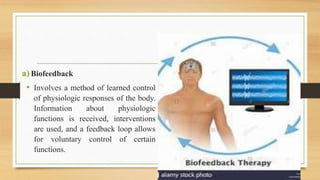
Complementary therapies are medical interventions not currently part of conventional medicine. They can be categorized into five groups: alternative medical systems, mind-body interventions, manipulative and body-based methods, energy therapies, and biologically based treatments. Examples include aromatherapy, massage therapy, acupuncture, meditation, yoga, and herbal remedies. Nurses' roles regarding complementary therapies include assessing patient use and risks, promoting safety, providing holistic care, serving as providers, and participating in research.