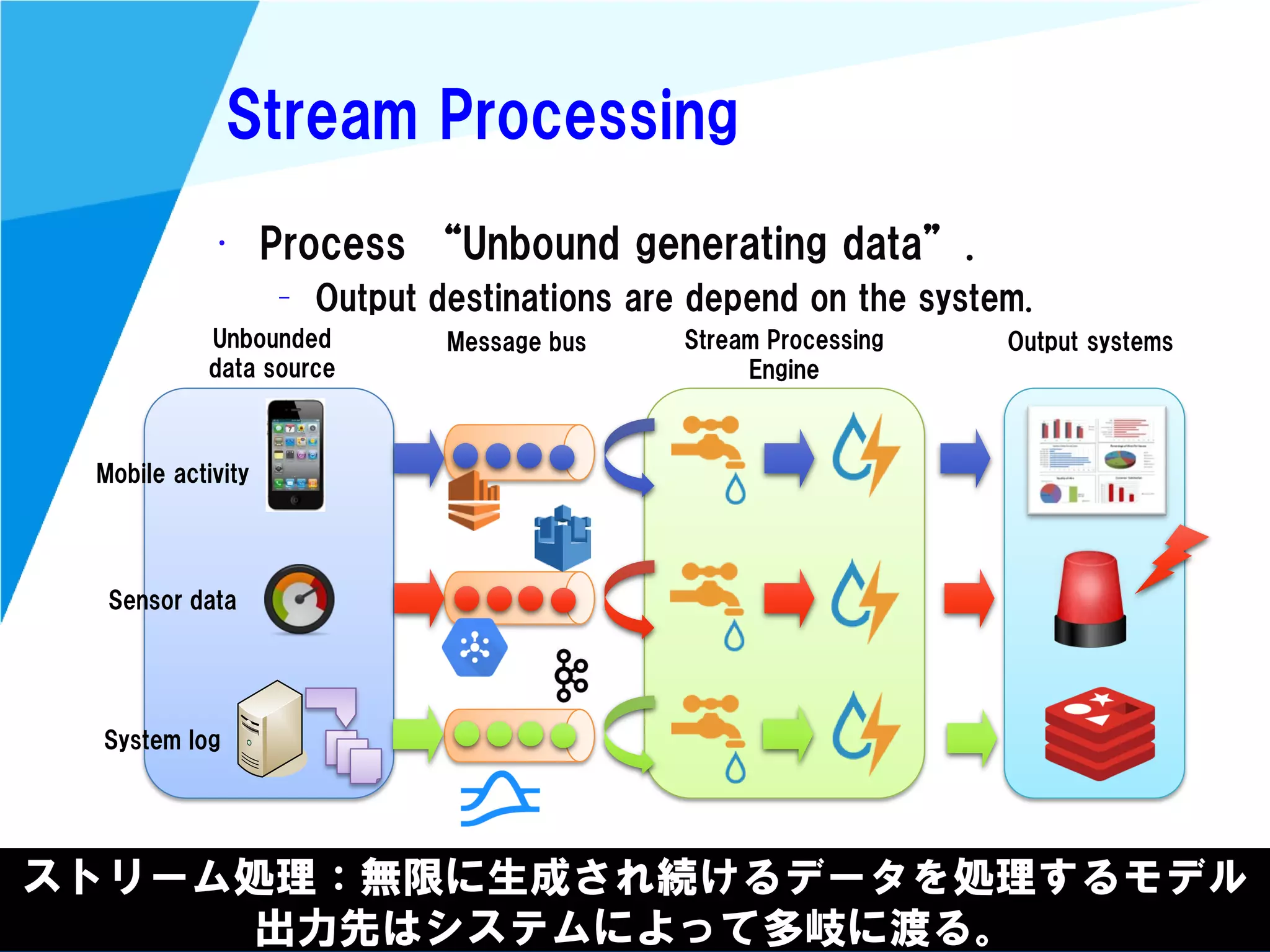
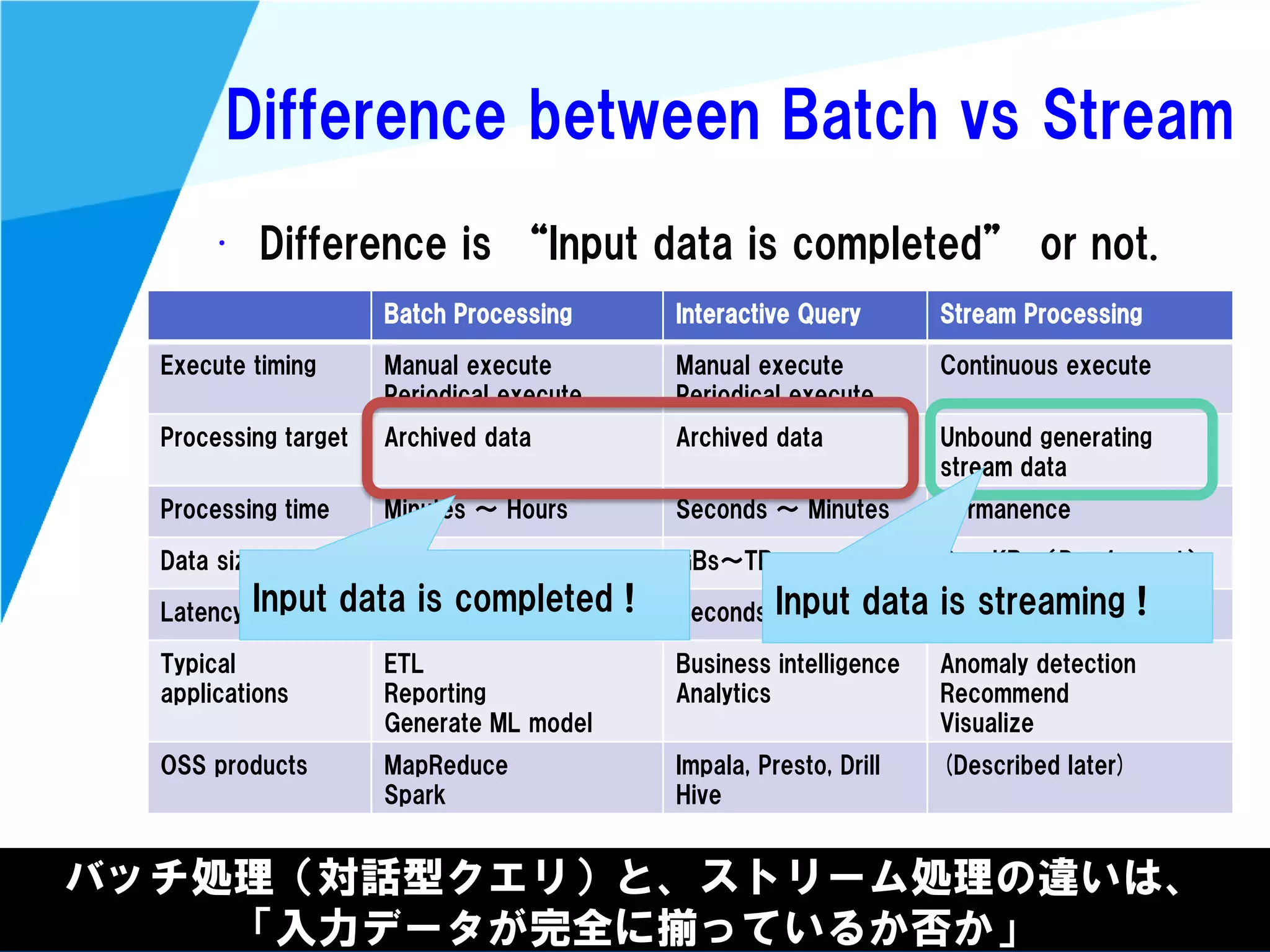
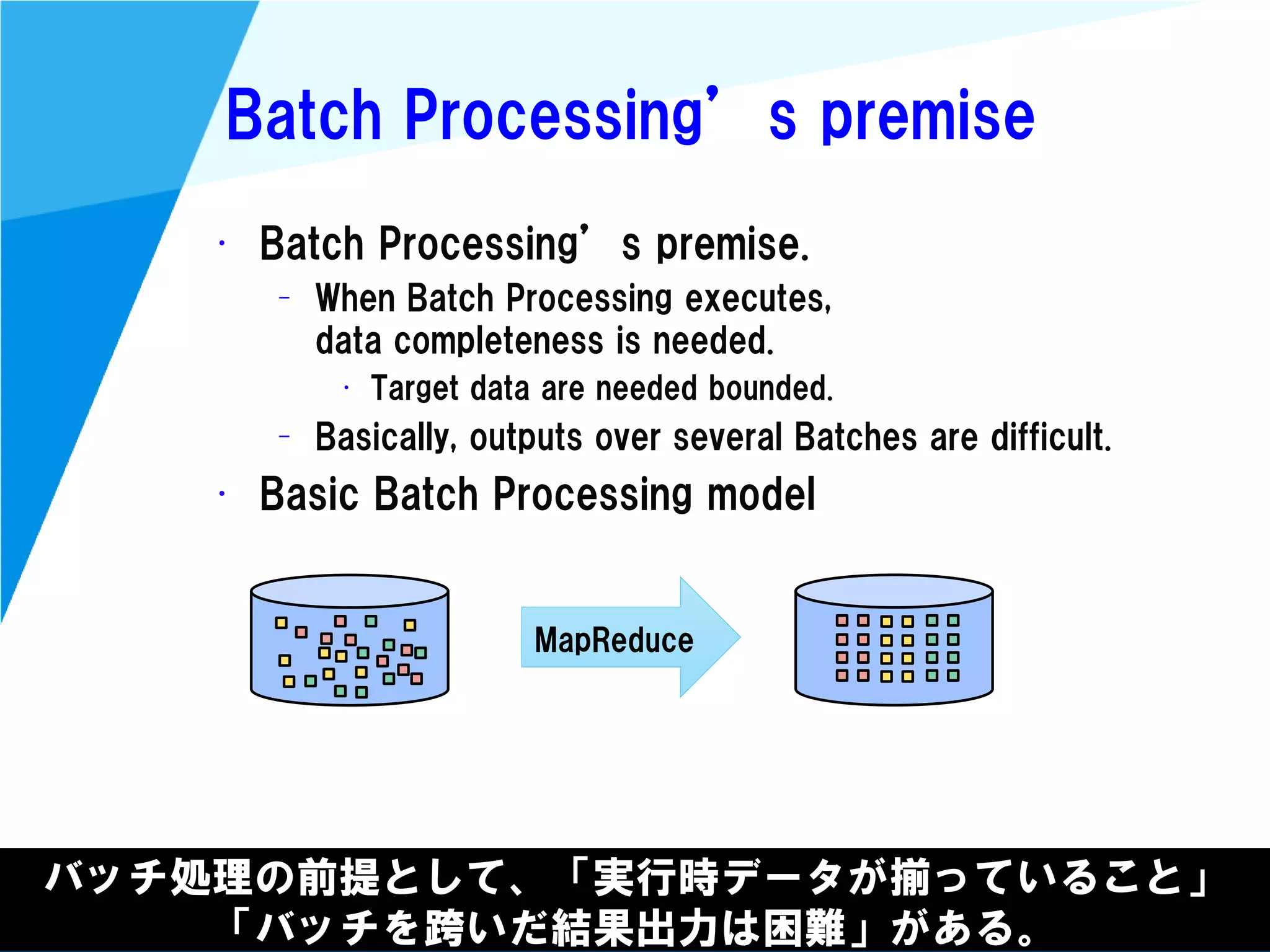
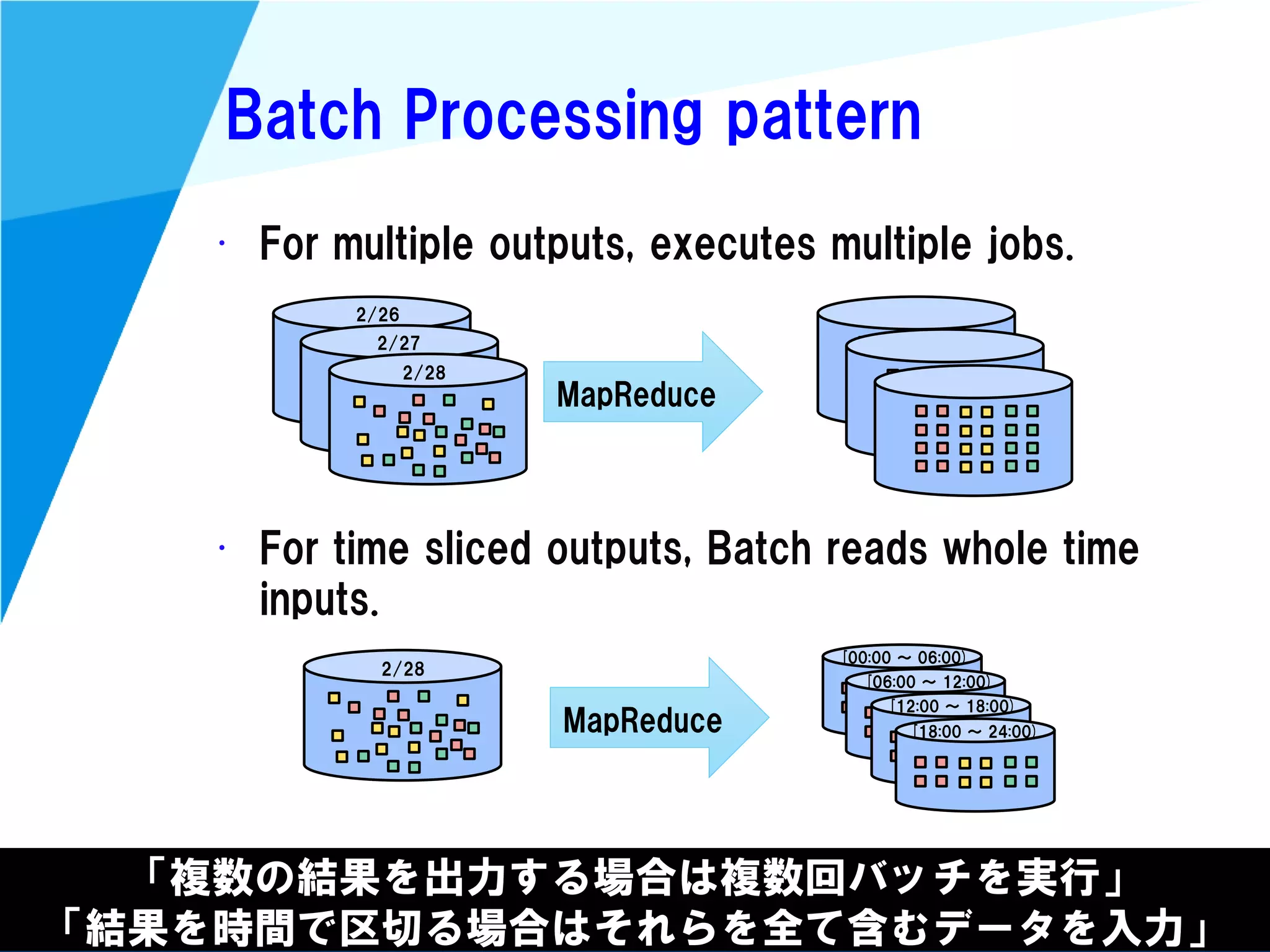
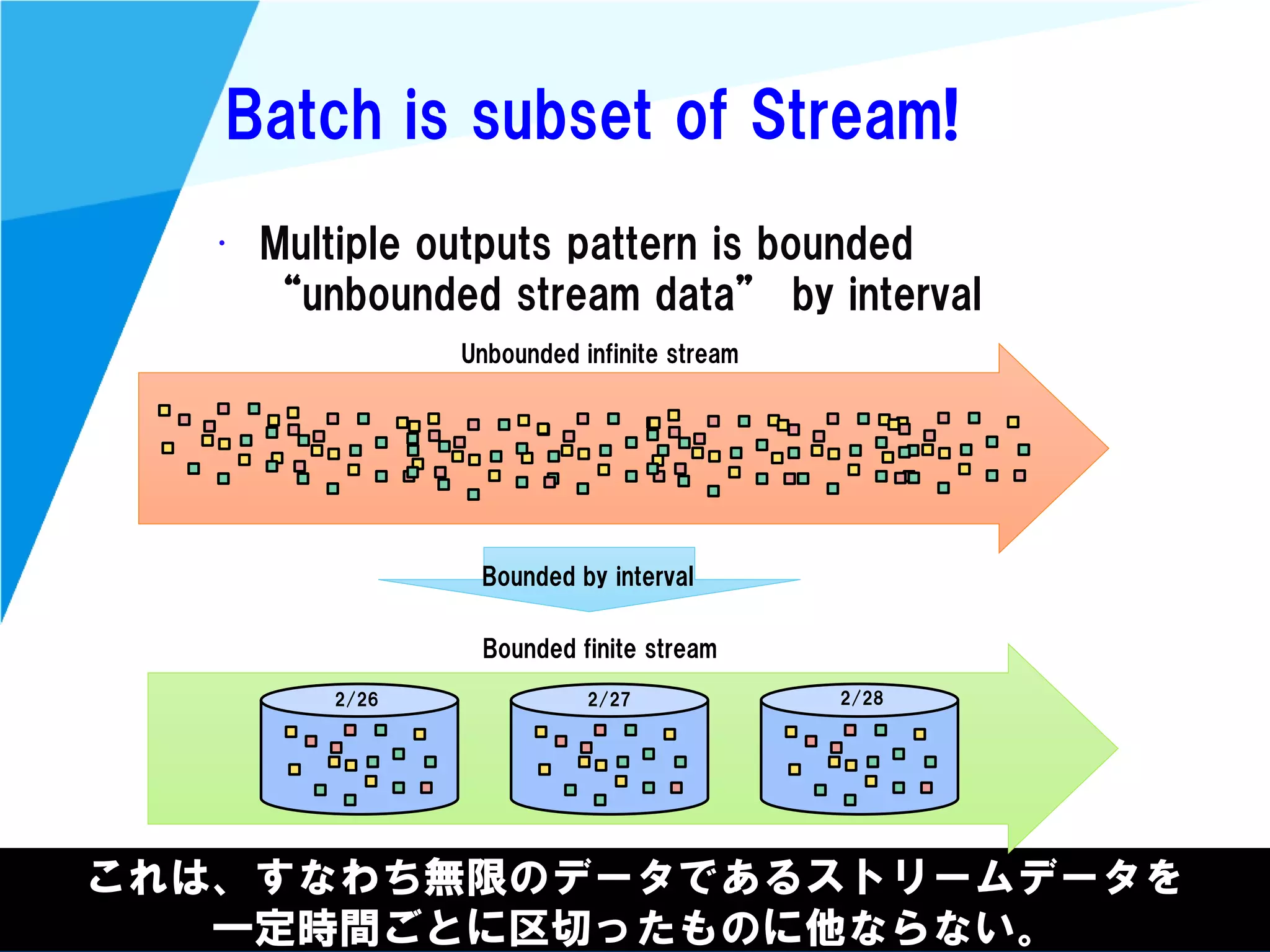
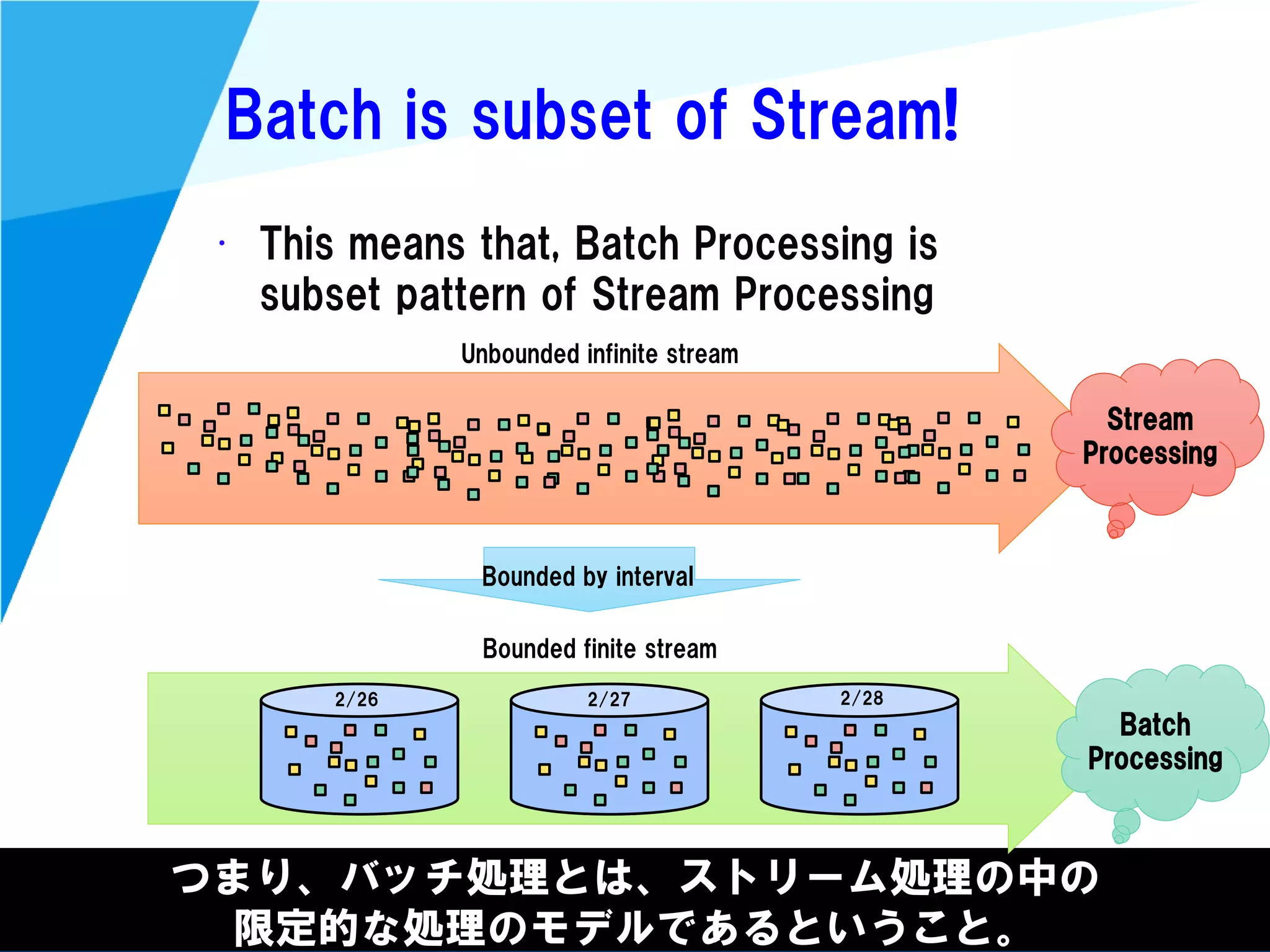
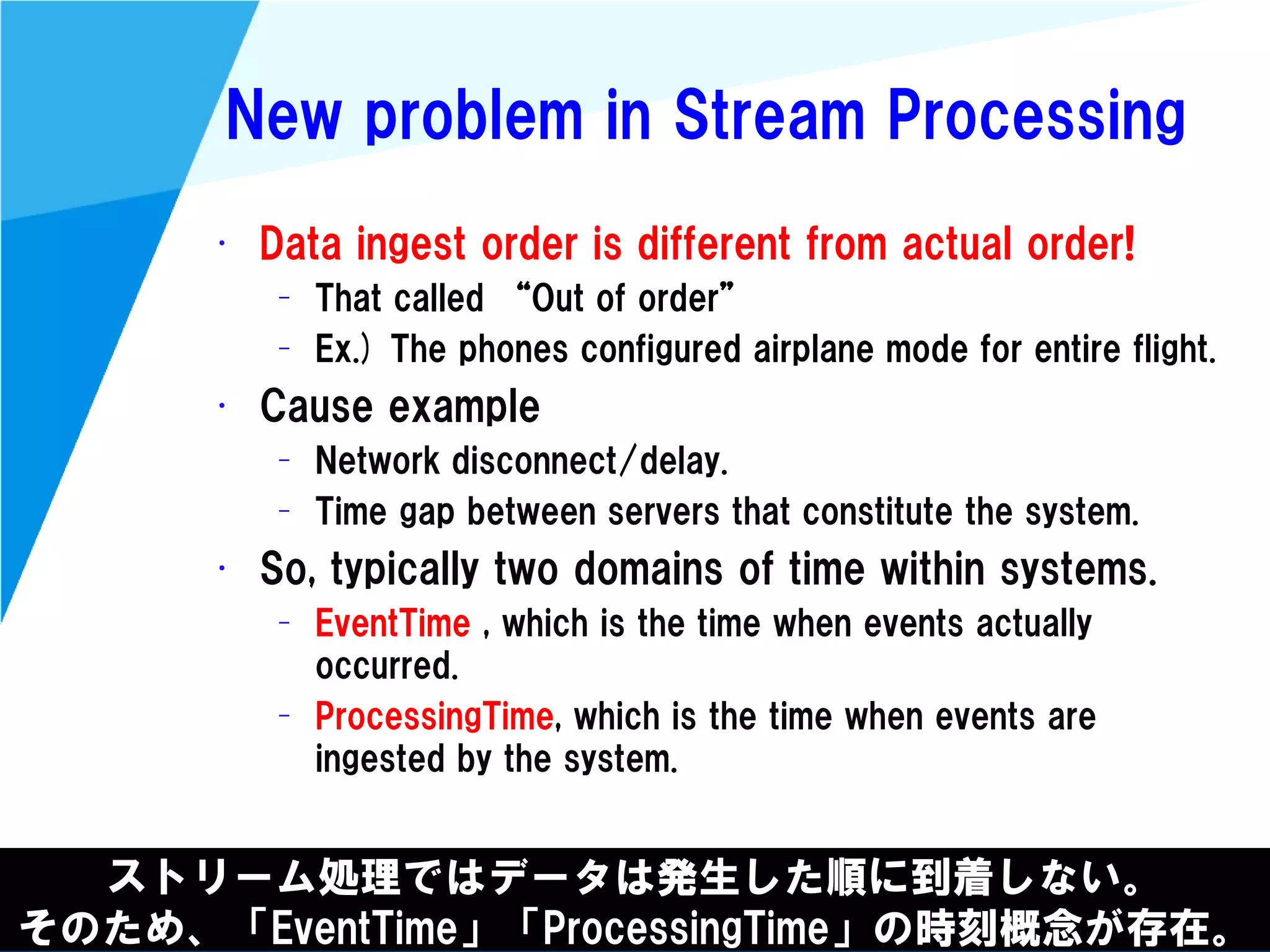
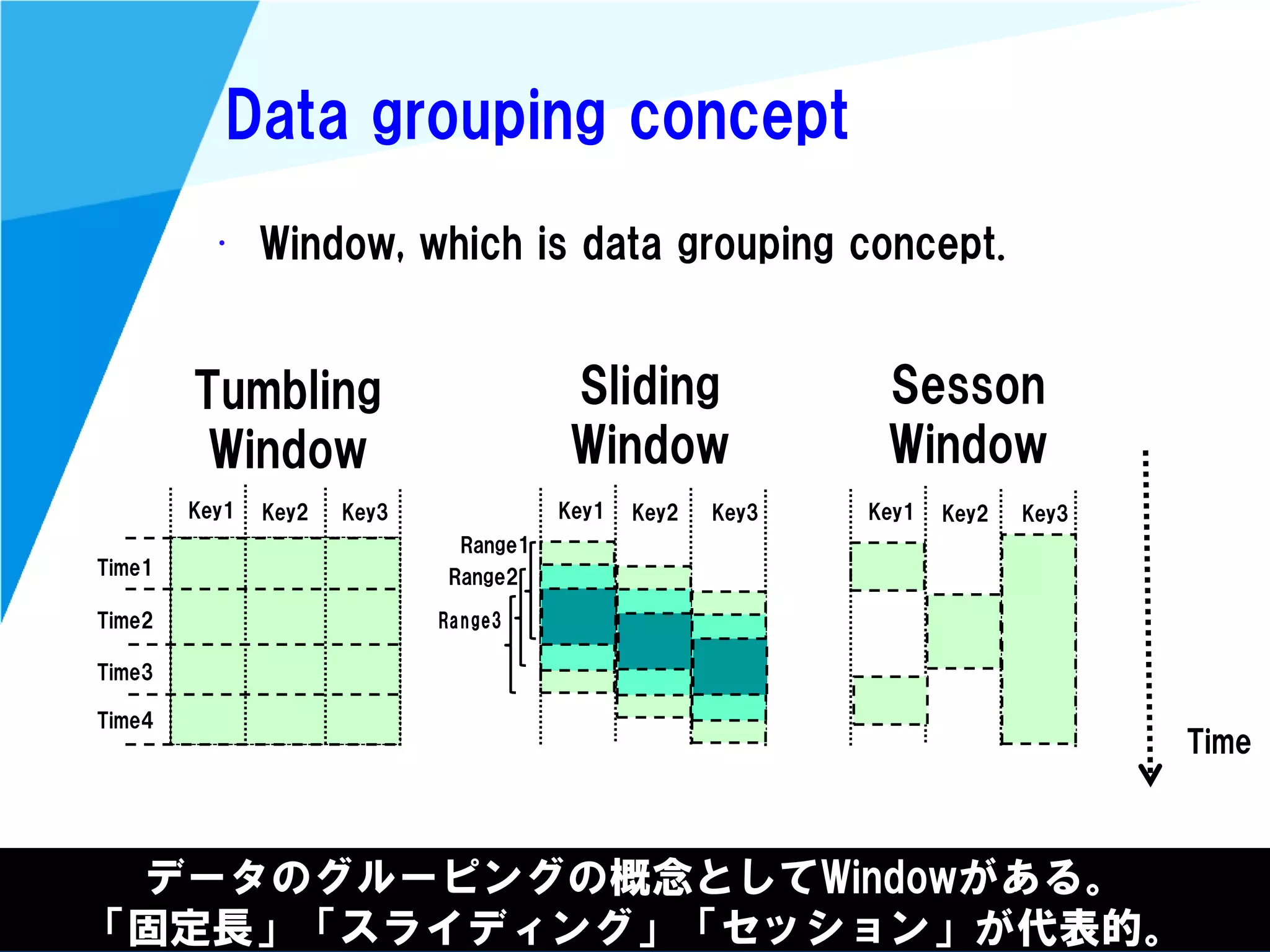
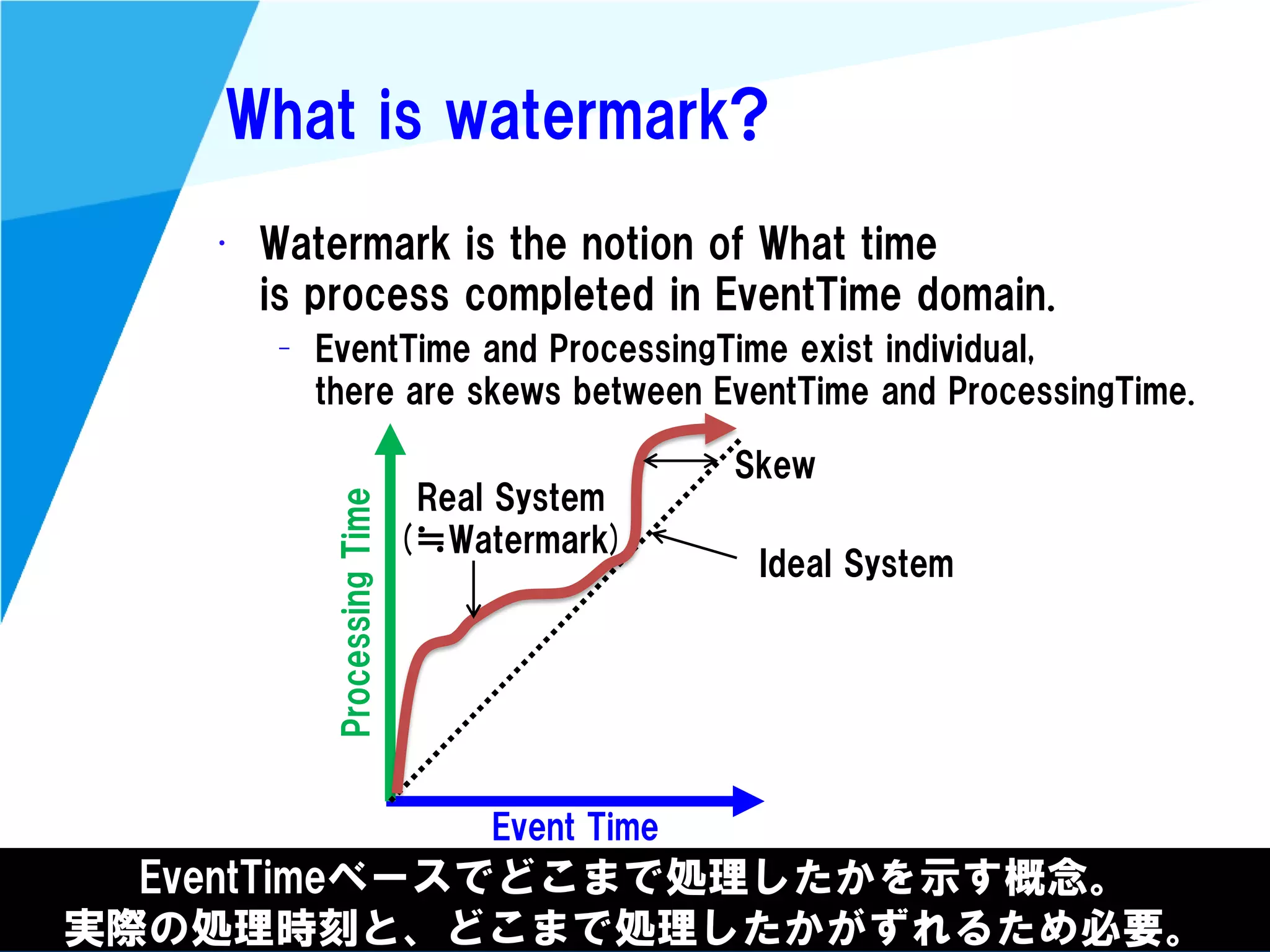
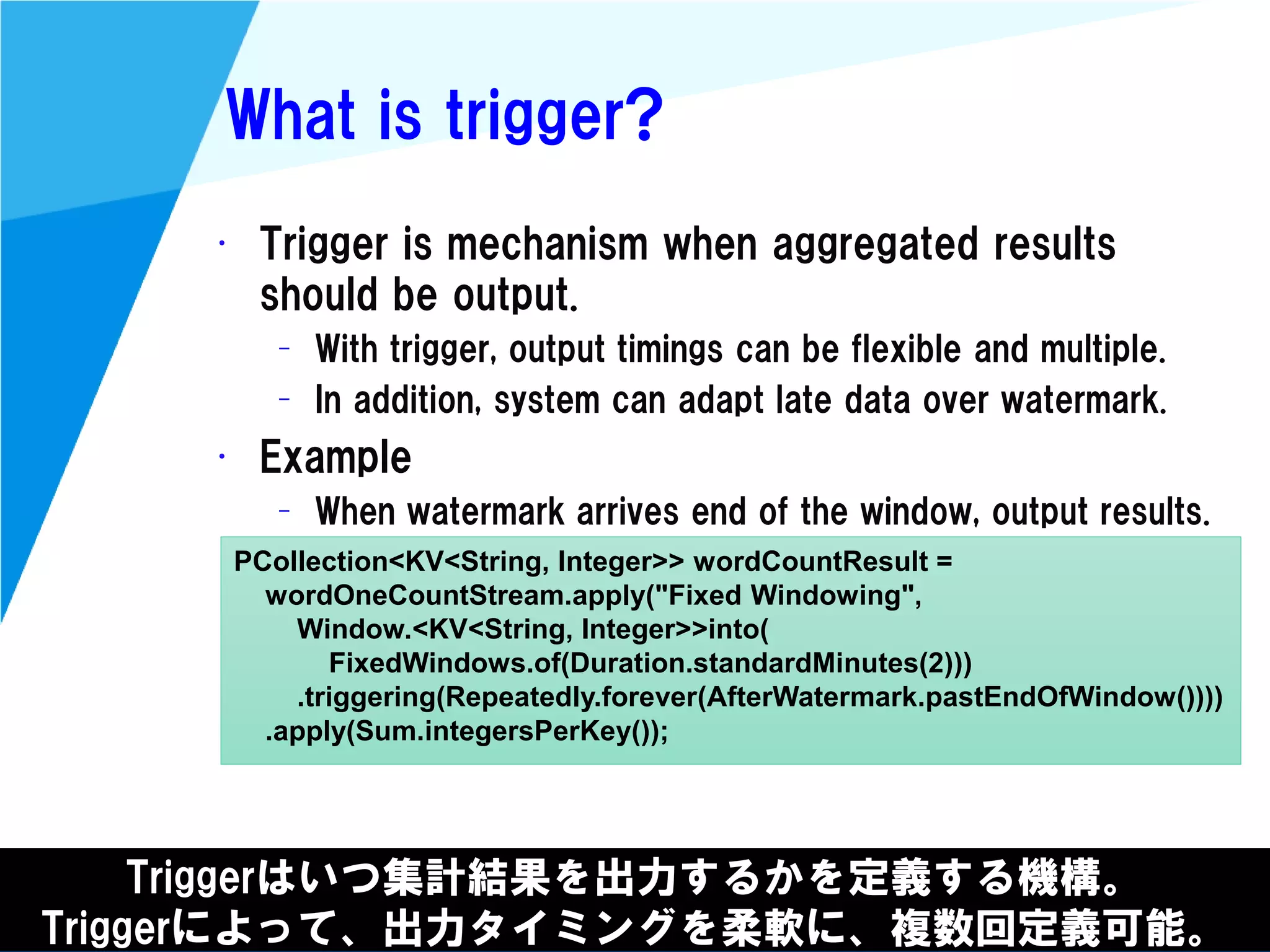
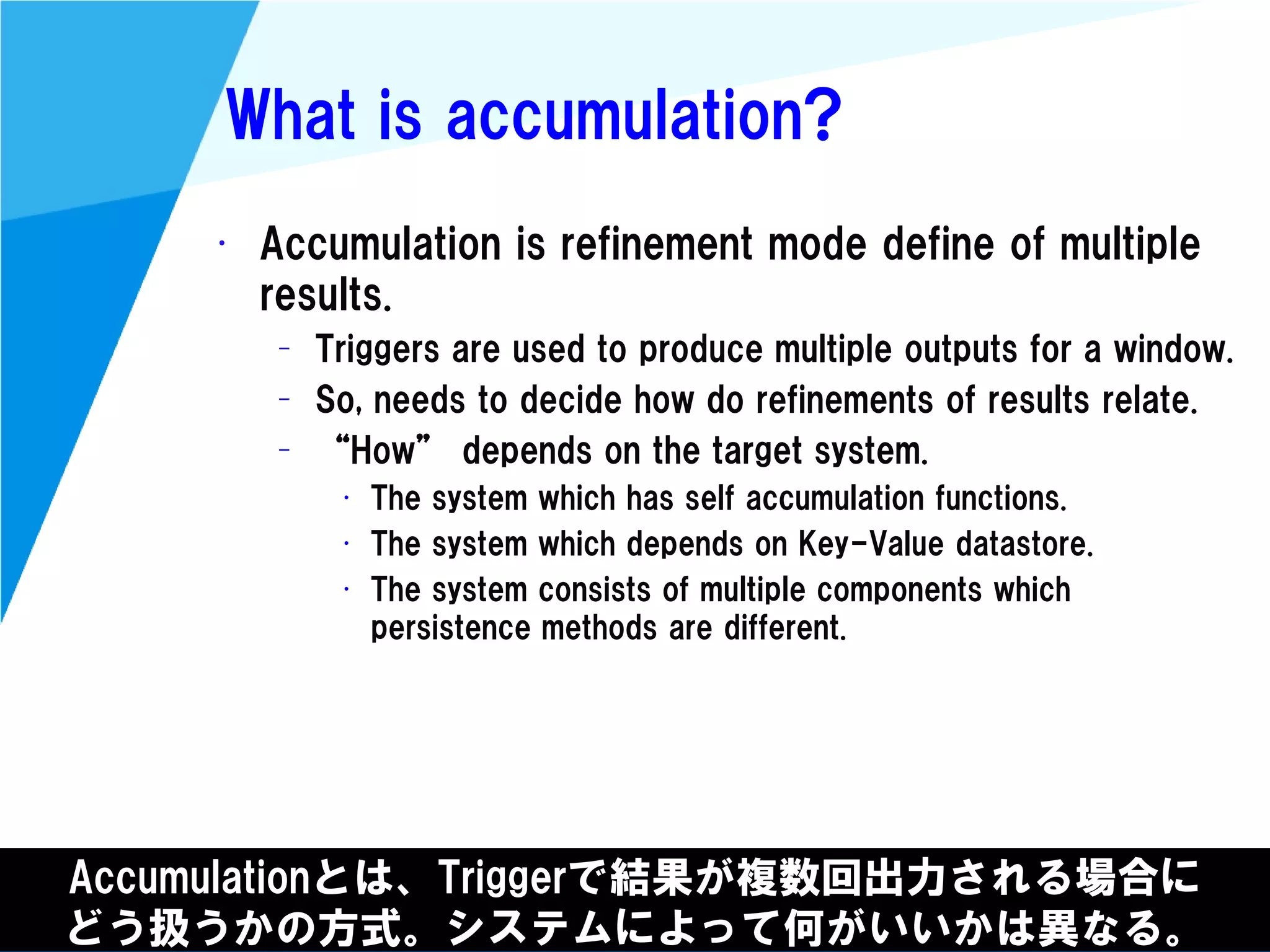
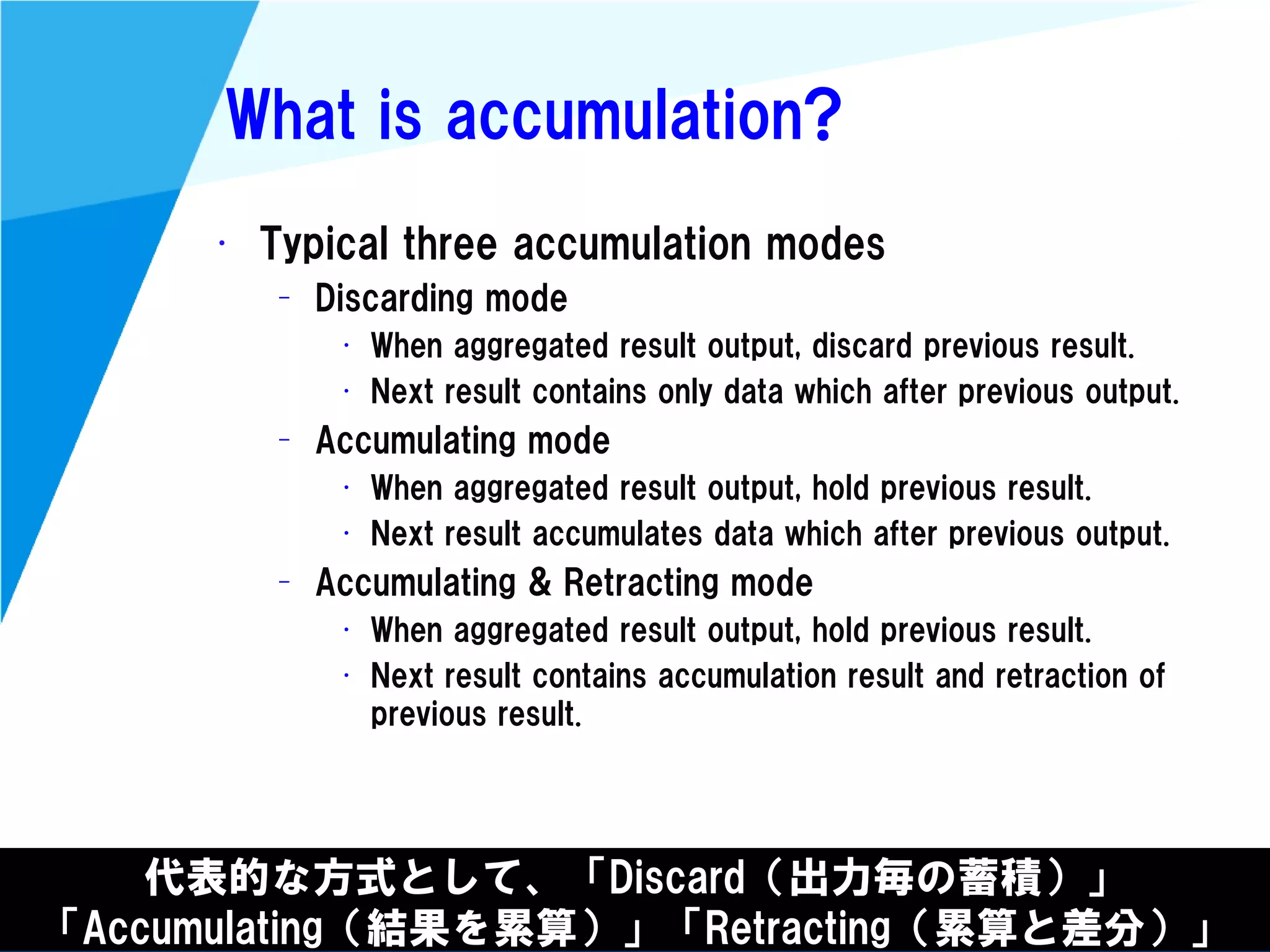
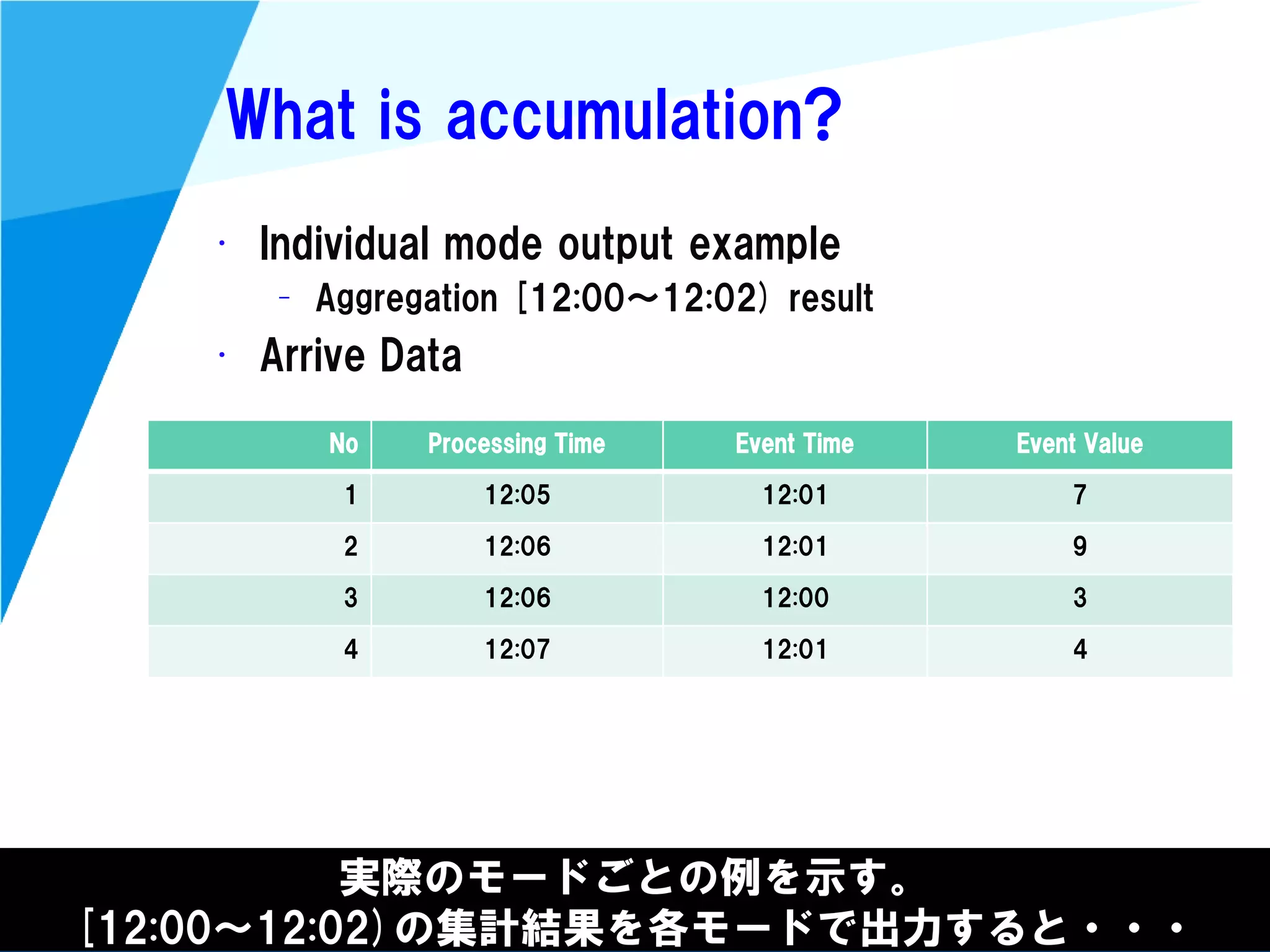
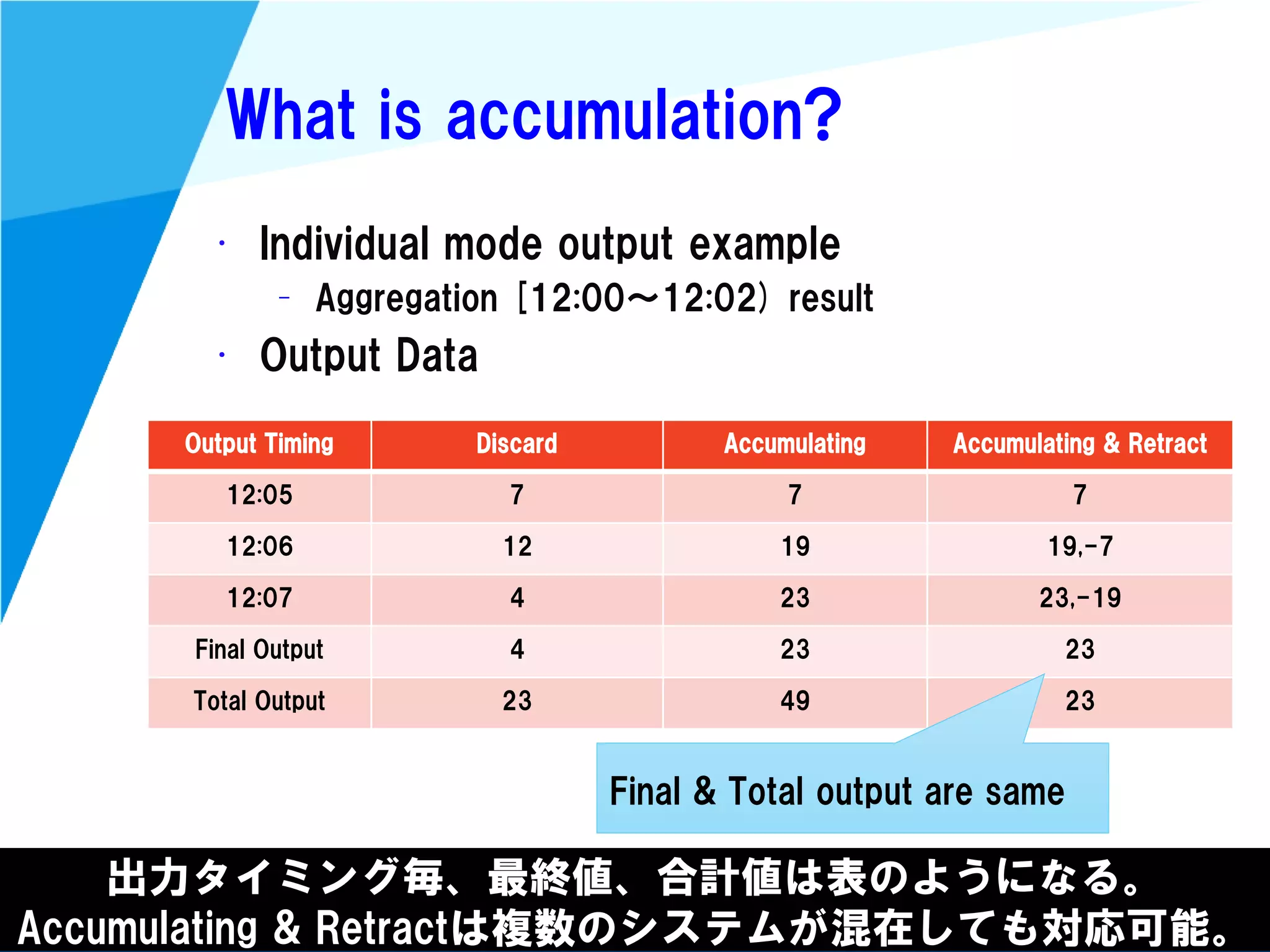
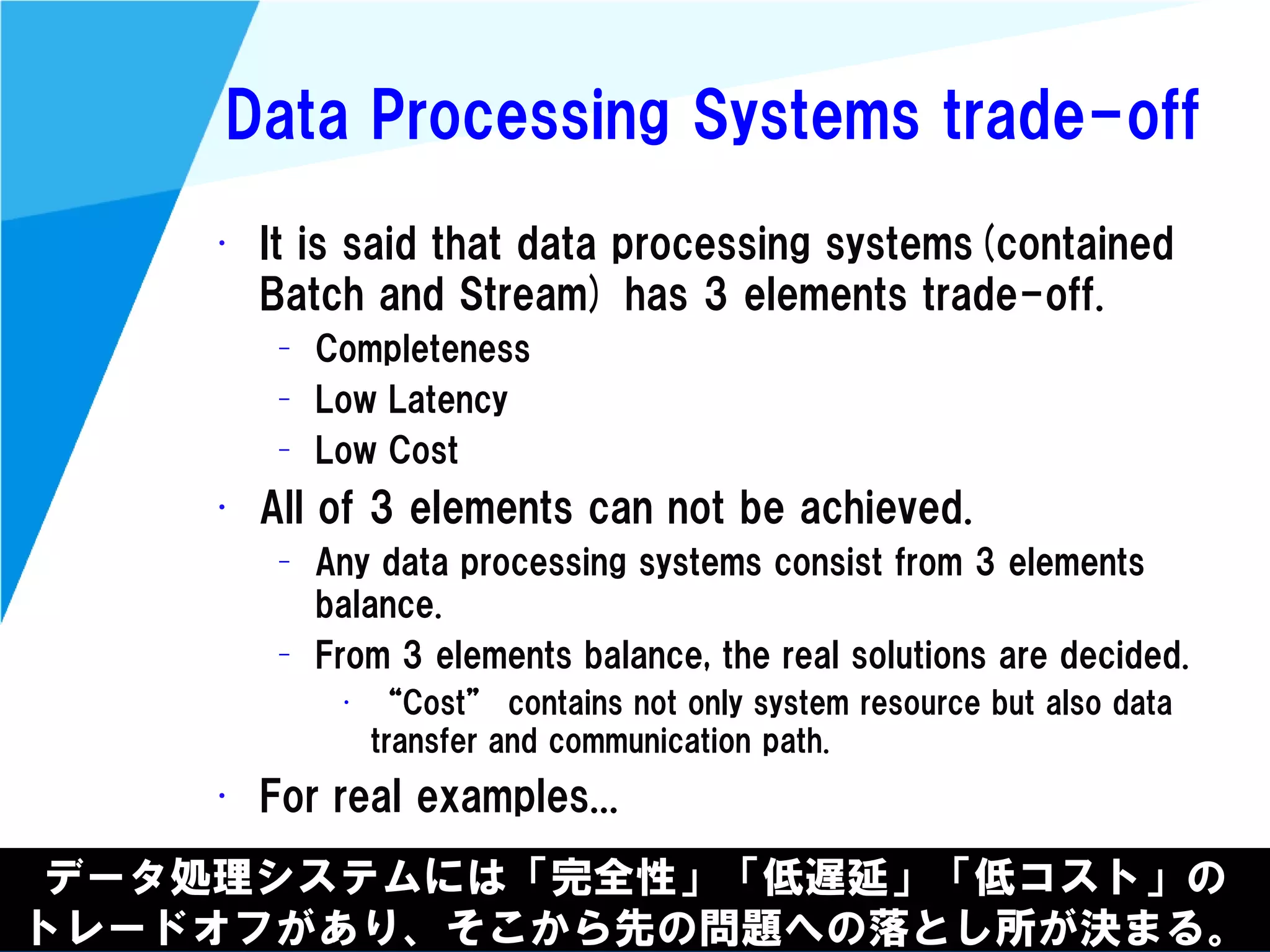
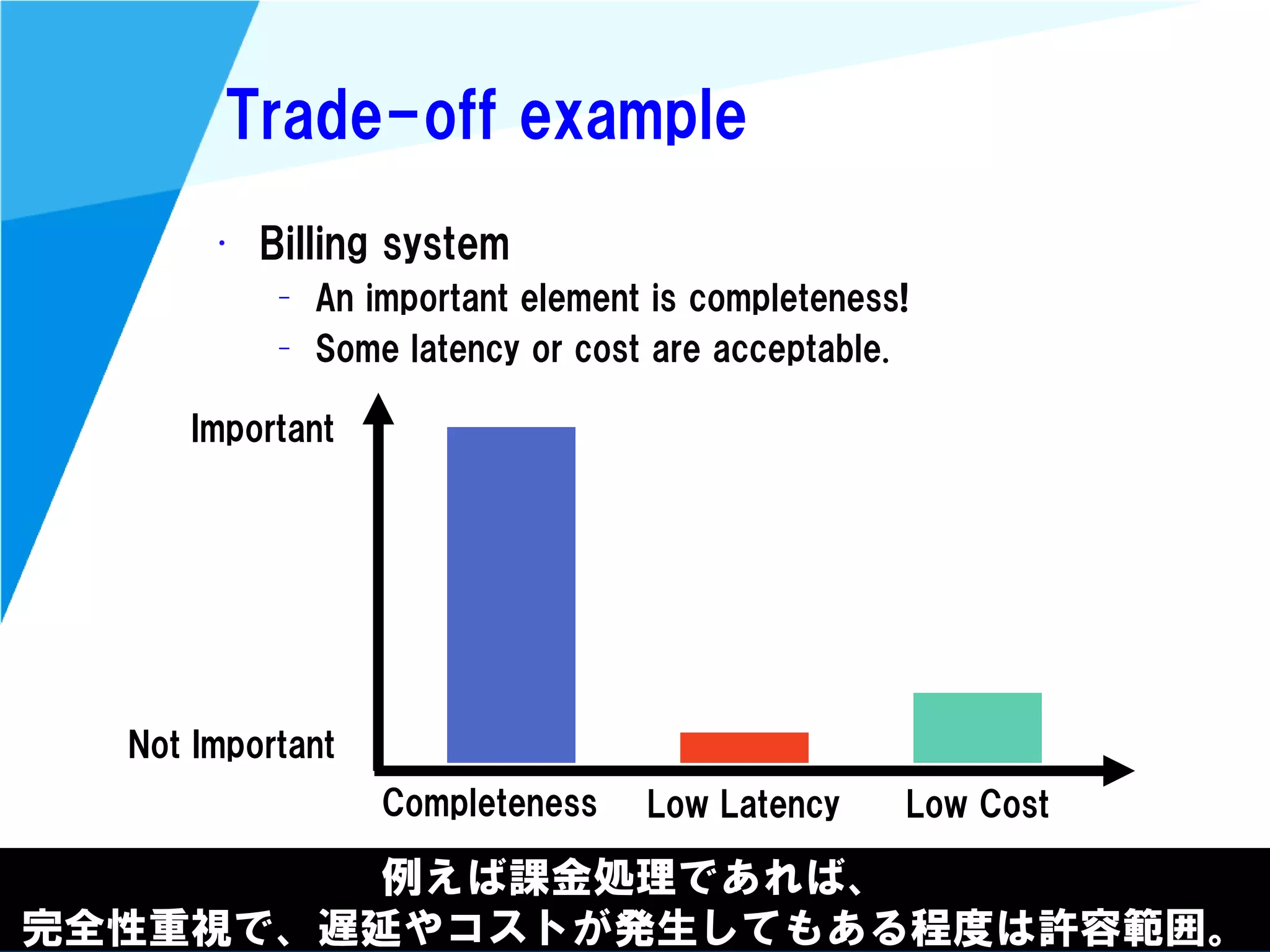
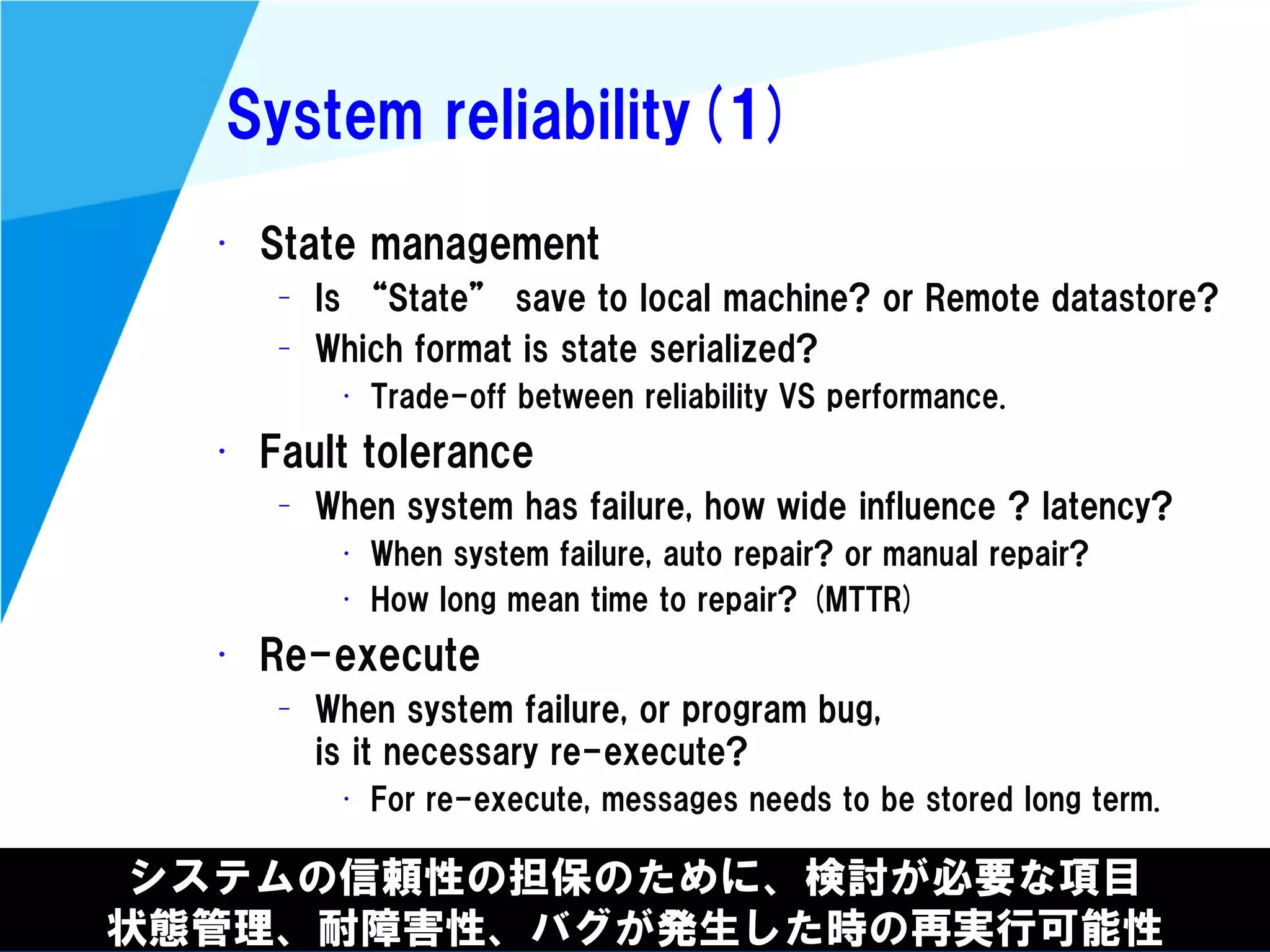
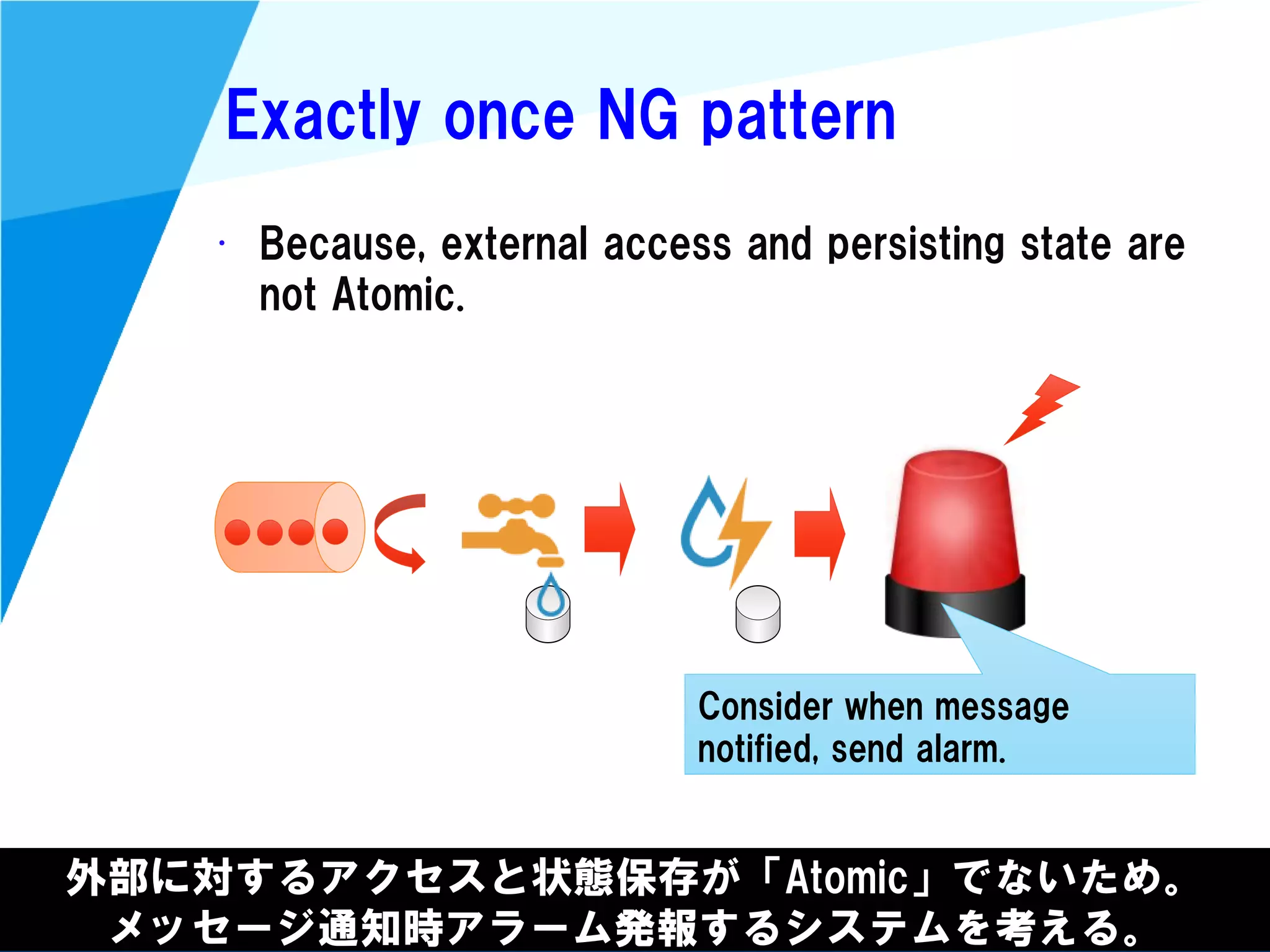
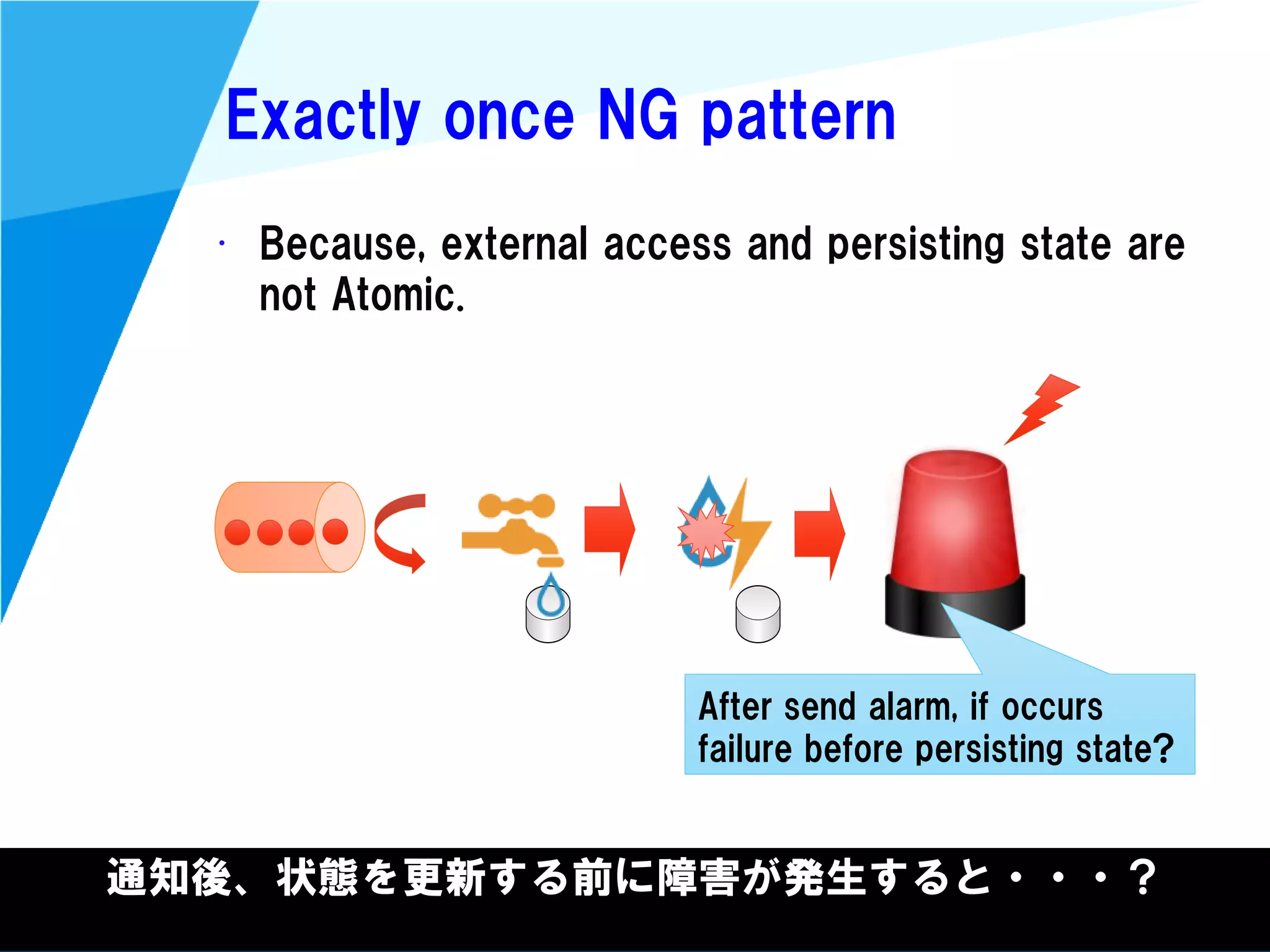
Stream processing is designed for continuously processing unbounded data streams. It allows for unbounded data inputs and continuous processing, unlike batch processing which requires bounded, finite data sets. The key challenges of stream processing include out-of-order data arrival and needing to relate events that occur close together in time but may be processed out of order. To address this, stream processing systems use watermarks to indicate processing progress, triggers to determine output timing, and accumulation to handle refinements from late data.














![@kimutansk
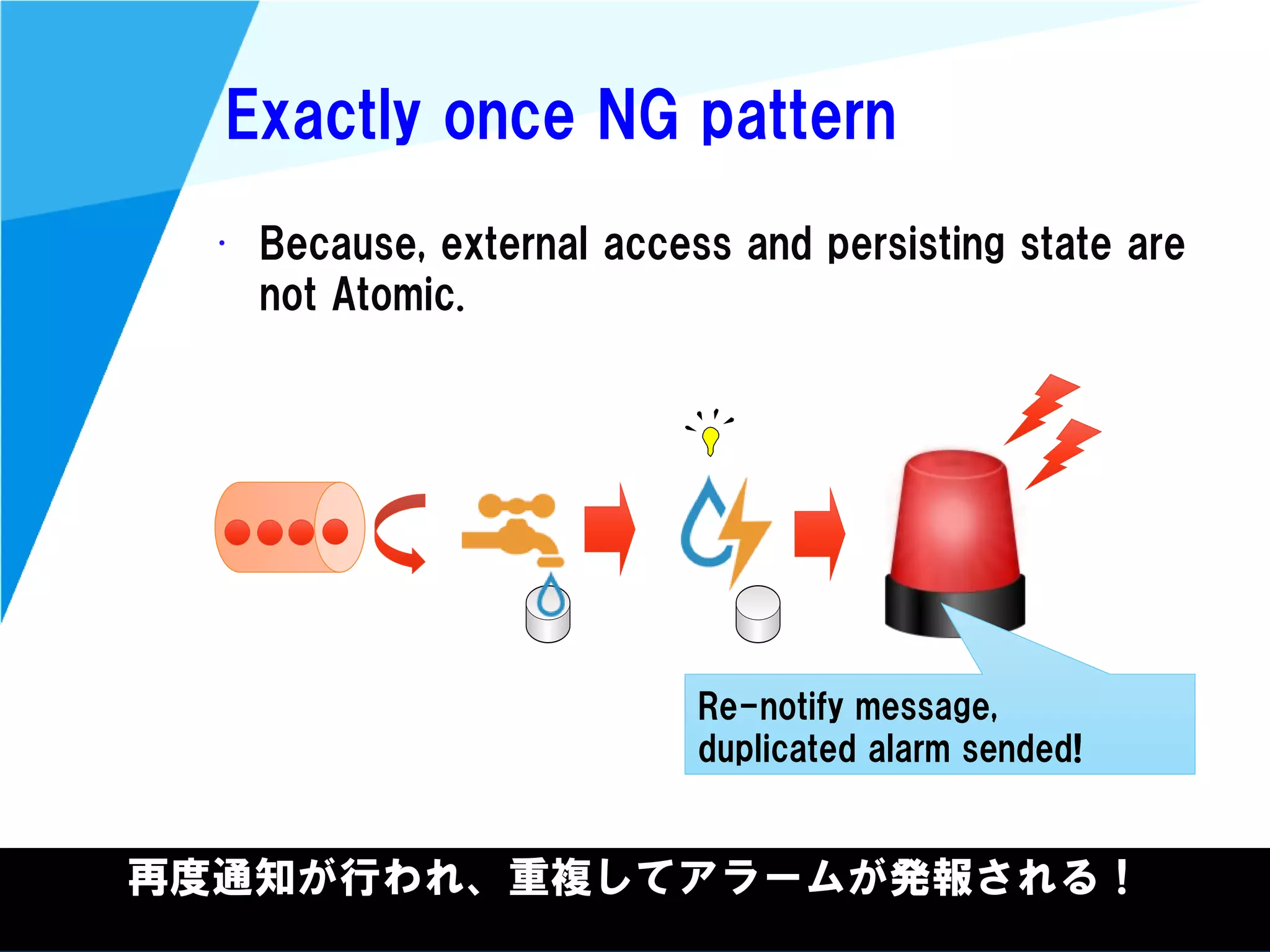
Out of order trouble
• With window, “Out of order” becomes trouble.
– If after [00:00 ~ 06:00] result output,
“05:55” data arrived...?
Windowを使うと「データが順番に到着しない」が問題になる。
結果出力後に該当時間帯のデータが到着したらどうする?
[00:00 ~ 06:00)
1. Output2. Arrive...?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamdataprocessing101-170224145924/75/Stream-dataprocessing101-26-2048.jpg)



























![@kimutansk
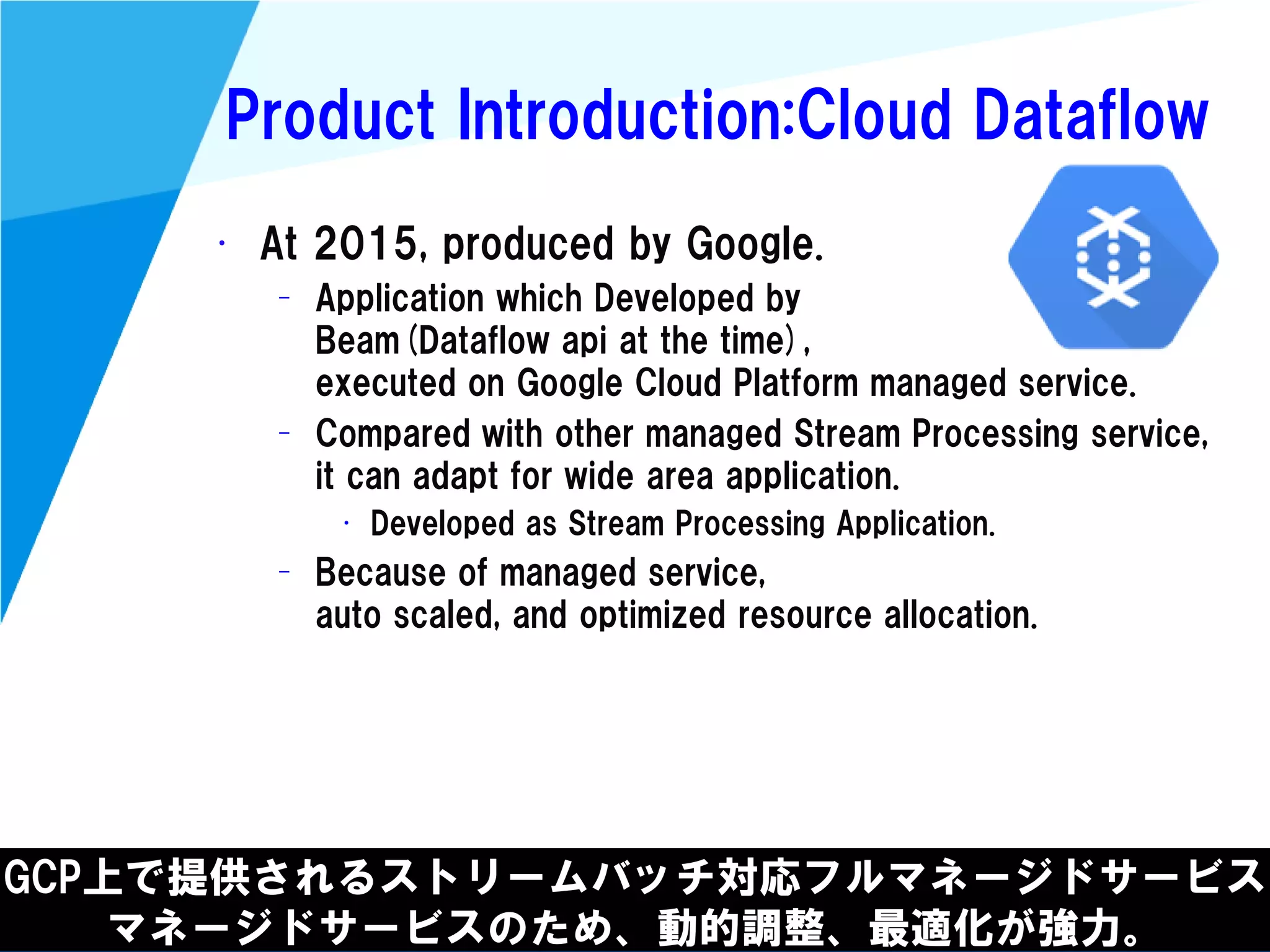
Development method(2)
宣言的なアプリケーション実装。
関数でStreamを加工し、個々の処理を行う。
• Declarative, expressive API Example
– By Flink
case class CarEvent(carId: Int, speed: Int, distance: Double, time: Long)
val DataStream[CarEvent] carEventStream = ...;
val topSeed = carEventStream
.assignAscendingTimestamps( _.time )
.keyBy("carId")
.window(GlobalWindows.create)
.evictor(TimeEvictor.of(Time.of(evictionSec * 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)))
.trigger(DeltaTrigger.of(triggerMeters, new DeltaFunction[CarEvent] {
def getDelta(oldSp: CarEvent, newSp: CarEvent): Double = newSp.distance - oldSp.distance
}, cars.getType().createSerializer(env.getConfig)))
.maxBy("speed")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamdataprocessing101-170224145924/75/Stream-dataprocessing101-71-2048.jpg)
![@kimutansk
Development method(3)
手続き的なアプリケーション実装。
processメソッドをStreamに適用し、個々の処理を行う。
• Imperative, lower-level API Example
– By Flink
val stream : DataStream[Tuple2[String, String]] = ...;
val result : DataStream[Tuple2[String, Long]] result =
stream
.keyBy(0)
.process(new CountWithTimeoutFunction());
case class CountWithTimestamp(key: String, count: Long, lastModified: Long)
class CountWithTimeoutFunction extends ProcessFunction[(String, Long), (String, Long)] {
lazy val state: ValueState[CountWithTimestamp] = getRuntimeContext()
.getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<>("myState", clasOf[CountWithTimestamp]))
override def processElement(value: (String, Long),
ctx: Context, out: Collector[(String, Long)]): Unit ...;
override def onTimer(timestamp: Long, ctx: OnTimerContext,
out: Collector[(String, Long)]): Unit = ...;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamdataprocessing101-170224145924/75/Stream-dataprocessing101-72-2048.jpg)
![@kimutansk
Development method(4)
Streaming SQLによるアプリケーション実装。
Streamにスキーマを設定し、SQLで処理を行う。
• Streaming SQL Example
– By Flink
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val tableEnv = TableEnvironment.getTableEnvironment(env)
// read a DataStream from an external source
val ds: DataStream[(Long, String, Integer)] = env.addSource(...)
// register the DataStream under the name "Orders"
tableEnv.registerDataStream("Orders", ds, 'user, 'product, 'amount)
// run a SQL query on the Table and retrieve the result as a new Table
val result = tableEnv.sql(
"SELECT product, amount FROM Orders WHERE product LIKE '%Rubber%'")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamdataprocessing101-170224145924/75/Stream-dataprocessing101-73-2048.jpg)