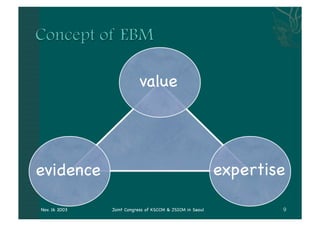
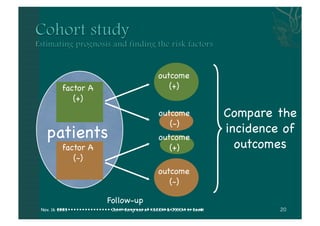
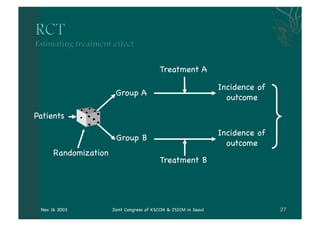
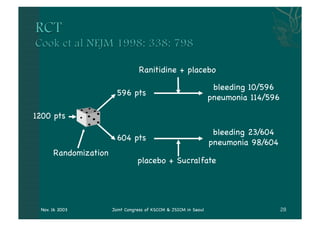
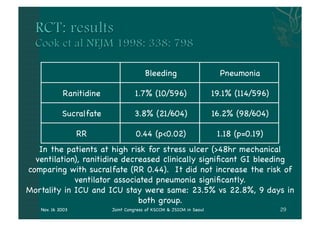
- The document discusses providing stress ulcer prophylaxis to critically ill patients. It outlines the history and risk factors for stress ulcers, results of clinical trials on different prophylaxis treatments, and guidelines on when to provide prophylaxis based on evidence and expertise. Key points include that mechanical ventilation over 48 hours and coagulopathy significantly increase risk of bleeding, ranitidine may reduce this risk but also increase risk of pneumonia, and prophylaxis decisions require considering individual patient risk factors and prognosis.