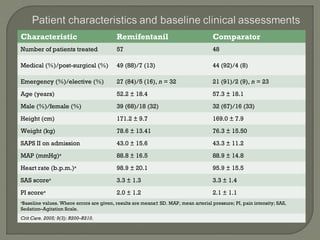
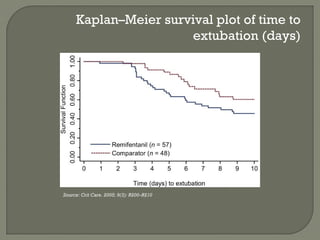
This randomized trial compared analgesia-based sedation using remifentanil versus standard hypnotic-based sedation for up to 10 days in intensive care unit patients requiring mechanical ventilation. It found that remifentanil reduced the duration of mechanical ventilation and improved the weaning process compared to standard sedation. Specifically, remifentanil decreased the time from starting treatment to extubation by an average of 53.5 hours and decreased the time from starting weaning to extubation by 26.6 hours on average. Remifentanil also required less sedative medication compared to standard therapy. The adverse event profiles were similar between the two groups.















![ Citation
Breen D, Karabinis A, Malbrain M, Morais R, Albrecht S, Jarnvig I-L, Parkinson P, Kirkham AJT:
Decreased time on mechanical ventilation when comparing analgesia-based sedation
using remifen-tanil versus standard hypnotic-based sedation for up to 10 days in ICU
patients: a randomised trial. [ISRCTN47583497].
Crit Care 2005, 9:R200-R210
Background
Sedation and analgesia on the ITU is a complex balancing act. At all times trying to
ensure optimal patient comfort in a group that have a variety of problems and
organ dysfunction as well as often quite protracted length of stay. All of which in
combination with the various drug interactions can alter the pharmacological effect
of all our therapies. Remifentanil in some respects ticks most of the boxes of an
ideal opioid, bar cost. Its use on the ITU seems to have a great deal of potential.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icuanalgesia-121108231212-phpapp01/85/ICU-analgesia-17-320.jpg)











![1. Breen, D; Wilmer, A; Bodenham, A; Bach, V; Bonde, J; Kessler, P; Albrecht, S; Shaikh, S. Offset of
pharmacodynamic effects and safety of remifentanil in intensive care unit patients with various
degrees of renal impairment. Crit Care. 2004;8:R21–R30. doi: 10.1186/cc2399.
2. Muellejans, B; Lopez, A; Cross, MH; Bonome, C; Morrison, L; Kirkham, AJT. Remifentanil versus
fentanyl for analgesia based sedation to provide patient comfort in the intensive care unit: a
randomised control trial [ISRCTN43755713]. Crit Care. 2004;8:R1–R11. doi: 10.1186/cc2398
3. Dahaba, AA; Grabner, T; Rehak, PH; List, WF; Metzler, H. Remifentanil versus morphine
analgesia and sedation for mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: a randomised double
blind study. Anesthesiology. 2004;101:640–646. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200409000-00012
4. Karabinis, A; Mandragos, K; Stergiopoulos, S; Komnos, A; Soukup, J; Speelberg, B; Kirkham,
AJT. Safety and efficacy of analgesia-based sedation using remifentanil versus standard
hypnotic-based regimens in intensive care unit patients with brain injuries: a randomised,
controlled trial [ISRCTN50308308]. Crit Care. 2004;8:R268–R280. doi: 10.1186/cc2896.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icuanalgesia-121108231212-phpapp01/85/ICU-analgesia-31-320.jpg)