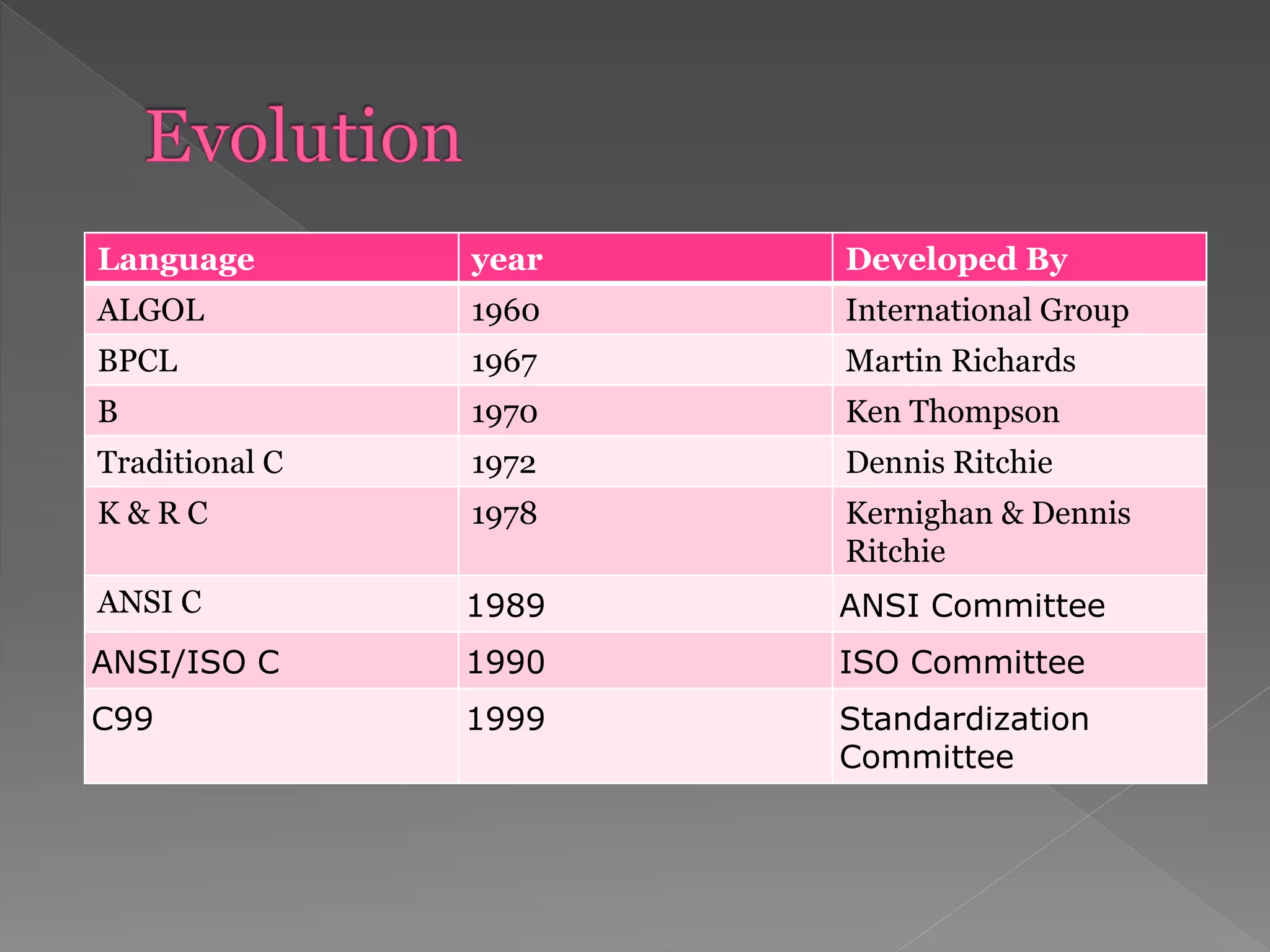
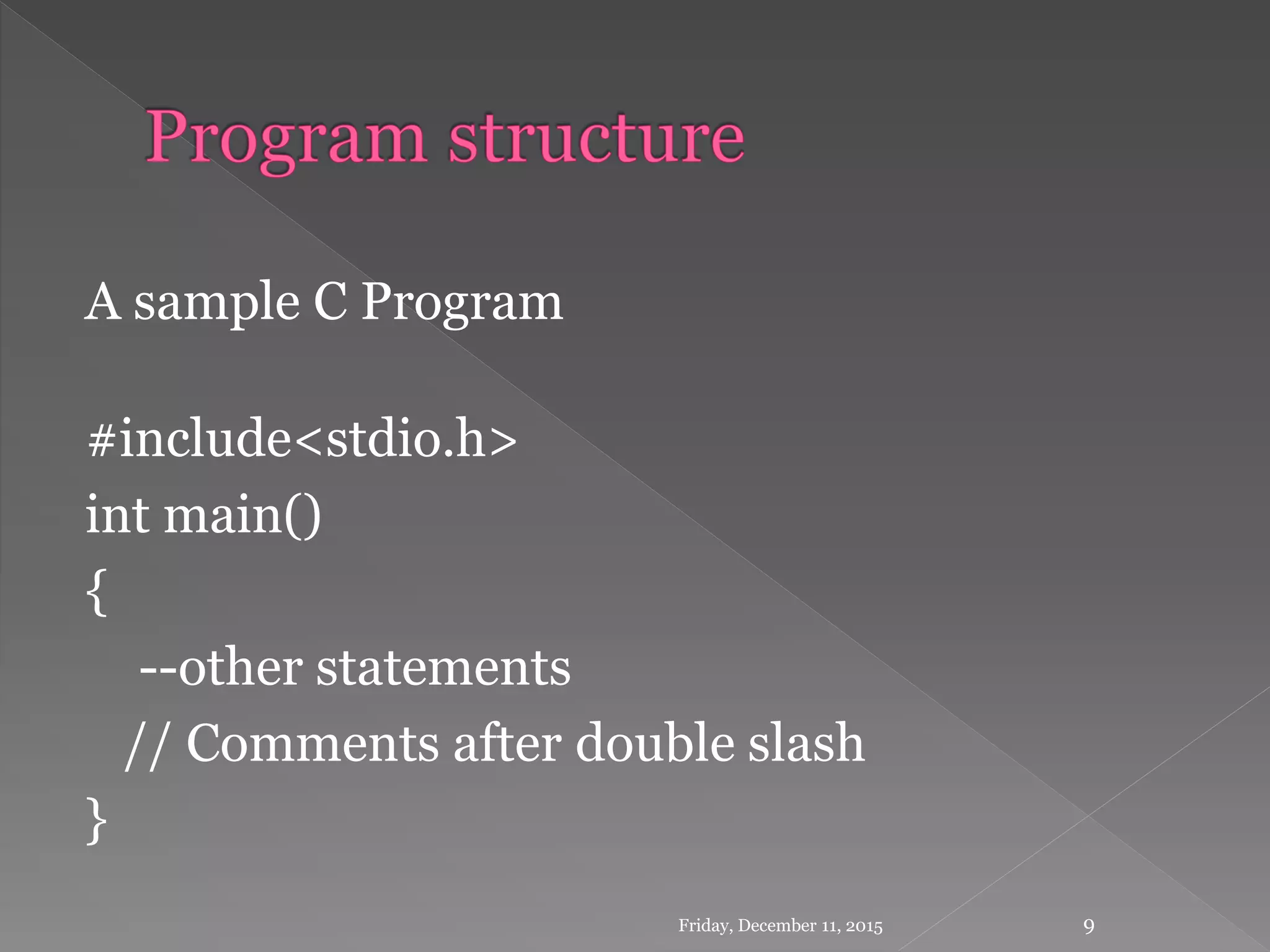
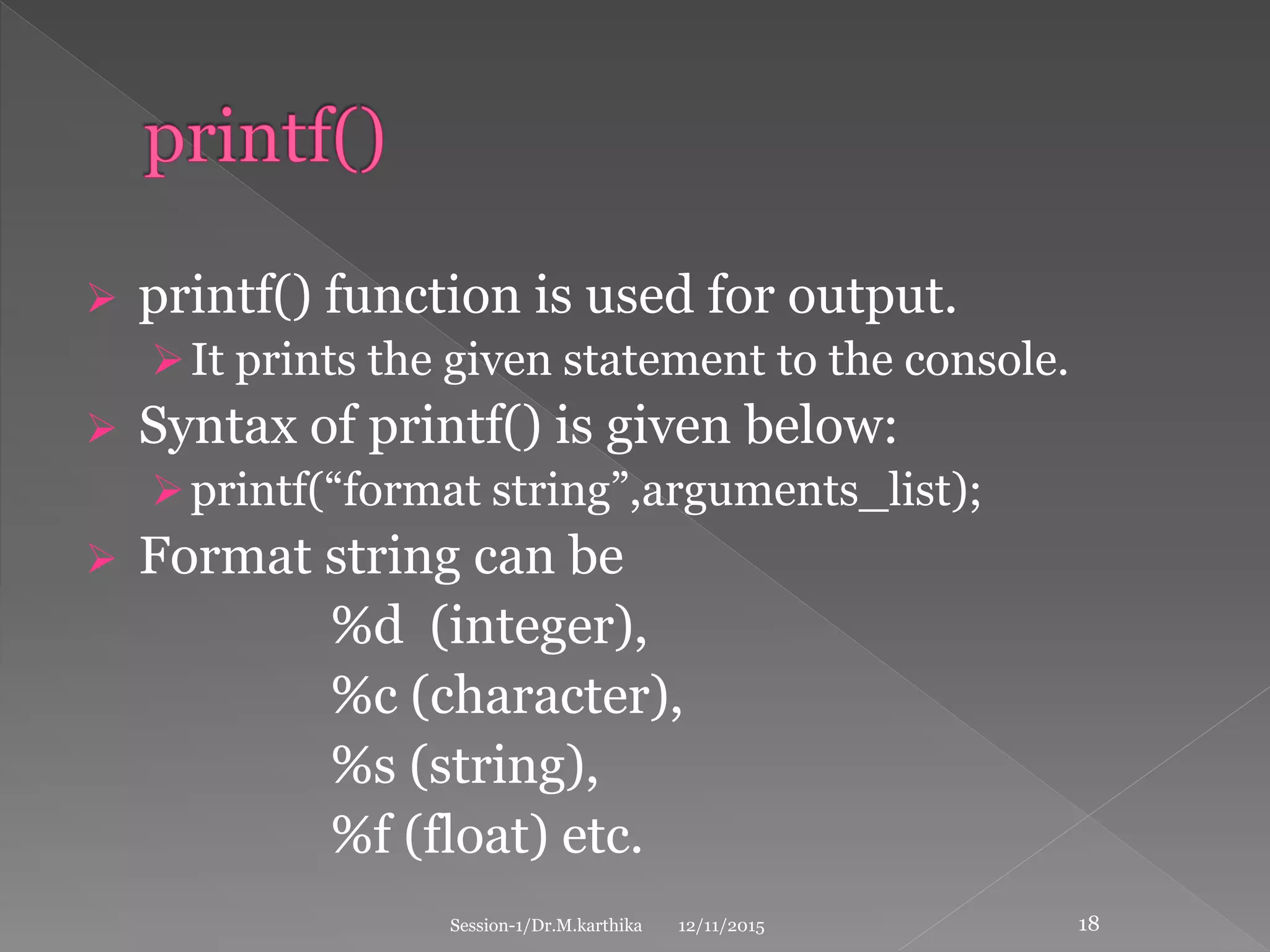
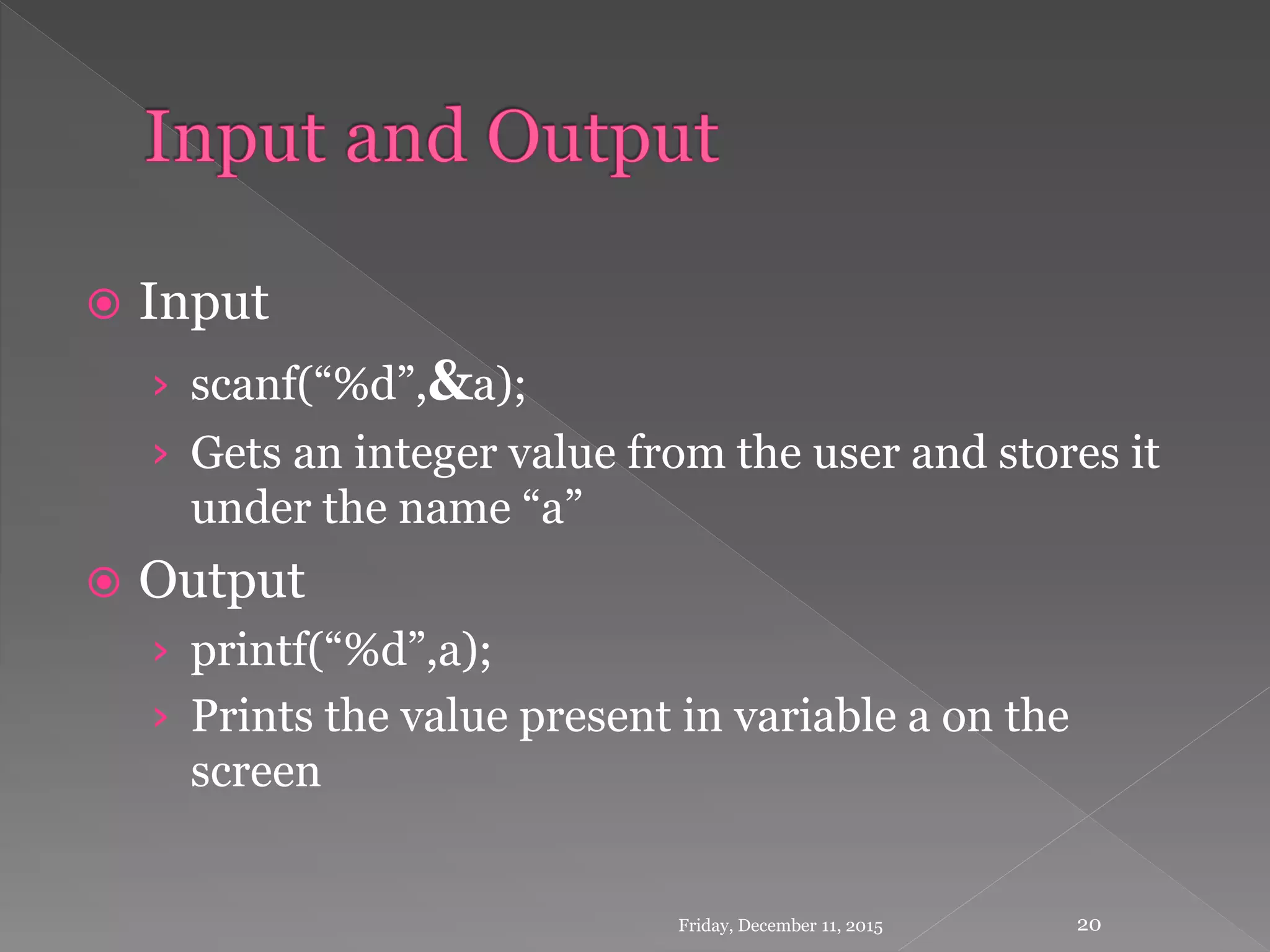
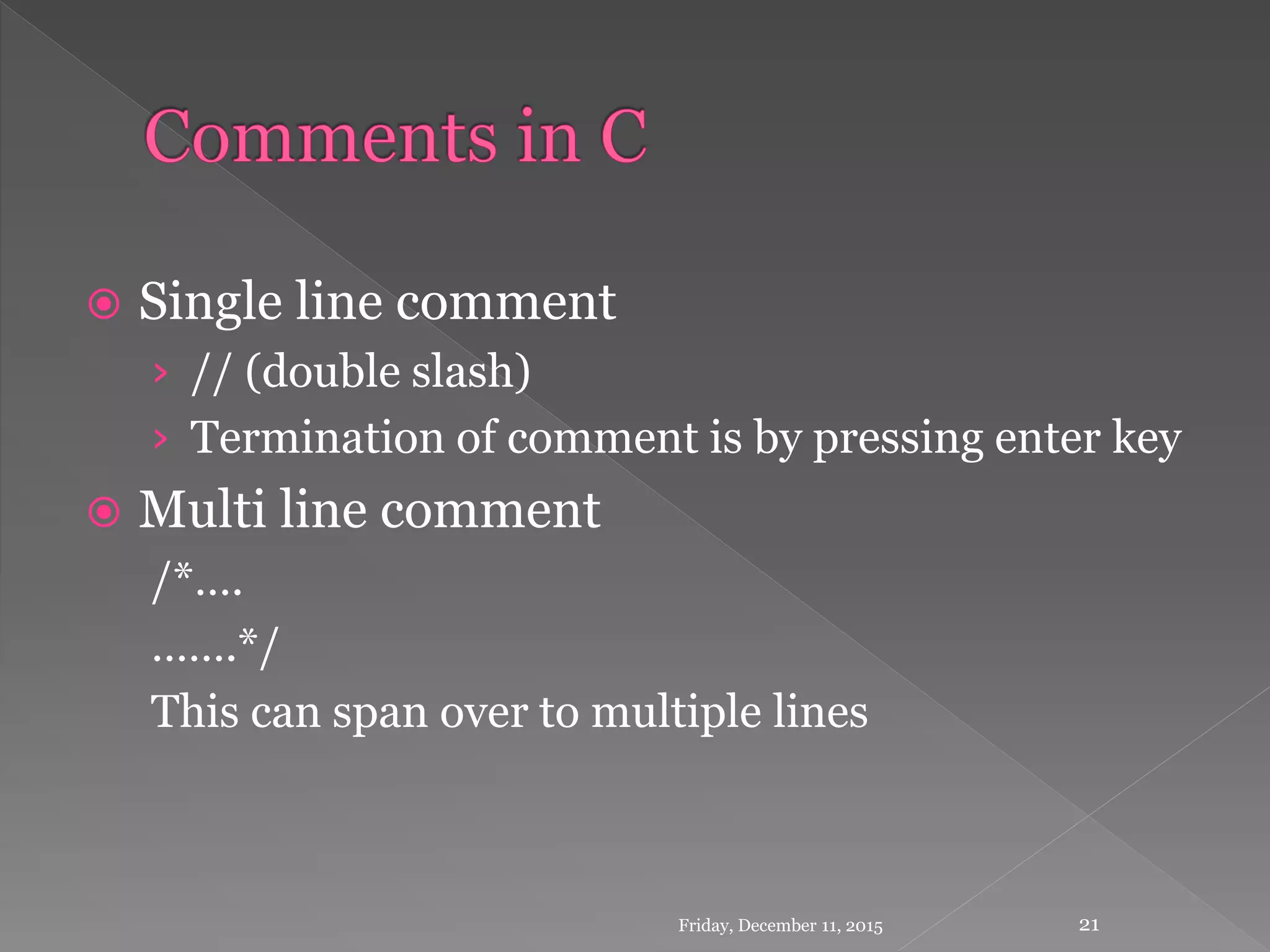
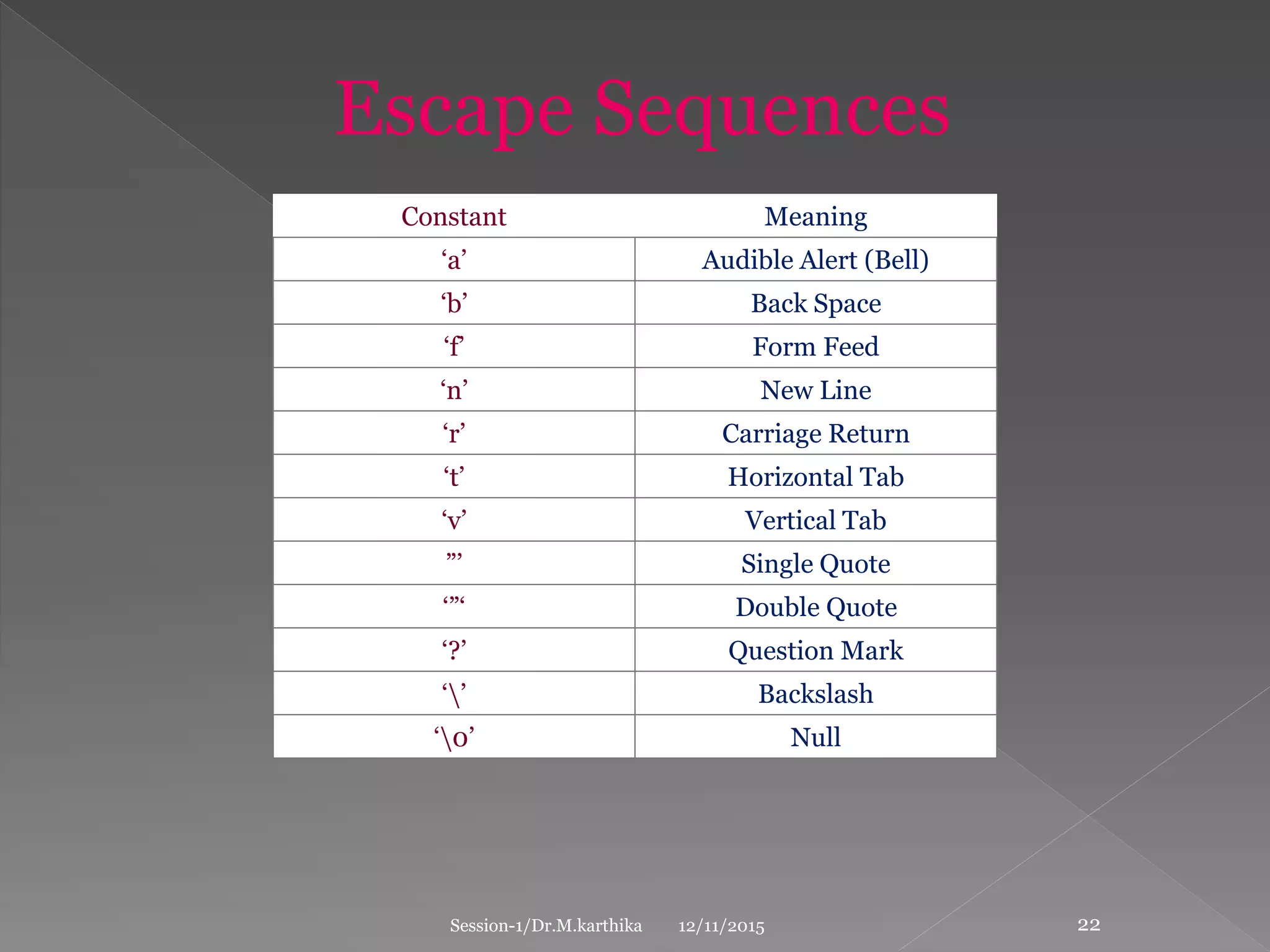
This document provides an introduction to the C programming language. It discusses that C was developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs to be used for the UNIX operating system. The document then covers some key characteristics of C including that it is a structured, low-level programming language. It also lists some common features of C like simple syntax, rich libraries, and pointers. The document concludes with examples of basic C programs and descriptions of input/output functions and escape sequences.