This document provides information about structures and unions in C programming. It discusses:
1) The structure definition syntax and examples of declaring structures with tags, variables, and typedef. Structures allow storing different data types together in a user-defined type.
2) How to initialize, access, and declare structure variables using dot operators and pointers. An example program demonstrates defining and accessing structure members.
3) The definition of a union, which allows storing different data types in the same memory location with only one active at a time for efficient multiple-purpose memory use.
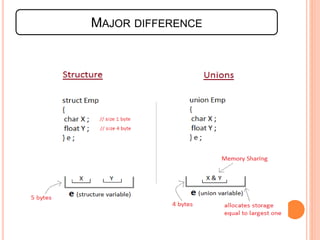
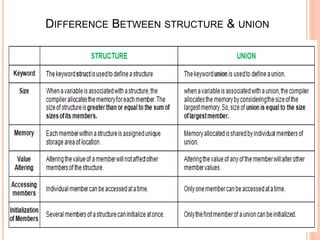
4) The major differences between structures, which allocate separate memory for each member, and unions, which share the same memory location for members

![INTRODUCTION
Structure in c is a user-defined data type that enables us
to store the collection of different data types. Each
element of a structure is called a member.
The struct keyword is used to define the structure.
Syntax : Example :
struct structure_name
{
data_type1 member_name1;
data_type2 member_name2;
.
.
data_typeN member_nameN;
};
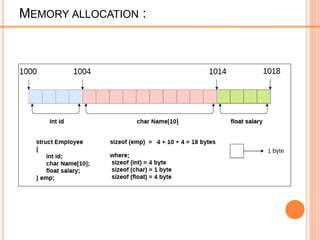
struct employee
{ int id;
char name[10];
float salary;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![ The structure definition associated with strucutre name is
called tagged strucutre.
Syntax : Example :
TAGGED STRUCTURE
struct tag_name
{
data_type1 member_name1;
data_type2 member_name2;
…… …….
…… …….
data_typeN member_nameN;
};
struct student
{ int rollno;
char name[10];
float avg;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![STRUCTURE VARIABLES
Syntax : Example :
struct
{
data_type1 member_name1;
data_type2 member_name2;
…… …….
…… …….
data_typeN member_nameN;
}
variable1, variable2,variableN;
struct
{ int empno;
char ename[30];
long int salary;
}
emp1, emp2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![The strucutre defined associated with keyword
typedef is called type-defined structure.This is the
most powerfull way of defining the structure.
TYPE DEFINED STRUCTURE
Syntax : Example :
typedef struct
{
data_type1 member_name1;
data_type2 member_name2;
…… …….
…… …….
data_typeN member_nameN;
}
TYOE_ID;
typedef struct
{ char cname[26];
int cid;
int run;
long int score;
}
CRICKETER;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![Syntax :
struct tag_name variable = {mv1,mv2,mvn};
Example :
struct employee
{
char name[20];
int salary;
int id;
}a={“Hemant”,10000,420};
STRUCTURE INITIALIZATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-9-320.jpg)

![PROGRAM :
#include<stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
struct employee
{
int id;
char name[50];
}e1;
void main( )
{
e1.id=420;
strcpy(e1.name,“Hemant Yadav”);
printf( "employee 1 id : %dn", e1.id);
printf( "employee 1 name : %sn", e1.name);
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-11-320.jpg)

![ A union is a special data type available in C that allows to store
different data types in the same memory location. You can define a
union with many members, but only one member can contain a value
at any given time. Unions provide an efficient way of using the same
memory location for multiple-purpose.
Syntax : Example :
union [union tag]
{
member definition;
member definition;
...
member definition;
} [one or more union variables];
UNION
union Data
{
int i;
float f;
char str[20];
} data;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancejava-240204074419-aa3f9995/85/Javaadvance-applet-and-applet-life-cycle-pptx-13-320.jpg)