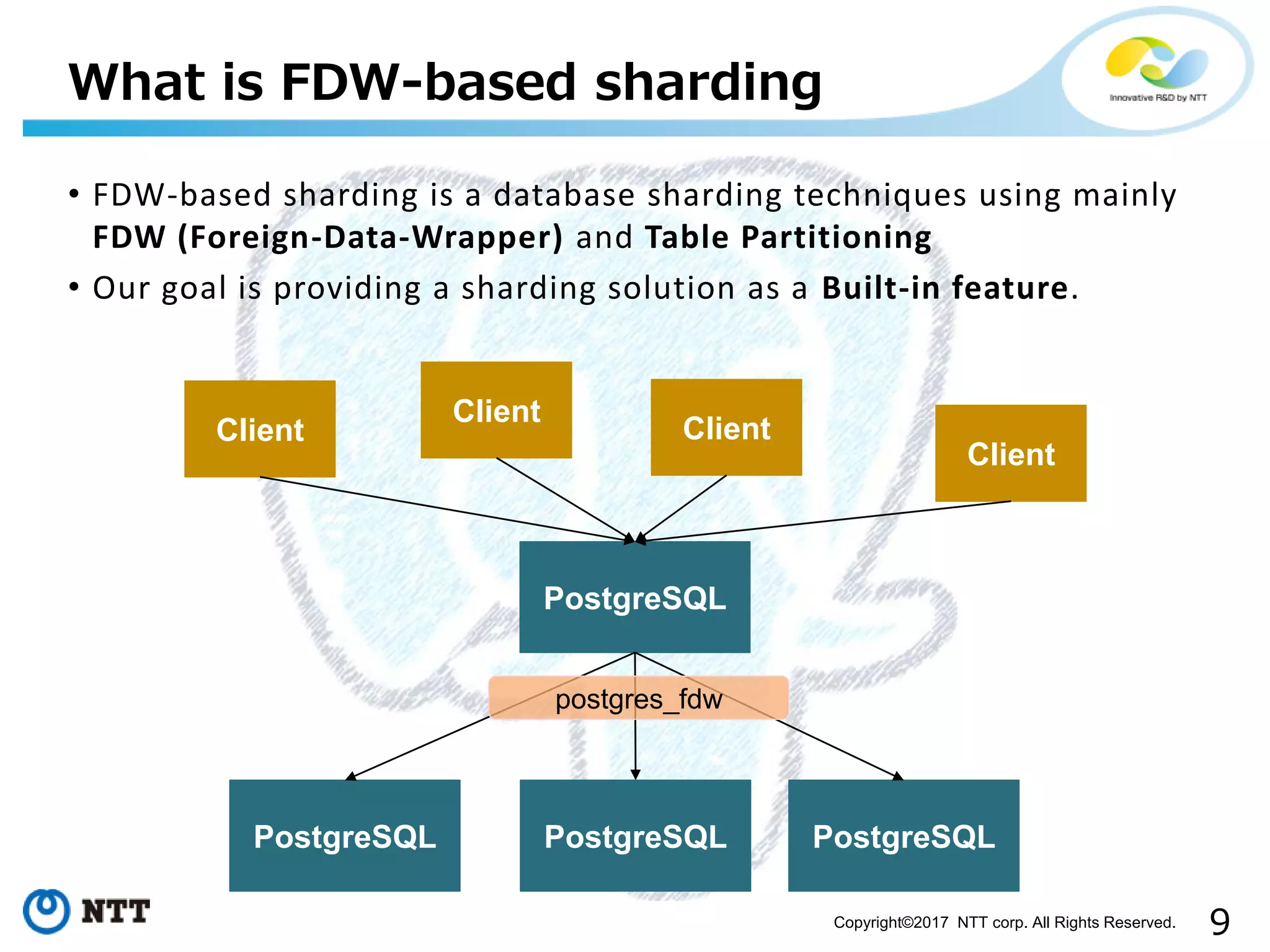
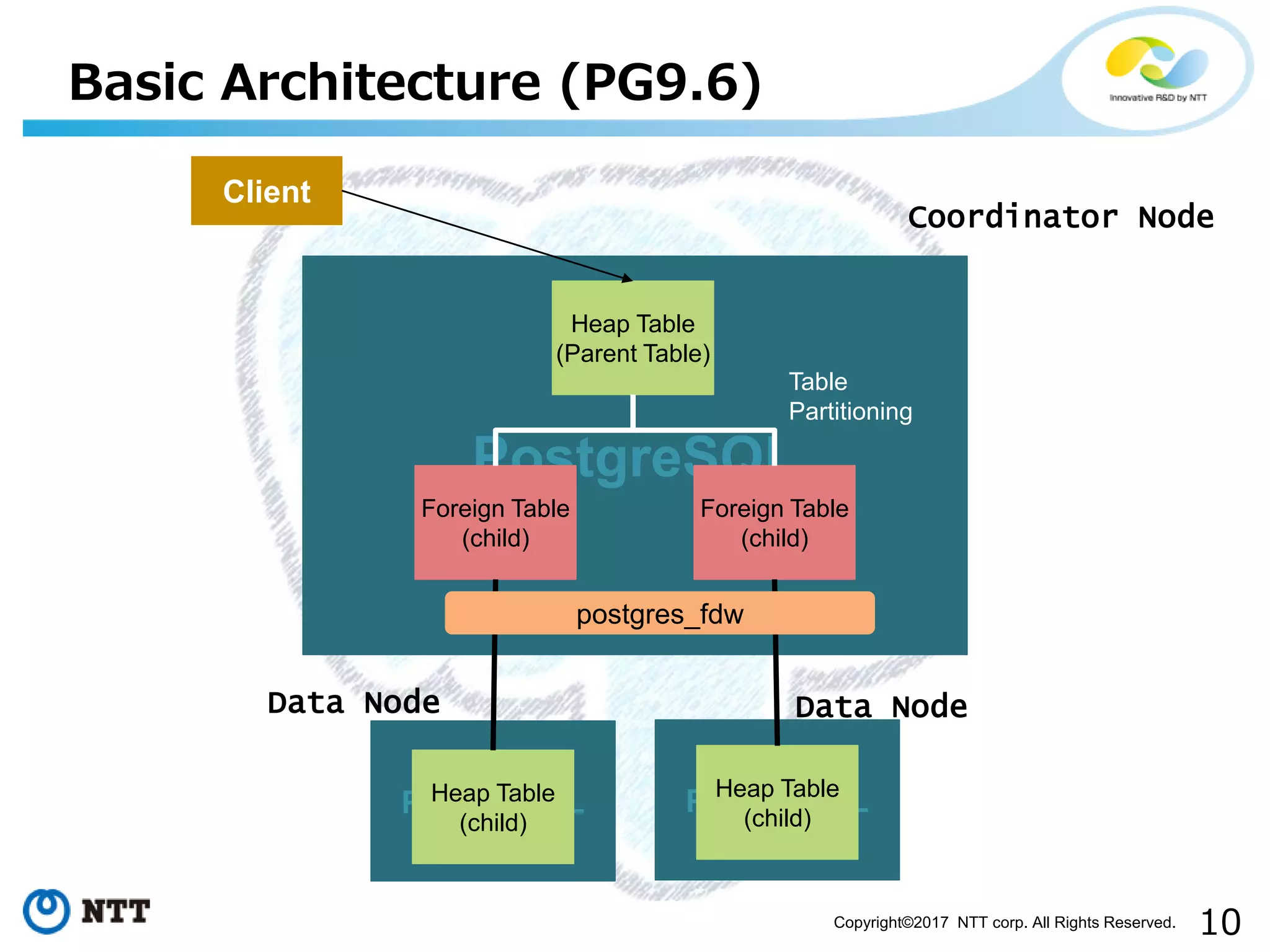
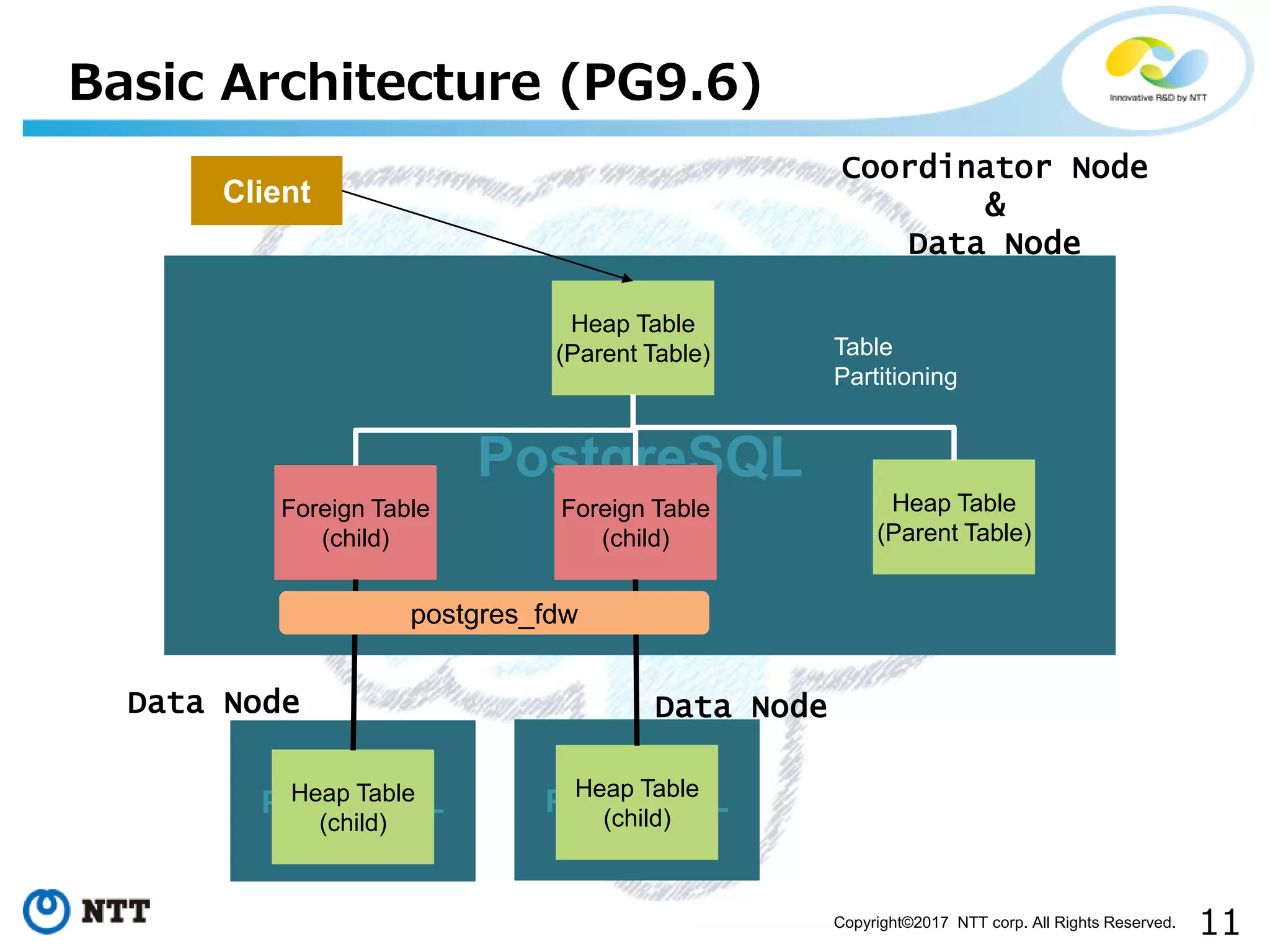
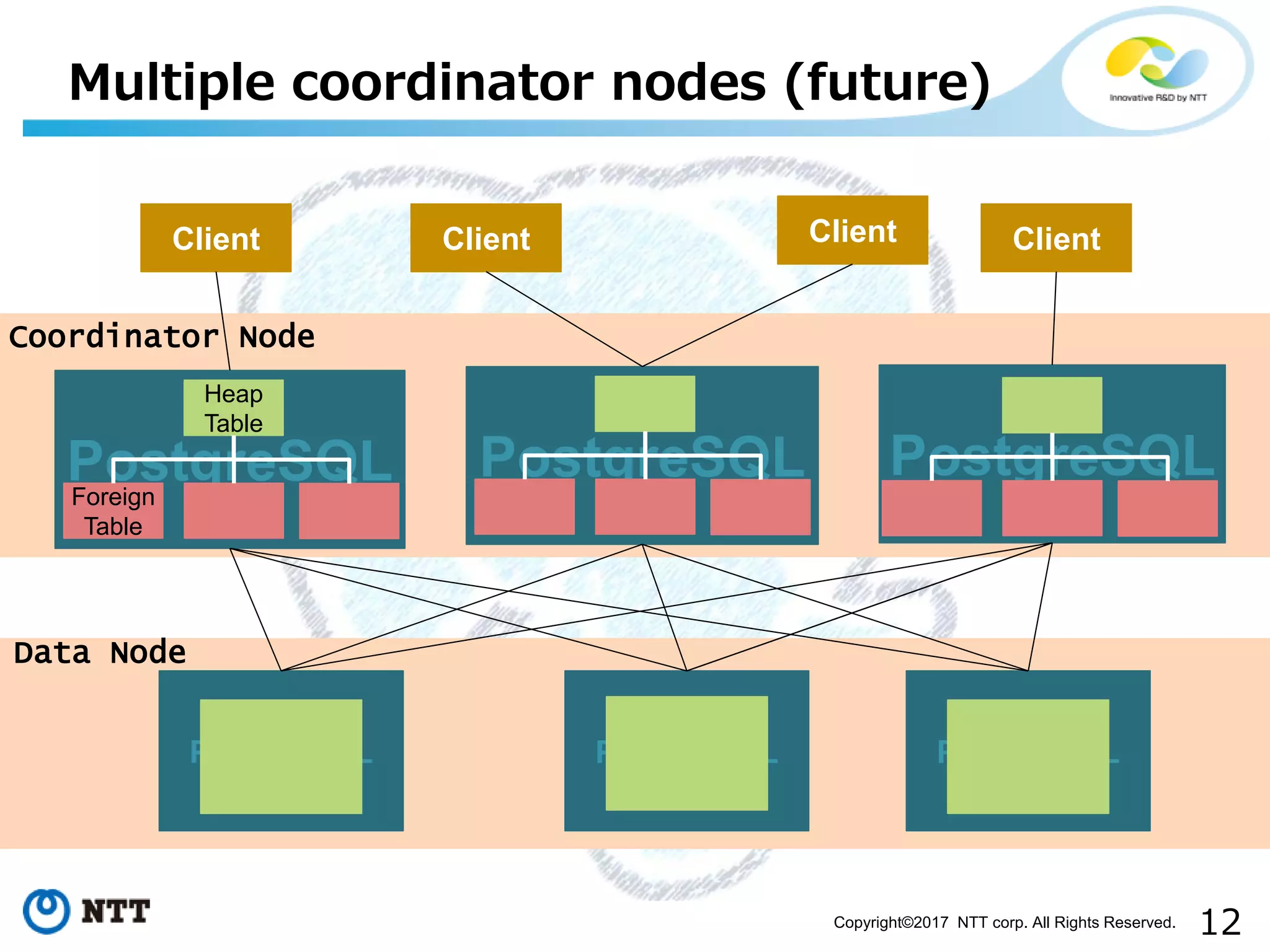
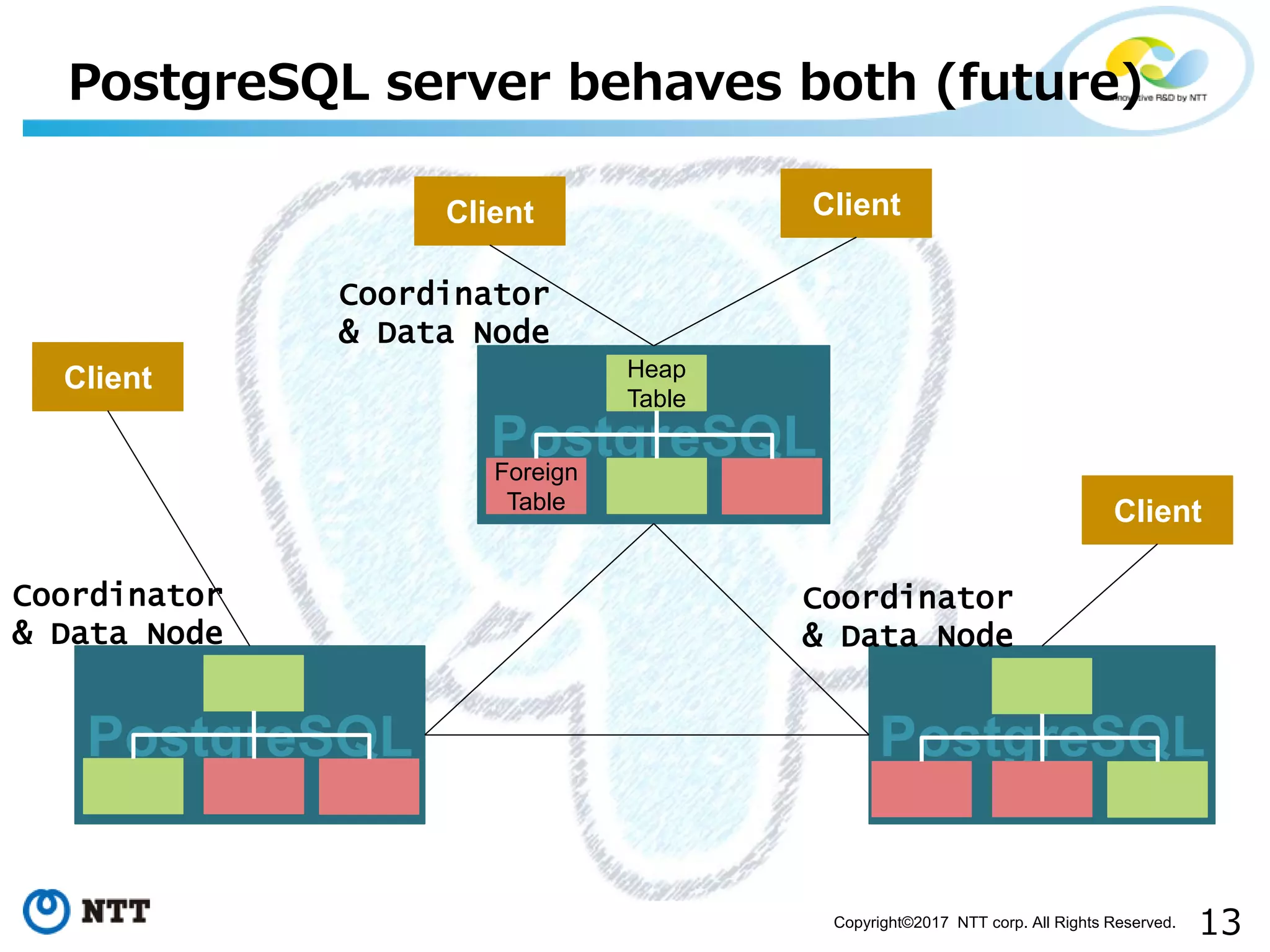
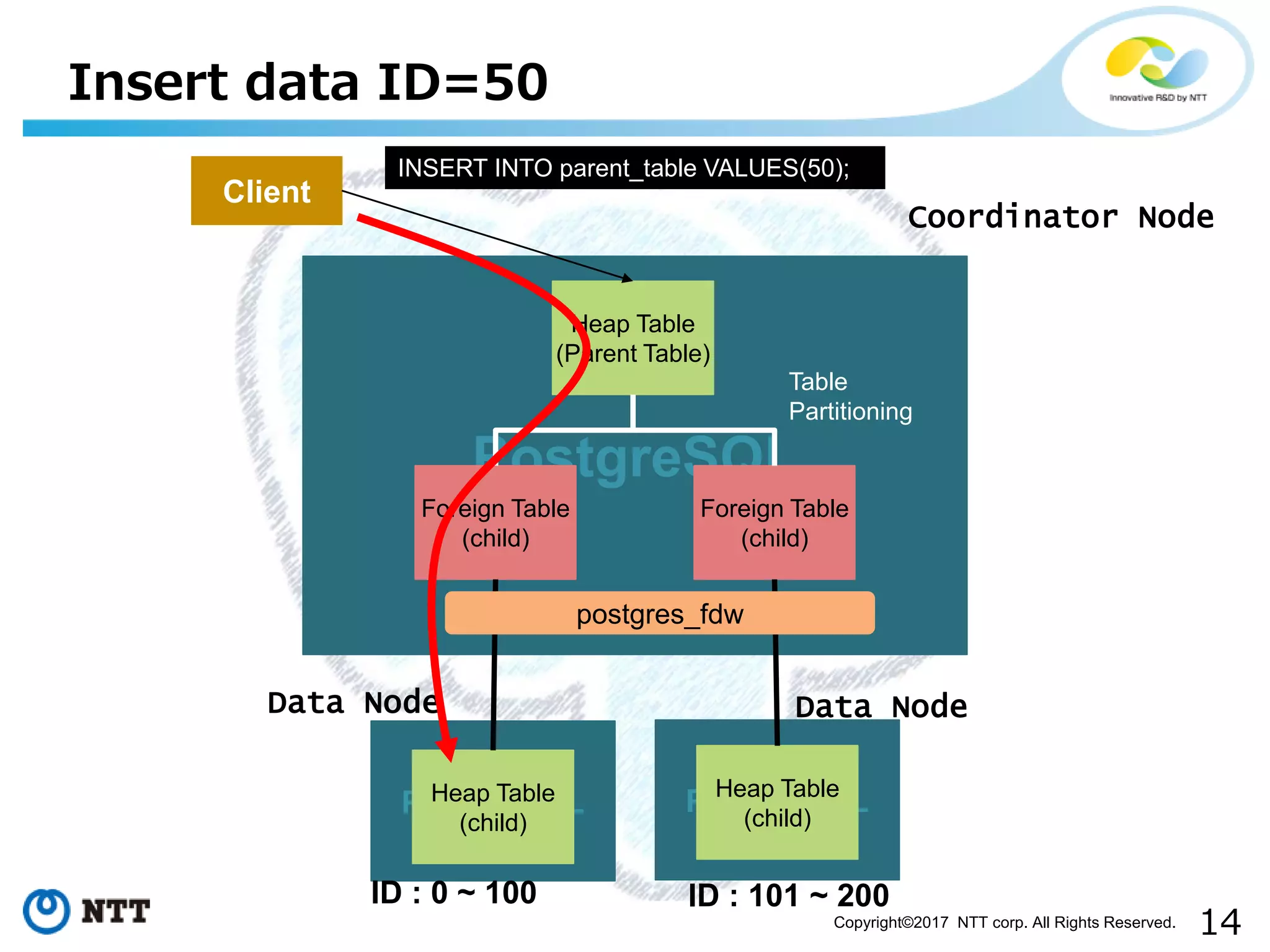
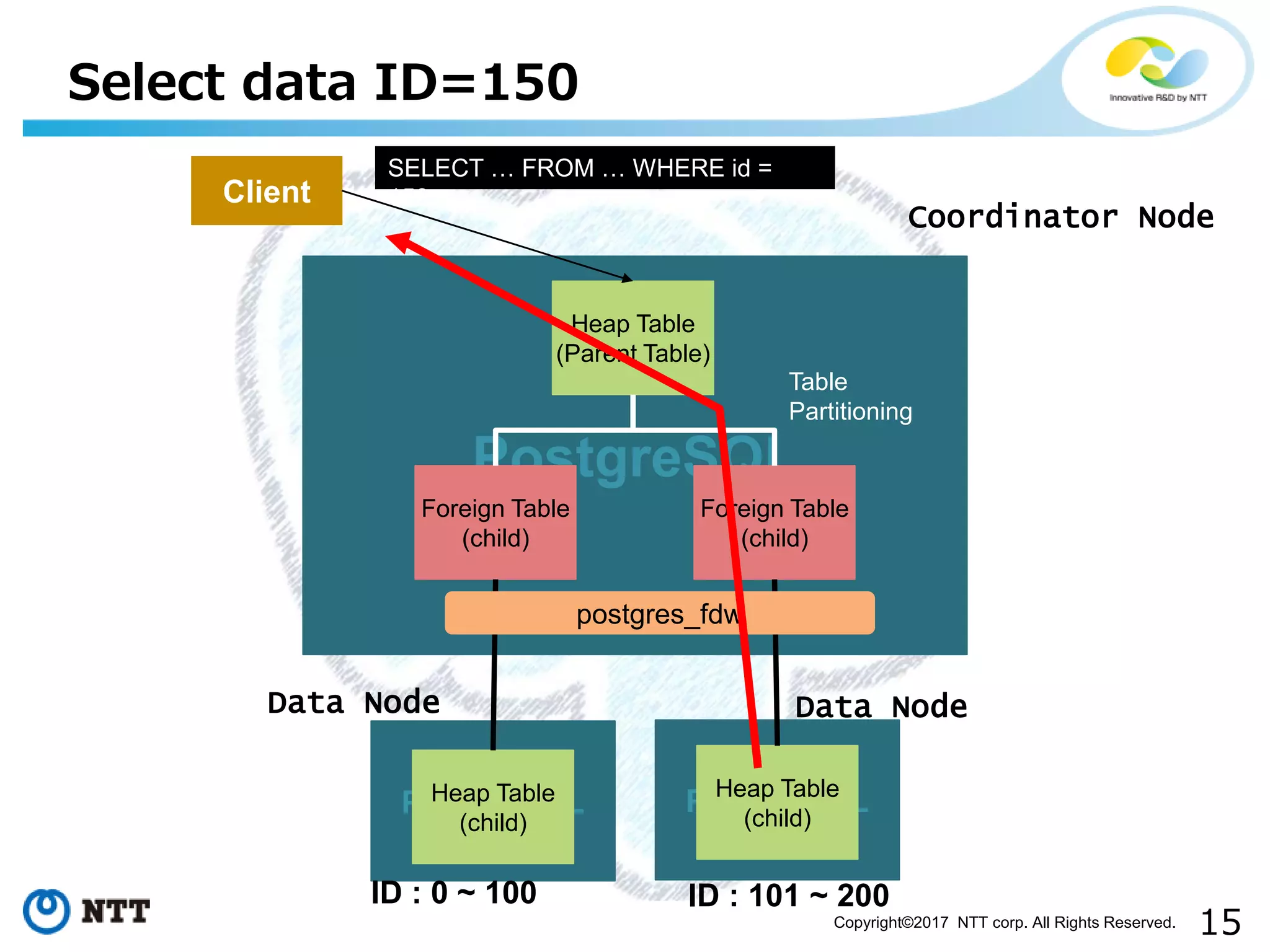
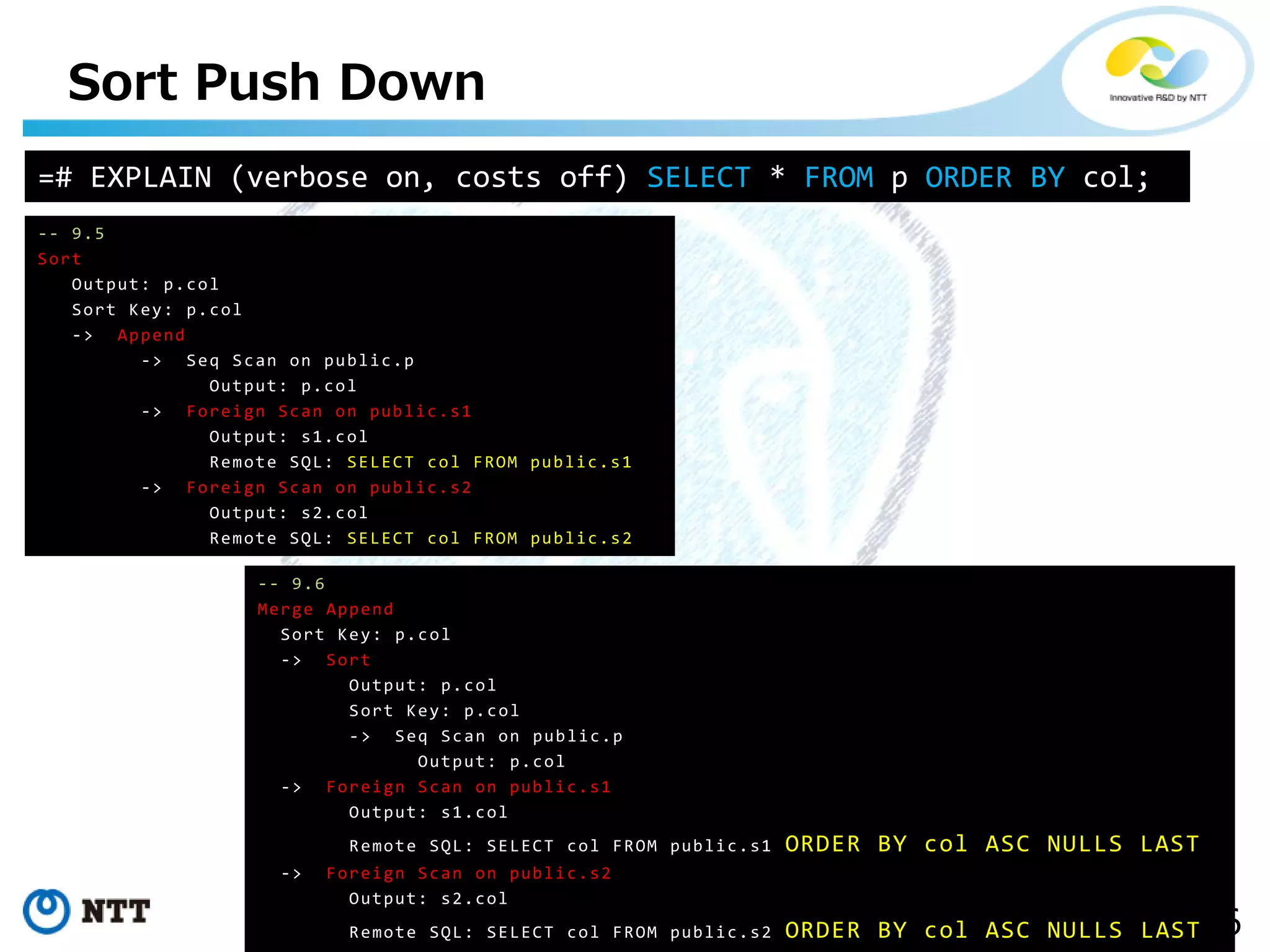
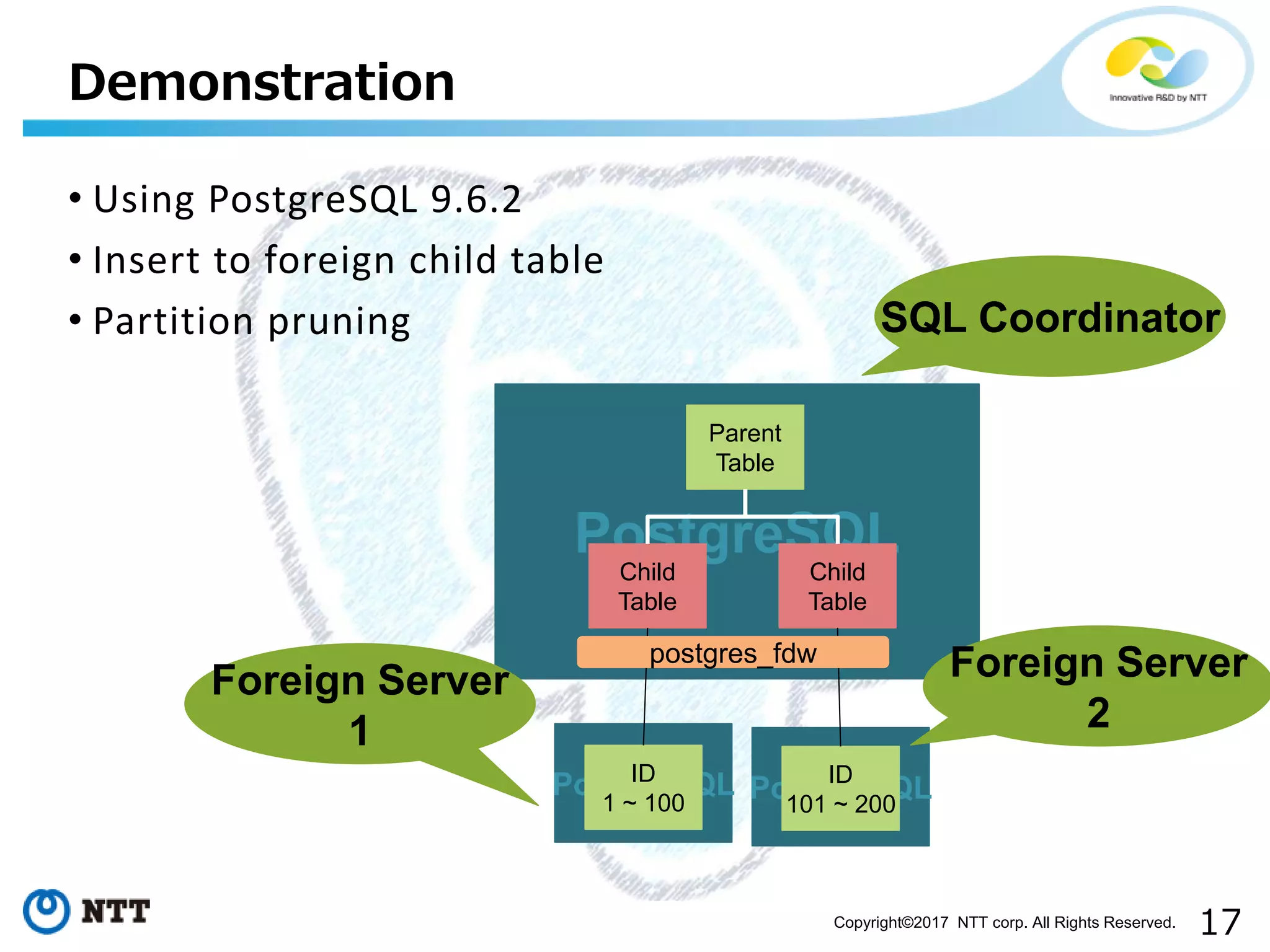
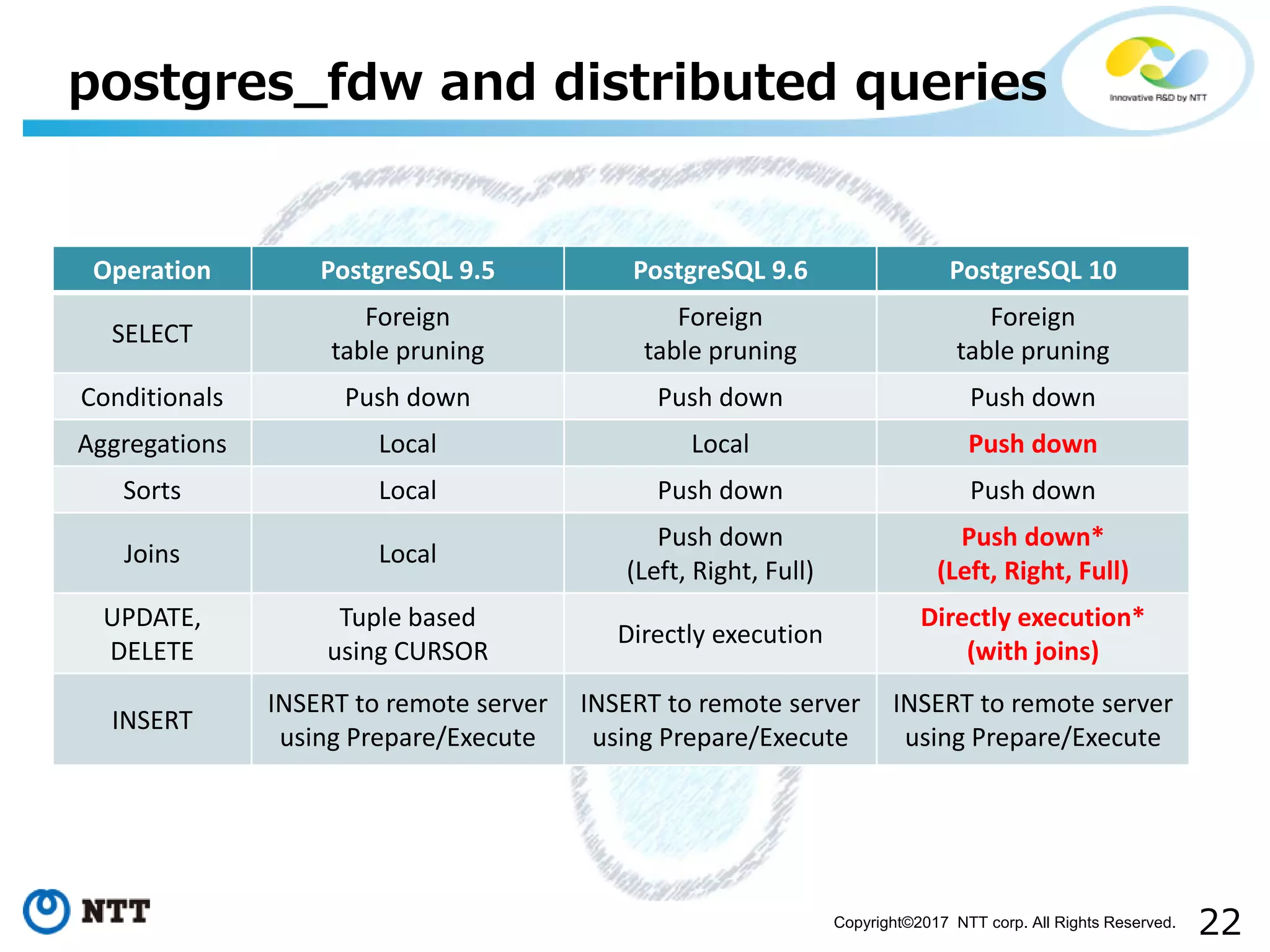
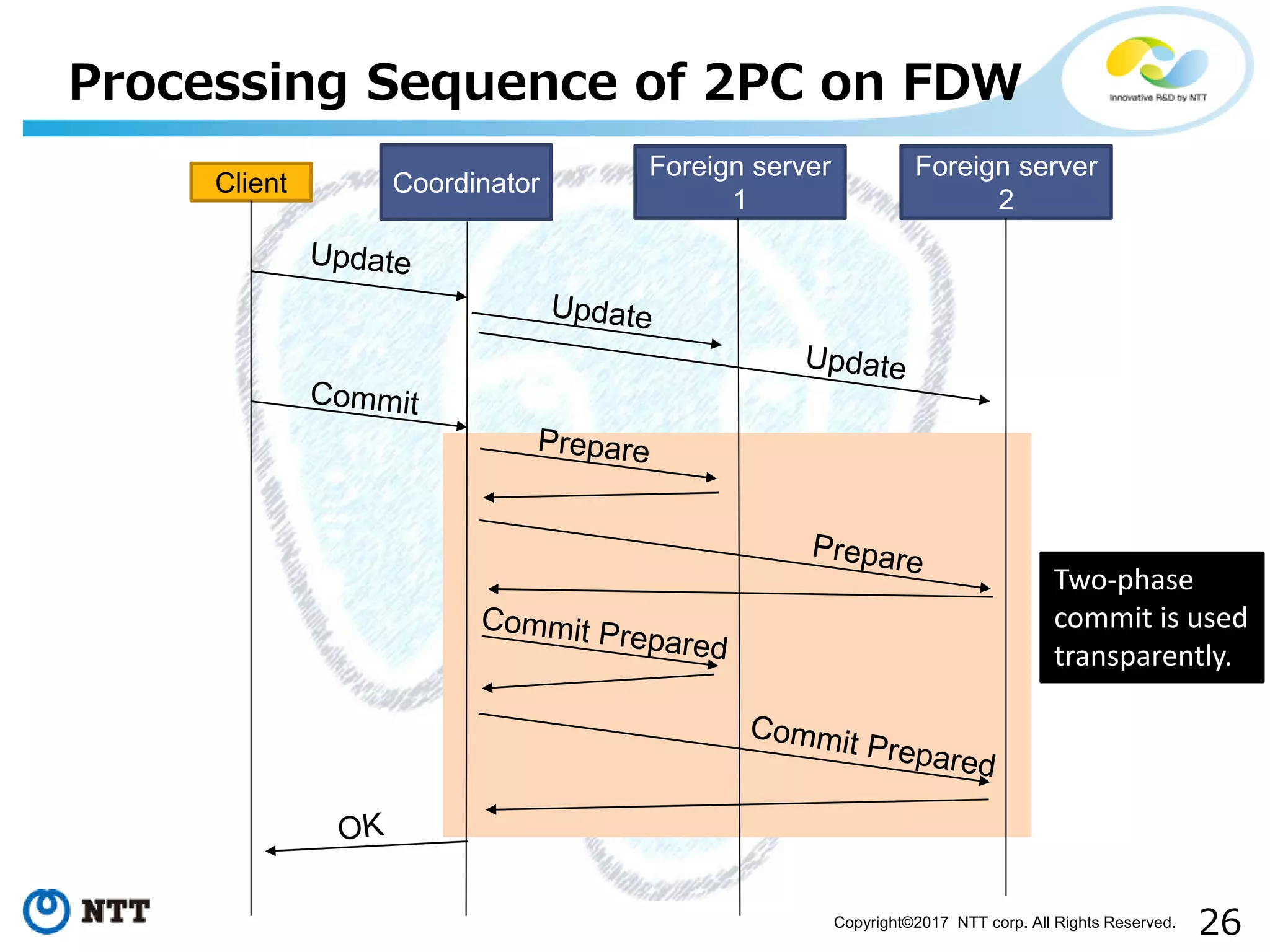
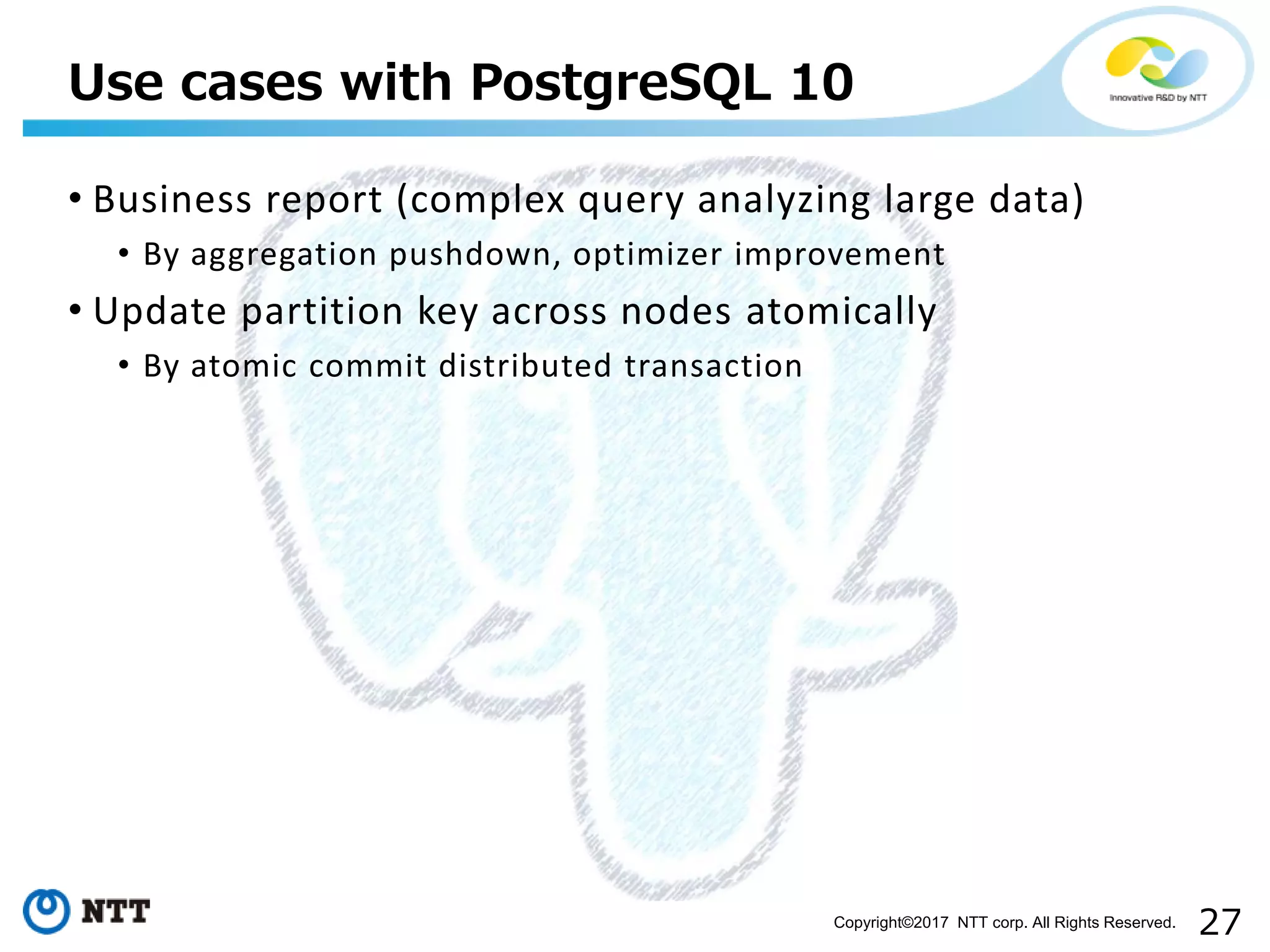
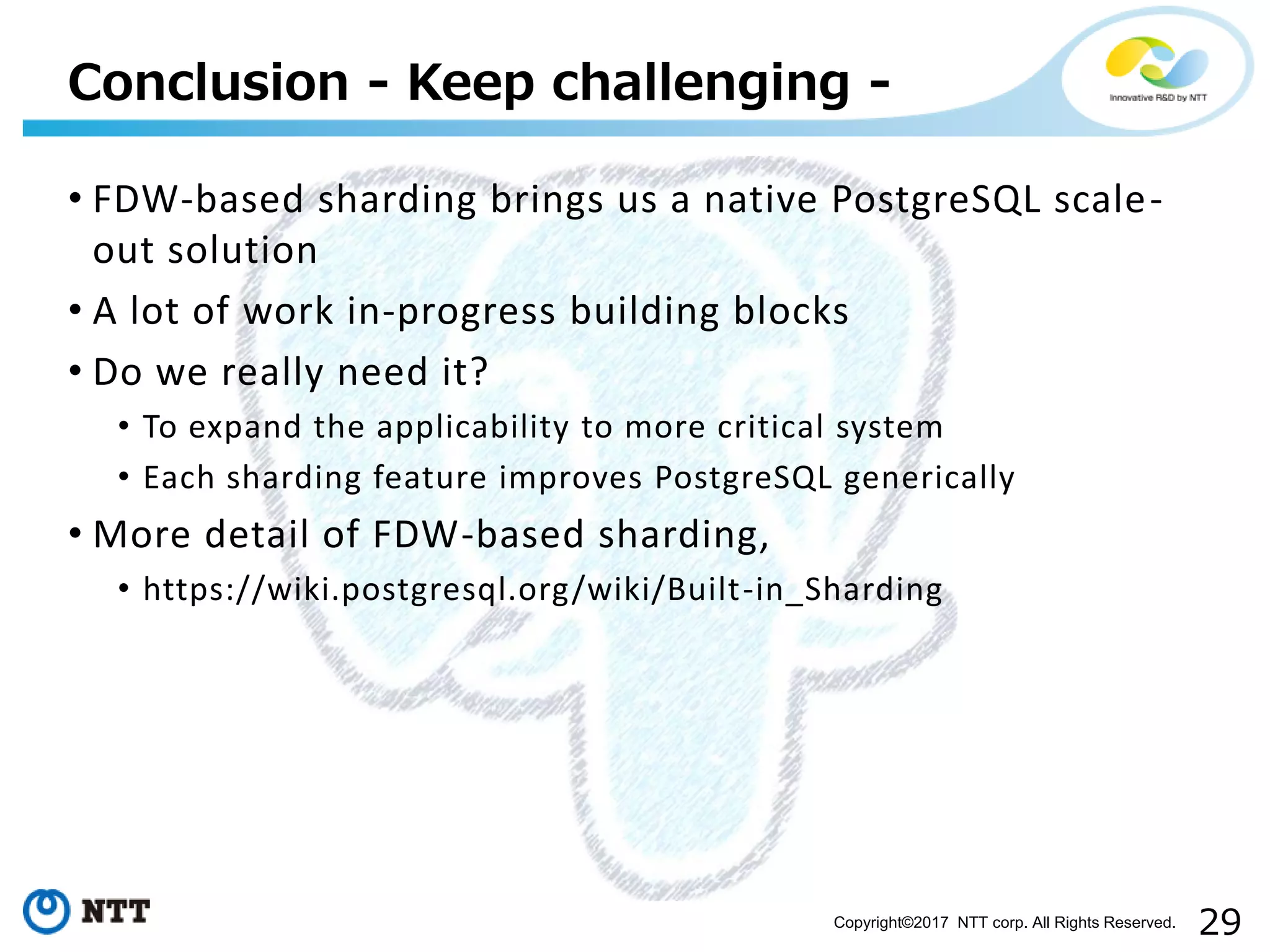
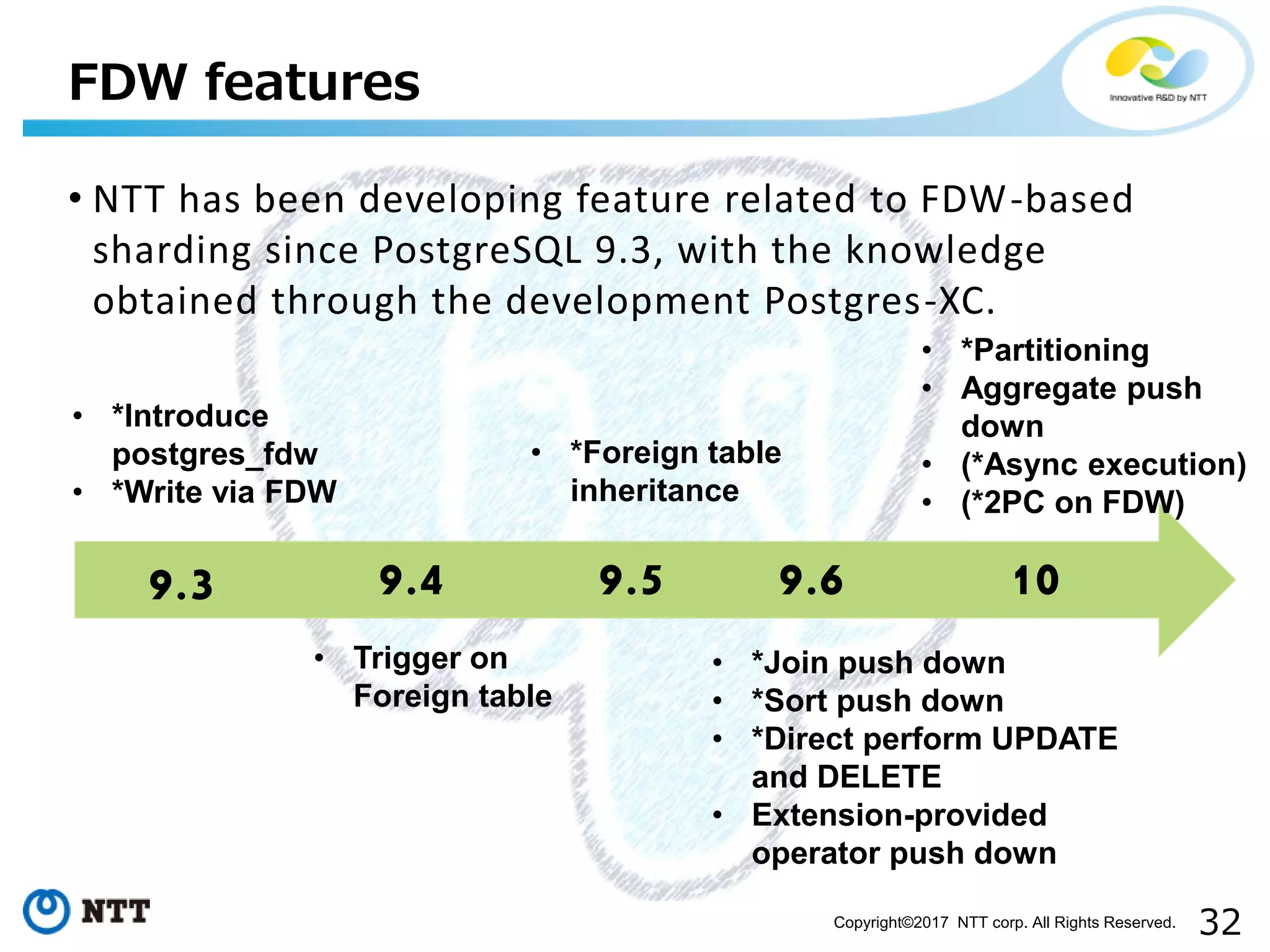
The document discusses FDW-based sharding in PostgreSQL. It provides an overview of what database sharding and FDW-based sharding are. It then demonstrates FDW-based sharding in PostgreSQL 9.6, covering how data is inserted and queried across foreign child tables. The document outlines several challenges for FDW-based sharding like distributed transactions and asynchronous execution. It also reviews key techniques being developed for PostgreSQL 10 like push down optimizations and declarative partitioning.