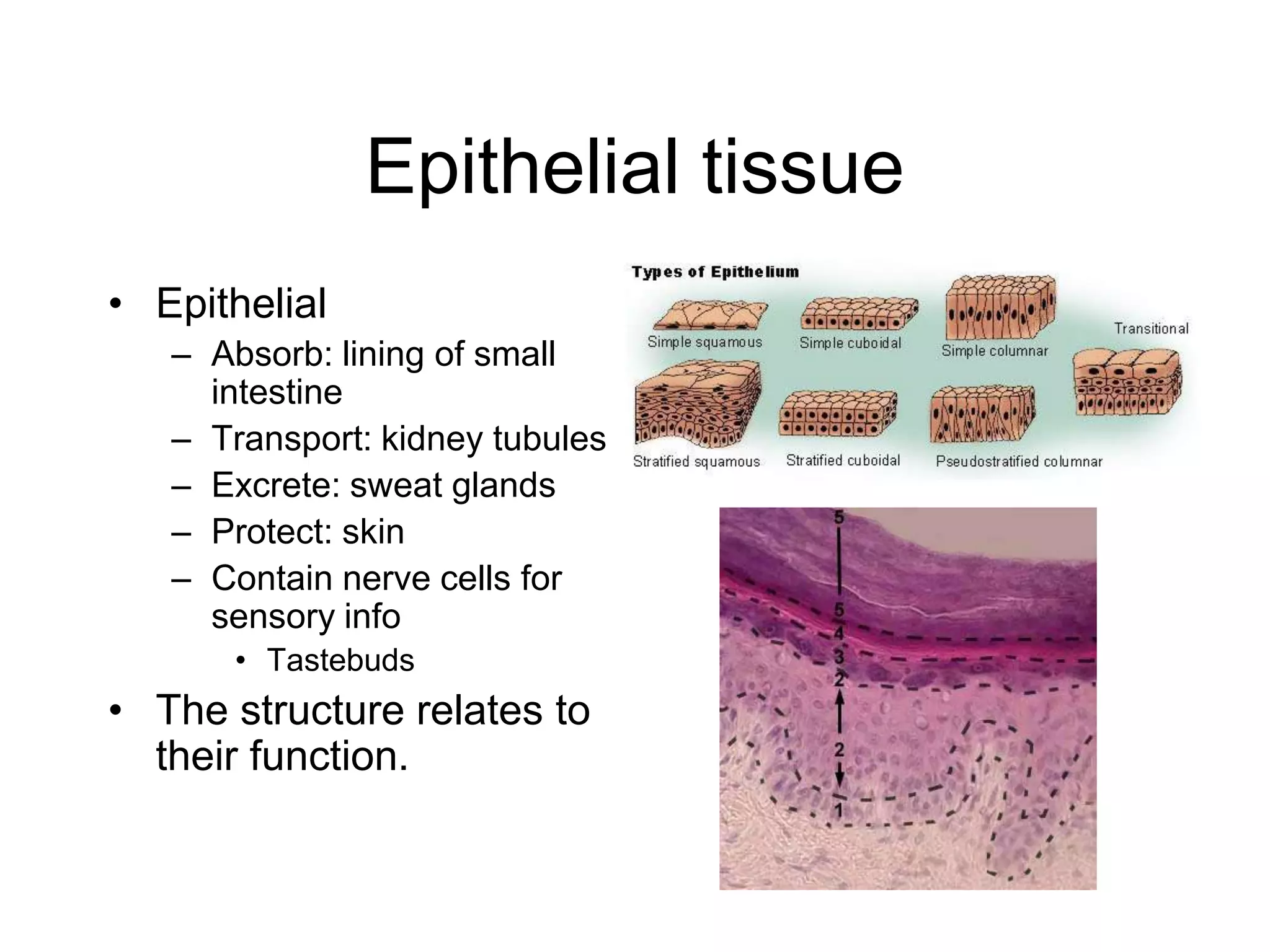
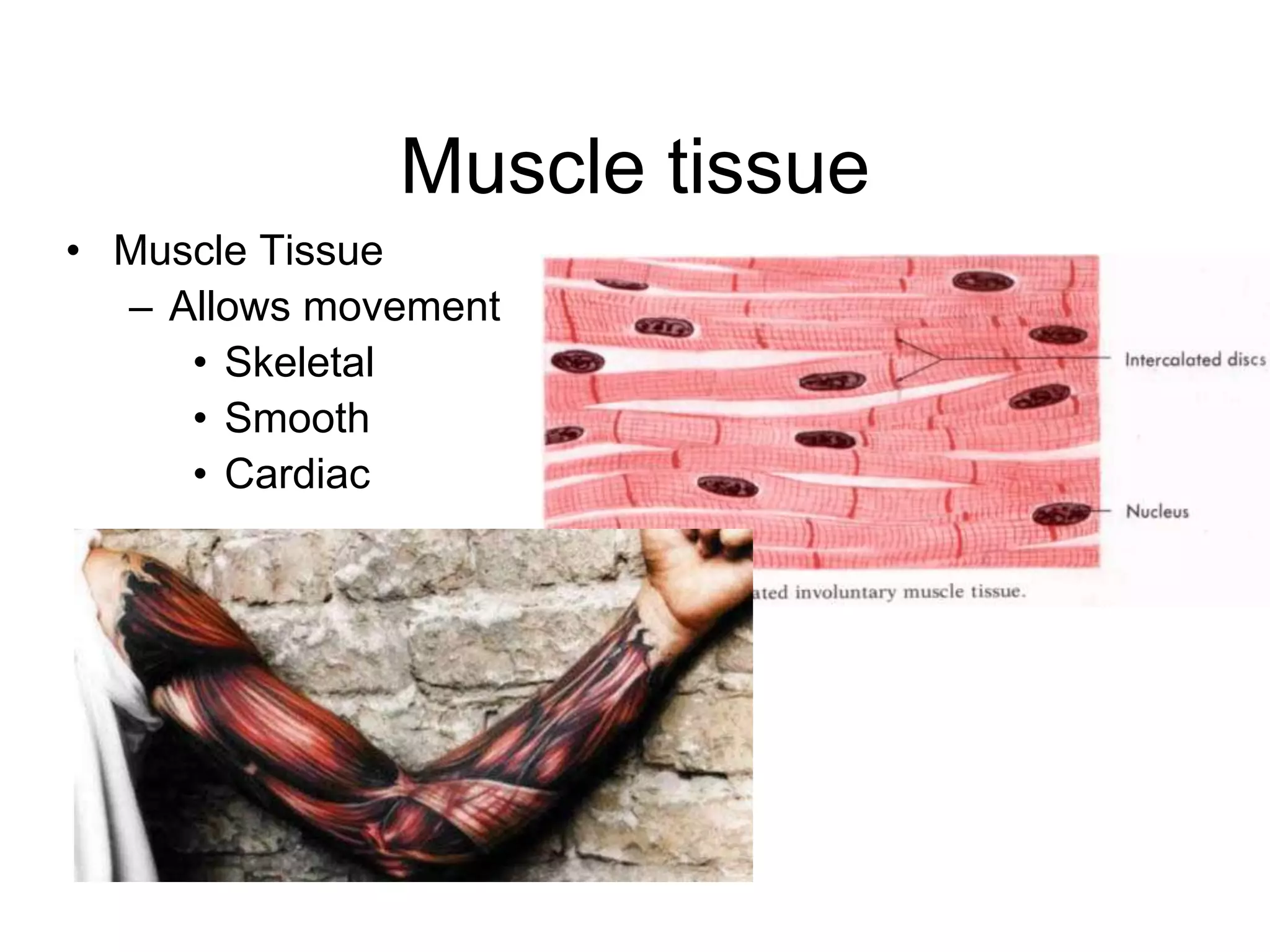
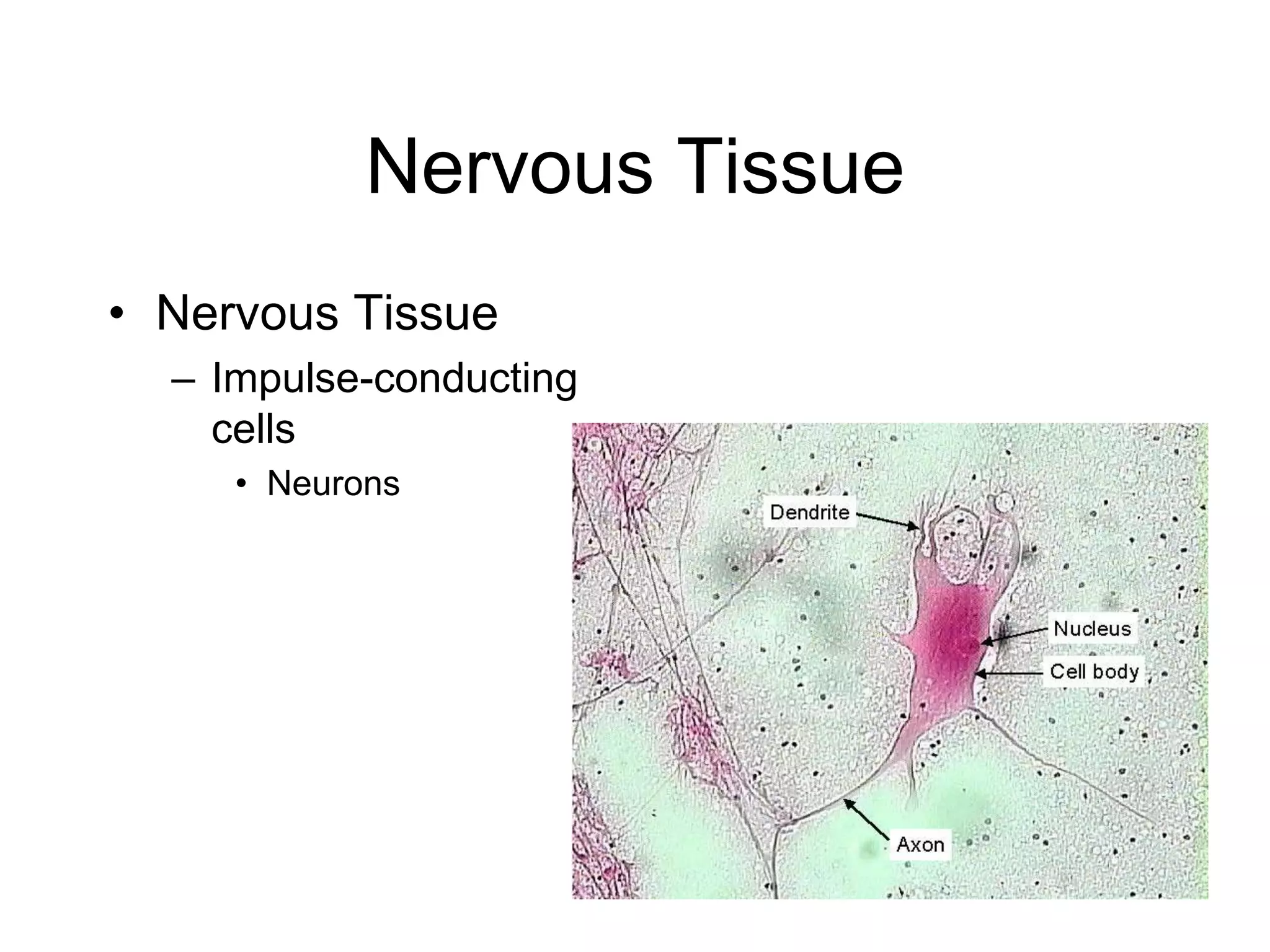
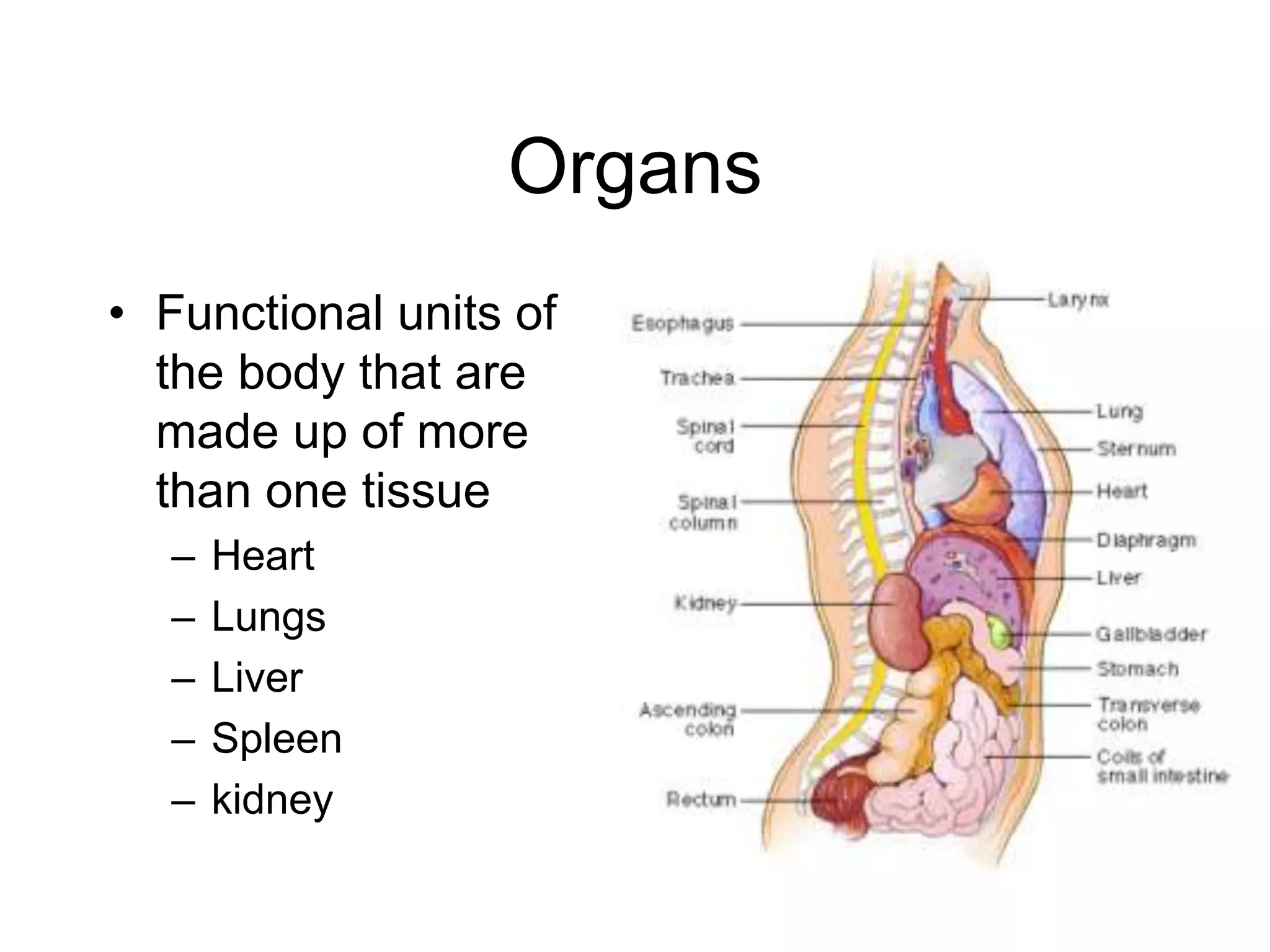
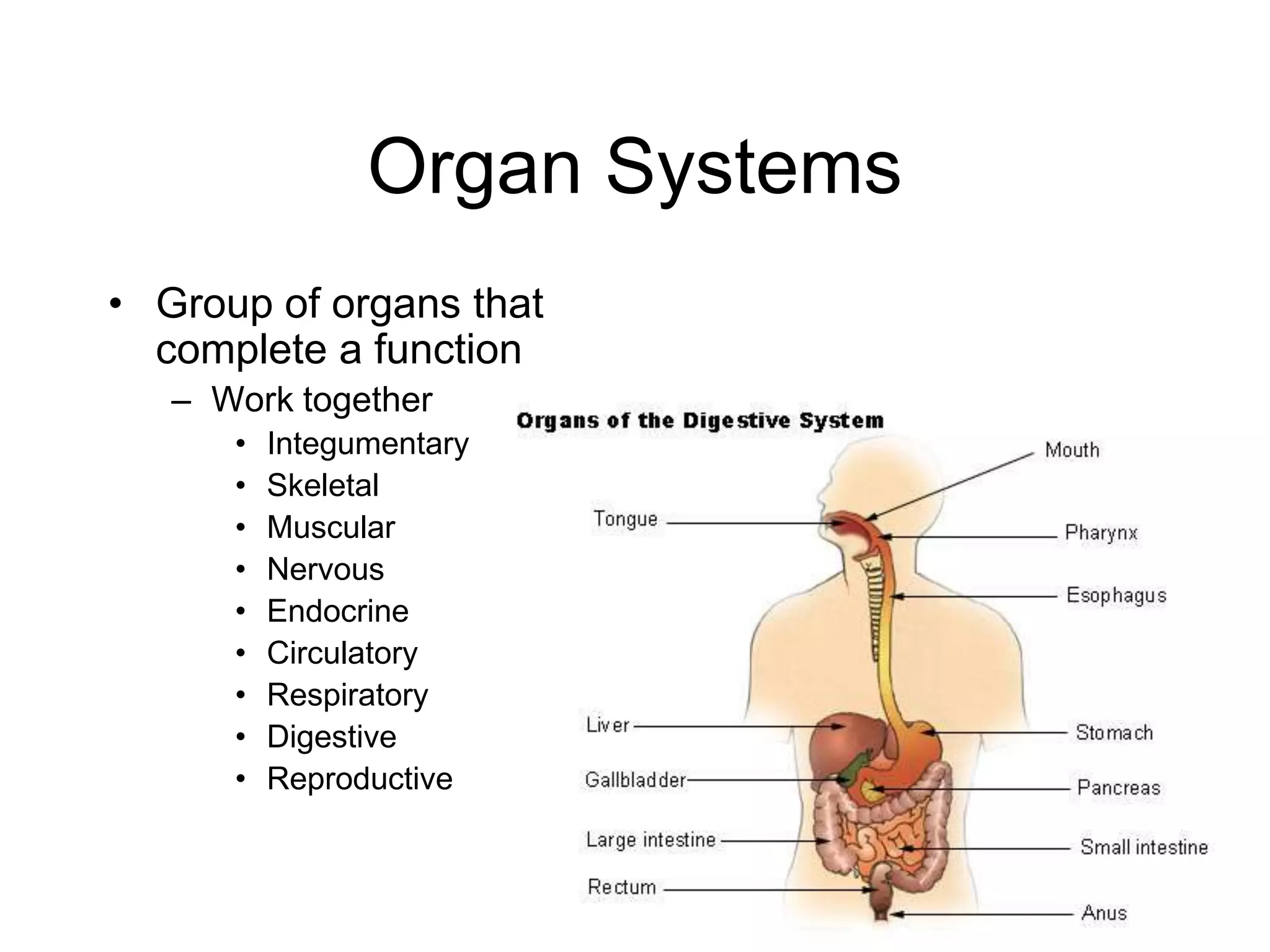
The cell membrane has a structure of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and cholesterol embedded within it. This structure allows the membrane to function as a selective barrier that regulates what enters and exits the cell, protects the cell, and maintains intracellular gradients. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids align to form the bilayer structure, while the hydrophilic heads allow interaction with water and polar molecules. Membrane proteins and cholesterol further contribute to the membrane's structure and functions.