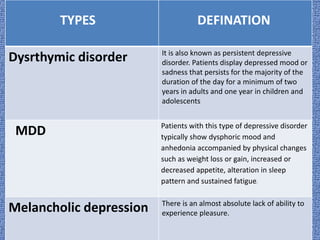
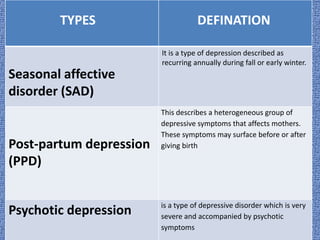
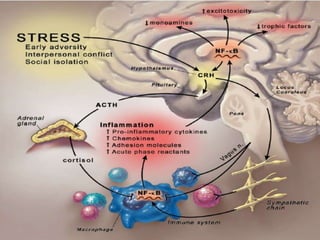
Stress and depression can arise from a variety of causes and have physical, psychological, and social impacts. Treatment involves both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches. Non-pharmacological treatments include cognitive behavioral therapy, which helps patients change negative thought patterns, and interpersonal therapy, which addresses interpersonal issues that can contribute to depression. Stress and depression are associated with changes in the brain and involve neural circuits, stress response systems, and neurotransmitter levels.











































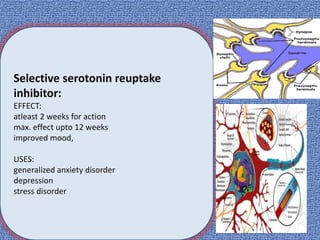
![Selective serotonin reuptake
inhibitor:
• fluoxetin[Prozac],
•citalopram(Cipralex)
•escitalopram(Cipram )
MOA:
selectively inhibit reuptake of serotonin
little affect on dopamine, H1 receptor,
alpha adrenergic receprors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stressanddepression-191011093831/85/Stress-and-depression-53-320.jpg)
![KINETICS:
•food little affect on absorption
•well absorbed orally
•half life 16 to 36 hours(for dose calculation )
•CYP 450 dependent enzyme
•Urine excretion except sertaline (fecal)…[dose adjustment]
ADVERSE EFFECT:
•Suicidal attempt in children
•Withdrawl symptoms
•Insomnia
•Nausea
•Drowsiness](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stressanddepression-191011093831/85/Stress-and-depression-55-320.jpg)