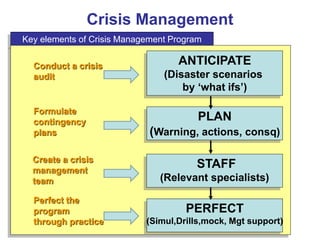
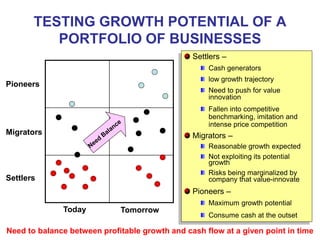
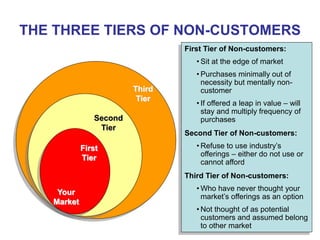
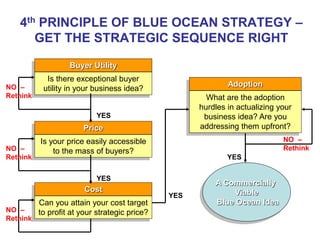
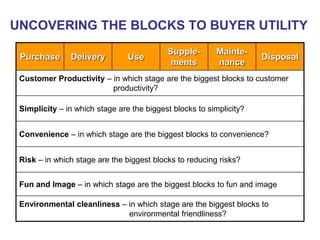
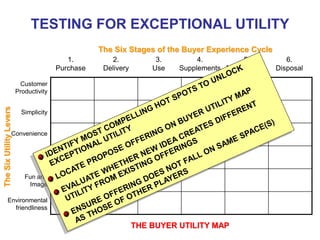
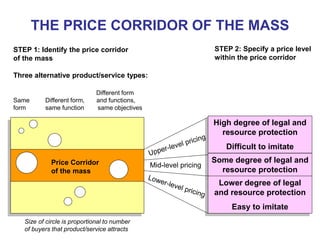
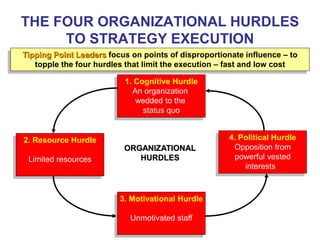
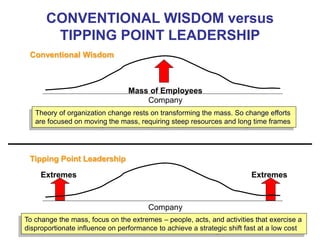
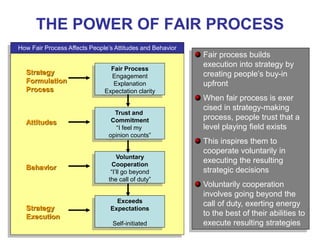
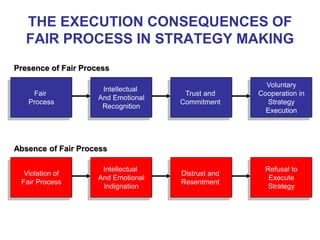
The document discusses stress management and provides information on what stress is, common signs and symptoms of stress, and how to manage stress. It defines stress as feelings of pressure or demands and notes that stress can affect people physically and mentally. Common signs listed include sleeping problems, sweating, and difficulty concentrating. The document recommends recognizing early signs of stress and provides tips for managing stress such as learning relaxation techniques, exercising regularly, and using good time management. It advises seeing a doctor if stress symptoms are severe or self-help methods are not working.