The document discusses C programming concepts including structures, unions, and data types. It covers defining and using structures, with examples of declaring structure variables, initializing members, accessing members, structure assignment, arrays of structures, and structures within structures. It also discusses defining and using unions, and provides an example union definition and memory allocation. The document is made up of multiple lectures on these topics presented in Busy Bee workshops.

![Lectures on Busy Bee Workshop 5
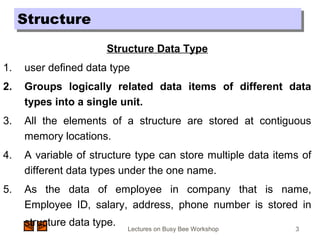
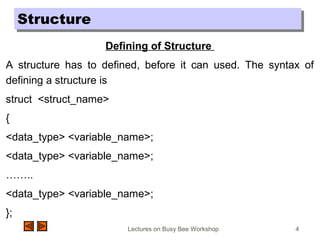
StructureStructure
Example of Structure
The structure of Employee is declared as
struct employee
{
int emp_id;
char name[20];
float salary;
char address[50];
int dept_no;
int age;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-c-151211040745/85/Structure-c-5-320.jpg)
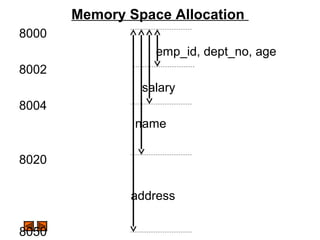
![Memory Space Allocation
8000
8002
8022
8024
8074
8076
employee
emp_id
name[20]
salary
address[50]
dept_no
age
StructureStructure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-c-151211040745/85/Structure-c-6-320.jpg)




![StructureStructure
Array of Structure
1. C allows to create an array of variables of
structure.
2. The array of structure is used to store the large
number of similar records.
3. For example to store the record of 100 employees
then array of structure is used.
4. This is similar to array.
5. The syntax to define the array of structure is
struct <struct_name> <var_name(array_name)>
[<value>];
For Example:-
struct employee e1[100];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-c-151211040745/85/Structure-c-12-320.jpg)


![StructureStructure
Example of Structure within Structure
The structure of Employee is declared as
struct employee
{
int emp_id;
char name[20];
float salary;
int dept_no;
struct date
{
int day;
int month;
int year;
}doj;
}e1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-c-151211040745/85/Structure-c-15-320.jpg)

![UnionUnion
Example of Union
The union of Employee is declared as
union employee
{
int emp_id;
char name[20];
float salary;
char address[50];
int dept_no;
int age;
}e;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-c-151211040745/85/Structure-c-19-320.jpg)