Embed presentation
Downloaded 32 times







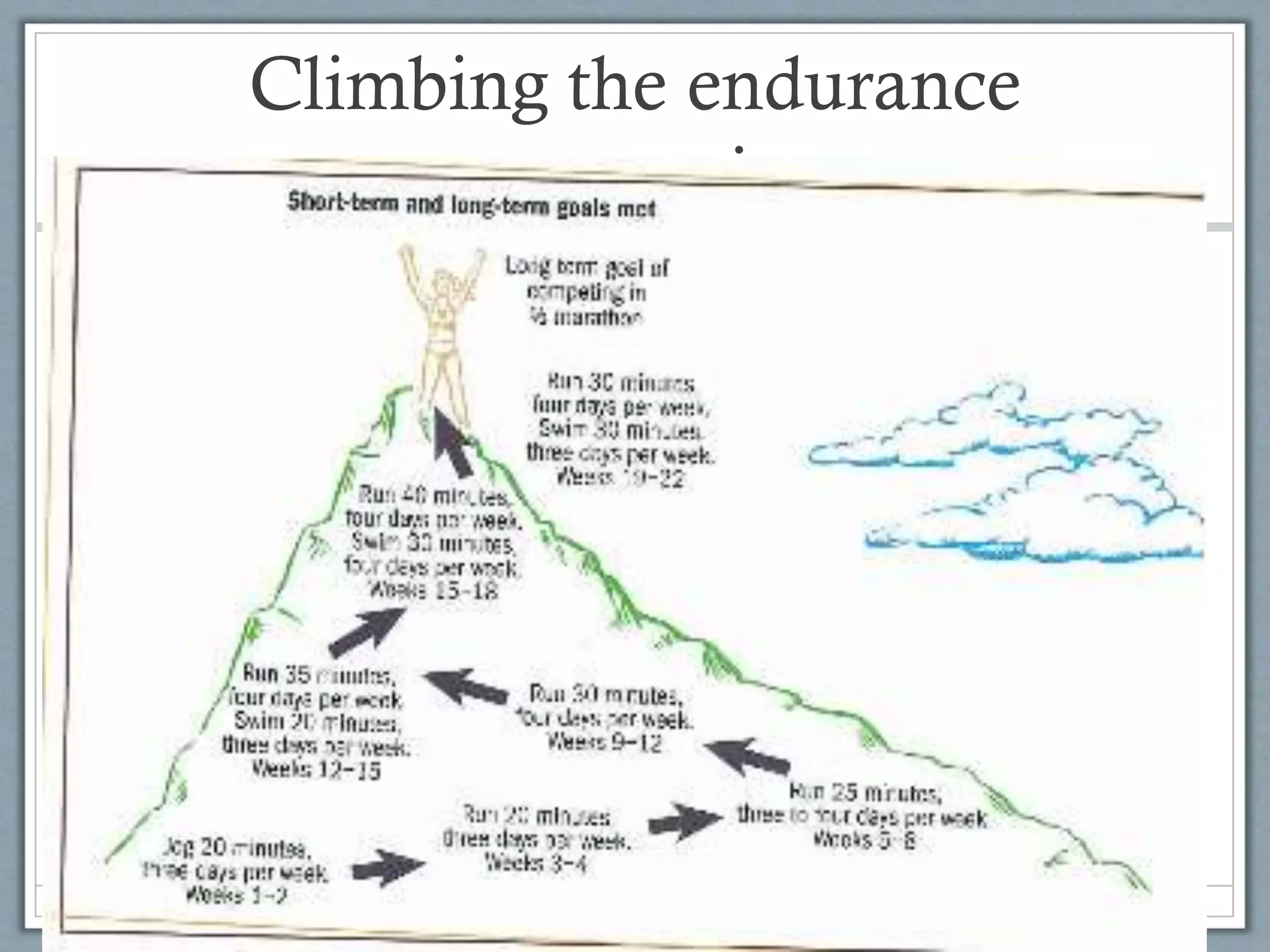


This document discusses goal setting for athletes. It outlines three types of goals - outcome goals, performance goals, and process goals. Outcome goals focus on the end result, performance goals compare to previous performances, and process goals focus on specific actions. The document recommends setting short-term performance goals to achieve long-term outcome goals. It also introduces the SMARTER framework for writing goals, which focuses the thoughts on being specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound, exciting, and recorded. Goal setting is shown to improve work output by 40-50% by focusing attention and encouraging perseverance.









