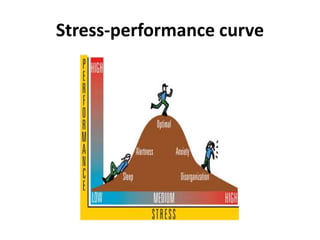
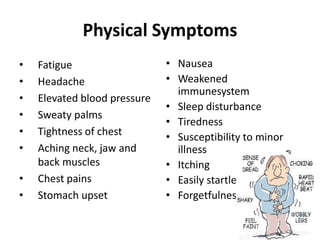
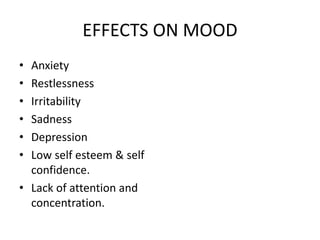
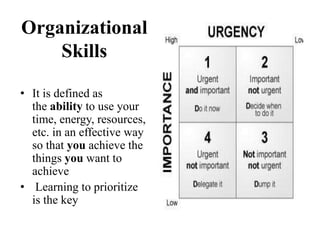
Dr. Mohit Bansal's presentation discusses stress management. It defines stress and notes that stress has positive and negative aspects. Moderate stress can improve performance while too much stress can harm health. The presentation covers common sources of stress for medical students like academic demands, examinations, and relationships. It then discusses the effects of stress on the body, mood, and behavior. Finally, it outlines various stress management techniques including relaxation, mindfulness meditation, anger management, assertiveness skills, time management, and maintaining a work-life balance.