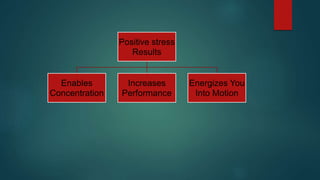
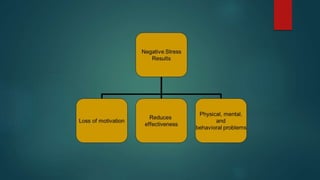
- Stress is defined as an organism's response to environmental stressors and can negatively impact mental and physical well-being. Moderate stress may improve performance while too much causes issues.
- Major causes of stress include life changes like job losses, promotions, deaths, and relocations. Chronic stress over long periods is most harmful.
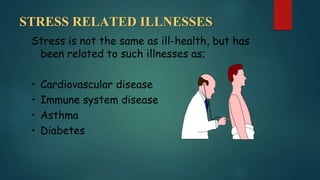
- Symptoms of stress can be physical, mental, behavioral, and emotional like headaches, digestive issues, mood changes, and eating/sleeping problems. Stress is linked to illnesses like heart disease.
- Managing stress involves time management, relaxation, cognitive techniques, asking for help from others, focusing on the present, self-care, and developing a stress control plan with