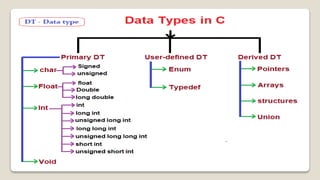
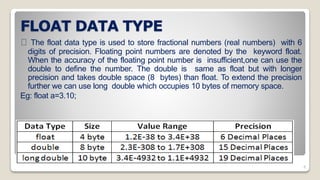
The document defines and describes various data types in the C programming language. It discusses integer data types like char, short int, int, long int; floating point data types like float, double, long double; void data type; and derived data types like arrays, pointers, structures, unions, enumerated data types, and user-defined data types using typedef. Each data type is explained along with its size, range of values it can hold, and examples.




![DERIVED DATA TYPE
Array: An array in C language is a collection of similar data-type, means an
array can hold value of a particular data type for which it has been declared.
Arrays can be created from any of the basic C data-types .
Eg: int a[10];
String variable contains a collection of characters surrounded by
double quotes. e.g string greeting = "Hello";
Pointer: C Pointer is a special variable that can be used to store address of
another variable using & operator. * operator is used to assign
memory location to a
Eg: *int a;
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinc-200123162920/85/Datatypes-in-c-10-320.jpg)

![STRUCTURE DATA TYPE
CStructure isa collection of different data types which are grouped together and
each element in a C structure is called member.
Example:
struct student { int roll_no;
char name[20];
char city[20];
}
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinc-200123162920/85/Datatypes-in-c-12-320.jpg)
![Union
It defines a type that contains a value that can be interpreted as different
types.
as it contains variables that uses the same space in the memory.
Its syntax is:
union union_name{
type1 name1;
type2 name2;
...
}
e.g union secretCode{
int i;
char str[4];
}
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinc-200123162920/85/Datatypes-in-c-13-320.jpg)
![User defined Data Types:ENUMERATED DATA TYPE
(ENUM)
Enumerated data type is a user defined data type having finite set of
enumeration constants. The keyword 'enum' is used to create enumerated data
type. Enumeration data type consists of named integer constants as a list.
It start with 0 (zero) by default and value is incremented by 1 for the sequential
identifiers in the list.
Syntax:
Enum [data_type] {const1, const2… constn};
Eg: enum month {Jan,Feb, Mar };or /* Jan, Feb and Mar variables will be
assigned to 0, 1 and 2 respectively by default */
enum month {Jan= 1, Feb, Mar };/* Feb and Mar variables will be assigned to 2
and 3 respectively by default */
enum month {Jan = 20, Feb,Mar };/* Jan is assigned to 20. Feb and Mar
variables will be assigned to 21 and 22 respectively by default */ 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinc-200123162920/85/Datatypes-in-c-14-320.jpg)
![TYPEDEF DATA TYPE
It is used to create new data type. But it is commonly used to change existing data
type with another name.
Syntax:
typedef [data_type] new_data_type;
here data_type is the basic type you want to substitute, while new_ data_type is the
name you want to give to it.
Eg:
typedef int integer;
integer roll_no;
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinc-200123162920/85/Datatypes-in-c-15-320.jpg)
