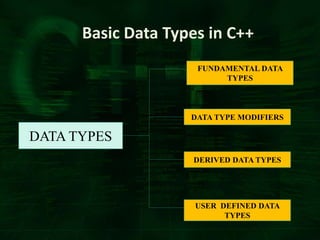
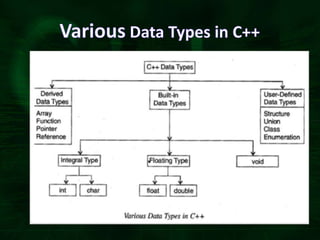
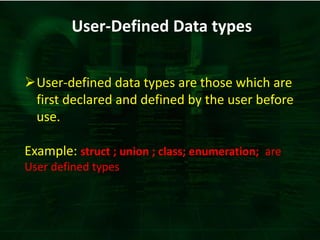
C++ provides built-in and user-defined data types. Built-in data types are pre-defined in C++ and include character, integer, floating point, double, void, and boolean. User-defined data types are composed of built-in types and include arrays, structures, unions, classes, and pointers. Data types determine the type of data that can be stored and the operations that can be performed on that data.