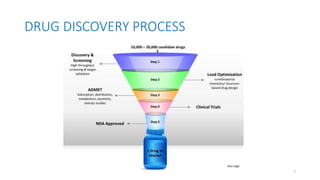
This document provides an overview of the drug discovery process. It discusses both discovery without a lead, like penicillin and Librium, as well as discovery with a lead. Methods of lead discovery discussed include random screening, non-random screening, drug metabolism studies, clinical observations, and rational drug design approaches. The drug discovery process is long, typically taking 12-15 years and costing $600-800 million to bring a new drug to market. Examples like penicillin, Librium, and other drugs are used to illustrate key concepts and approaches in drug discovery.









![Drug Discovery without lead
Penicillins and Librium are two important drugs that were discovered without a
lead [accidental discovery].
1. Penicillin
Penicillin G
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugdiscovery-220426152413/85/DRUG-DISCOVERY-pptx-11-320.jpg)



![2. LIBRIUM
• The first benzodiazepine tranquilizer drug, chlordiazepoxide HCI [7-chloro-2-
(methylamino-5-phenyl-3 H-1,4-benzodiazepine 4-oxide] (Librium) was
discovered by Dr. Leo Sternbach at Roche was involved in a program to
synthesize a new class of tranquilizer drugs. He originally set out to prepare a
series of benzheptoxdiazines.
• Chlordiazepoxide HCl
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugdiscovery-220426152413/85/DRUG-DISCOVERY-pptx-15-320.jpg)







![Drug metabolism studies :
During drug metabolism studies, metabolites that are isolated are screened to
determine if the activity observed is derived from the drug candidate or from
a metabolite.
Eg: The anti-inflammatory drug Sulindac[clinoril] is not the active agent.
The metabolic reduction product is responsible for the activity.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugdiscovery-220426152413/85/DRUG-DISCOVERY-pptx-23-320.jpg)