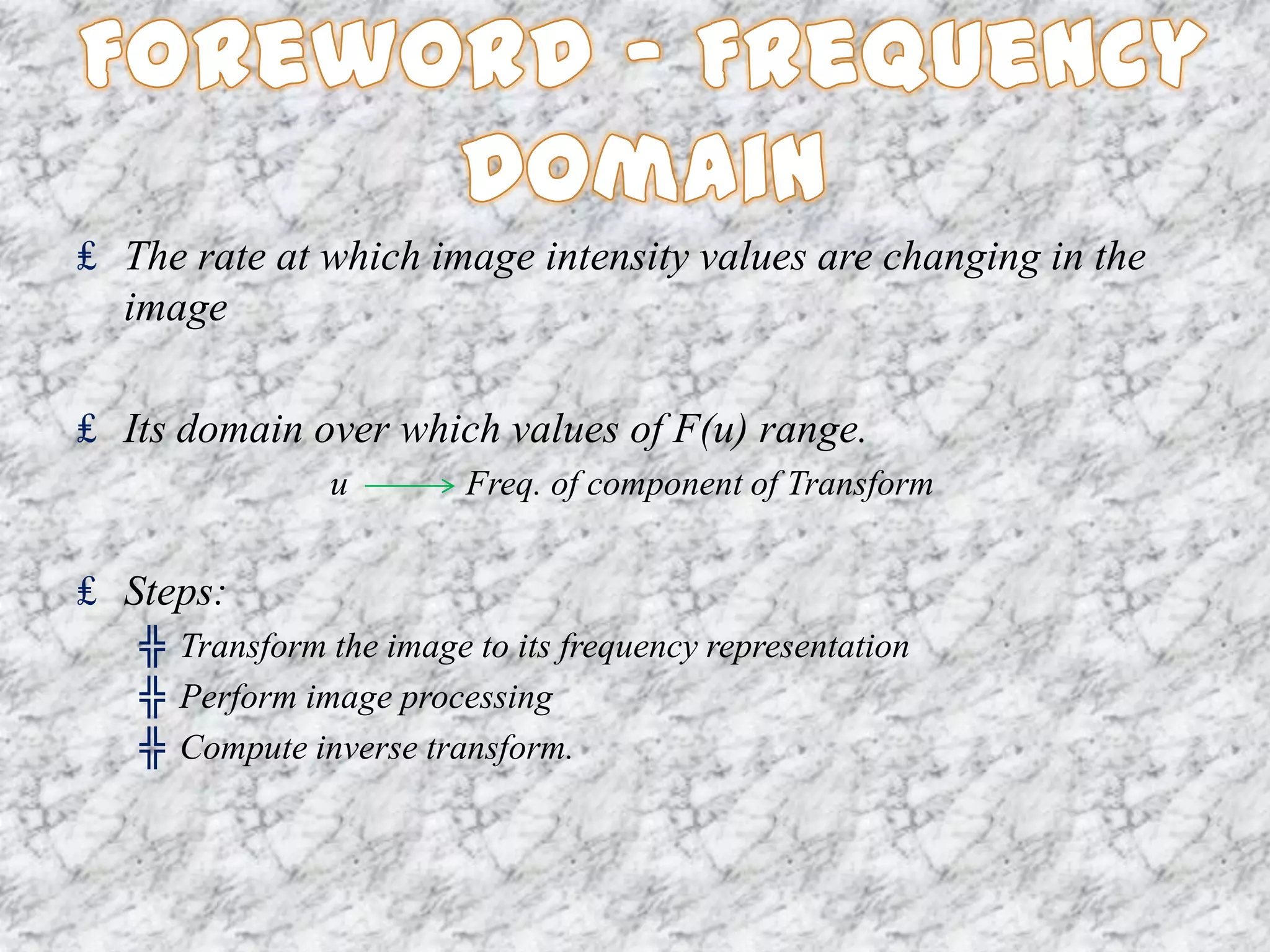
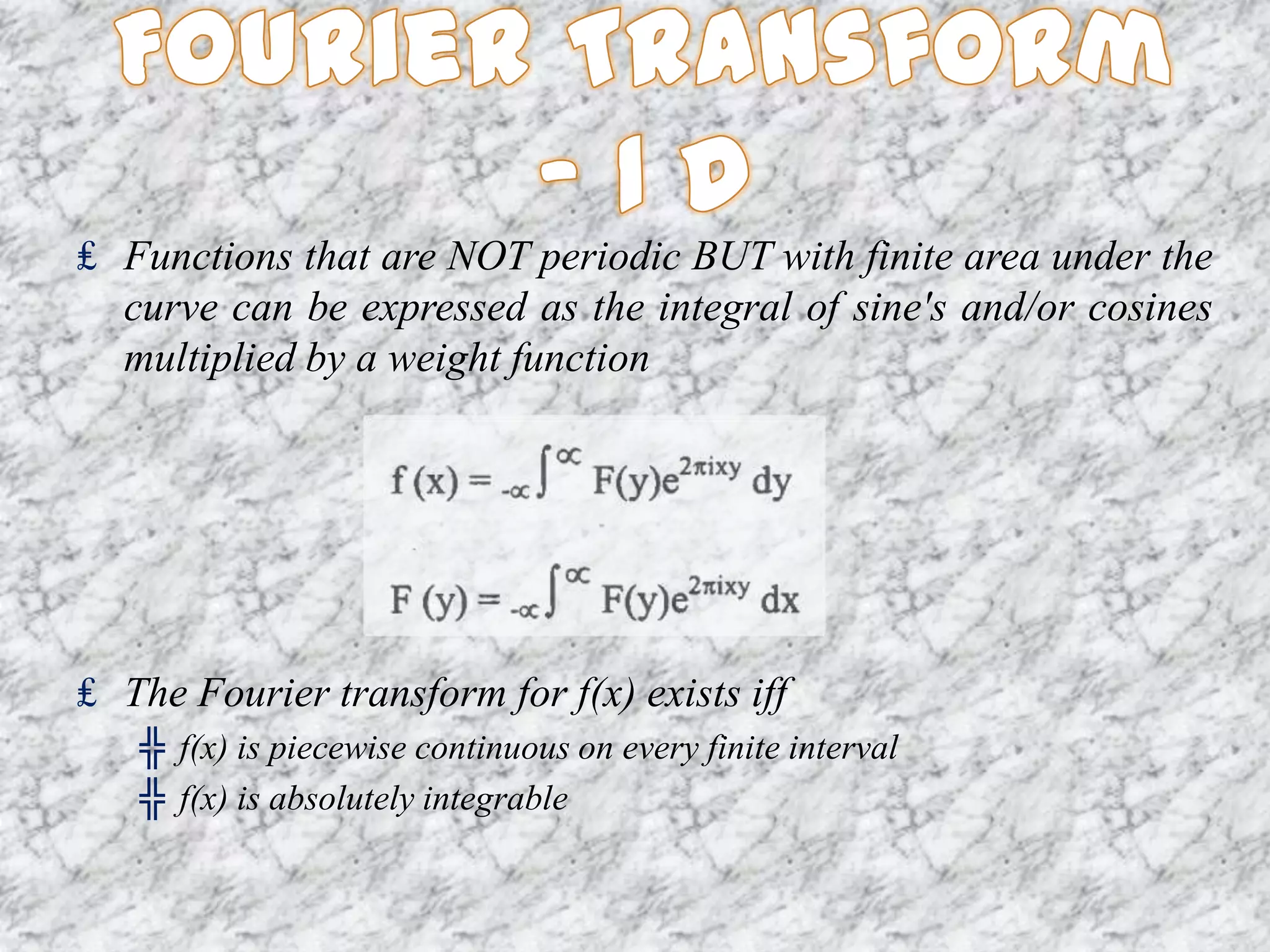
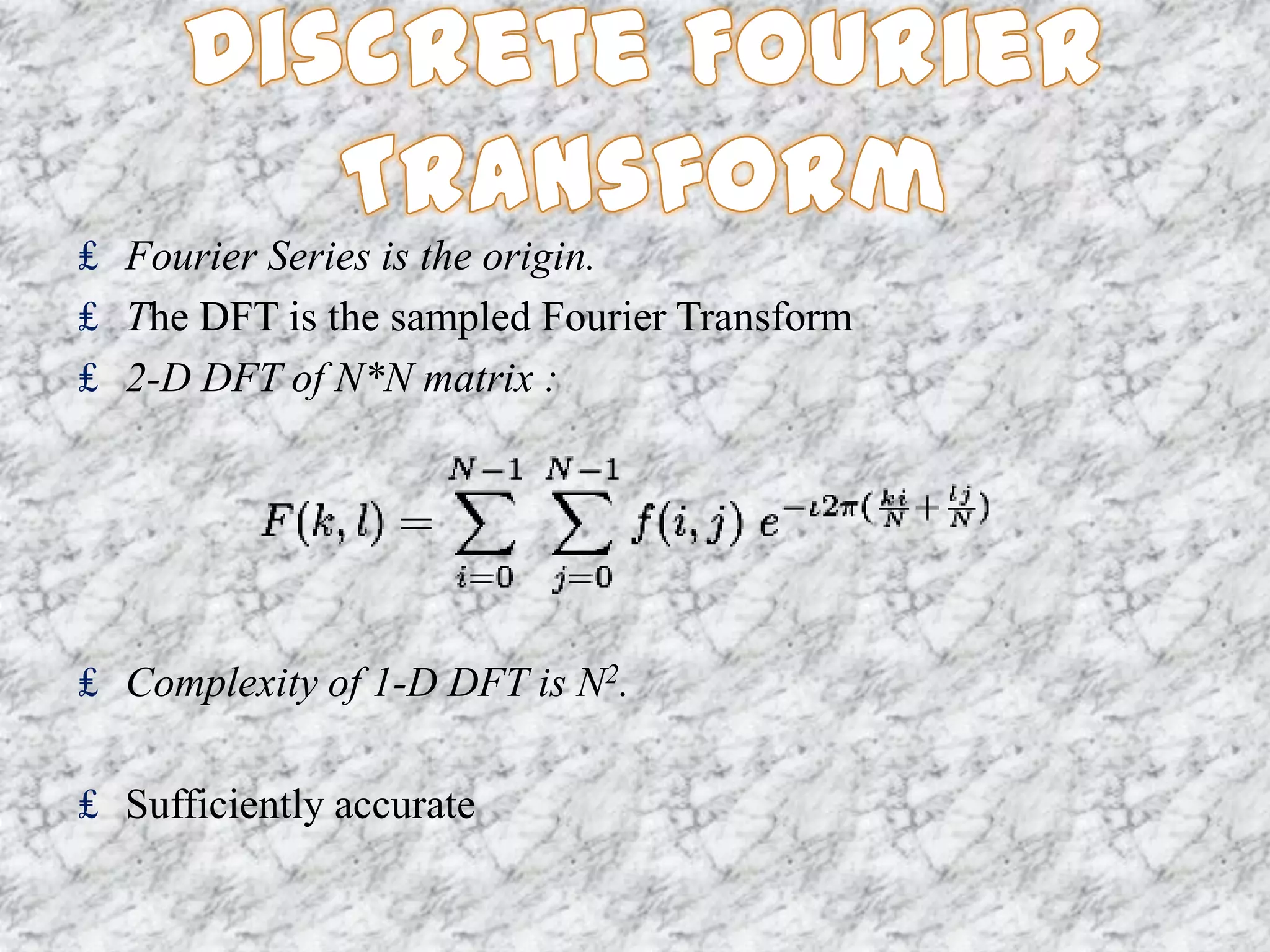
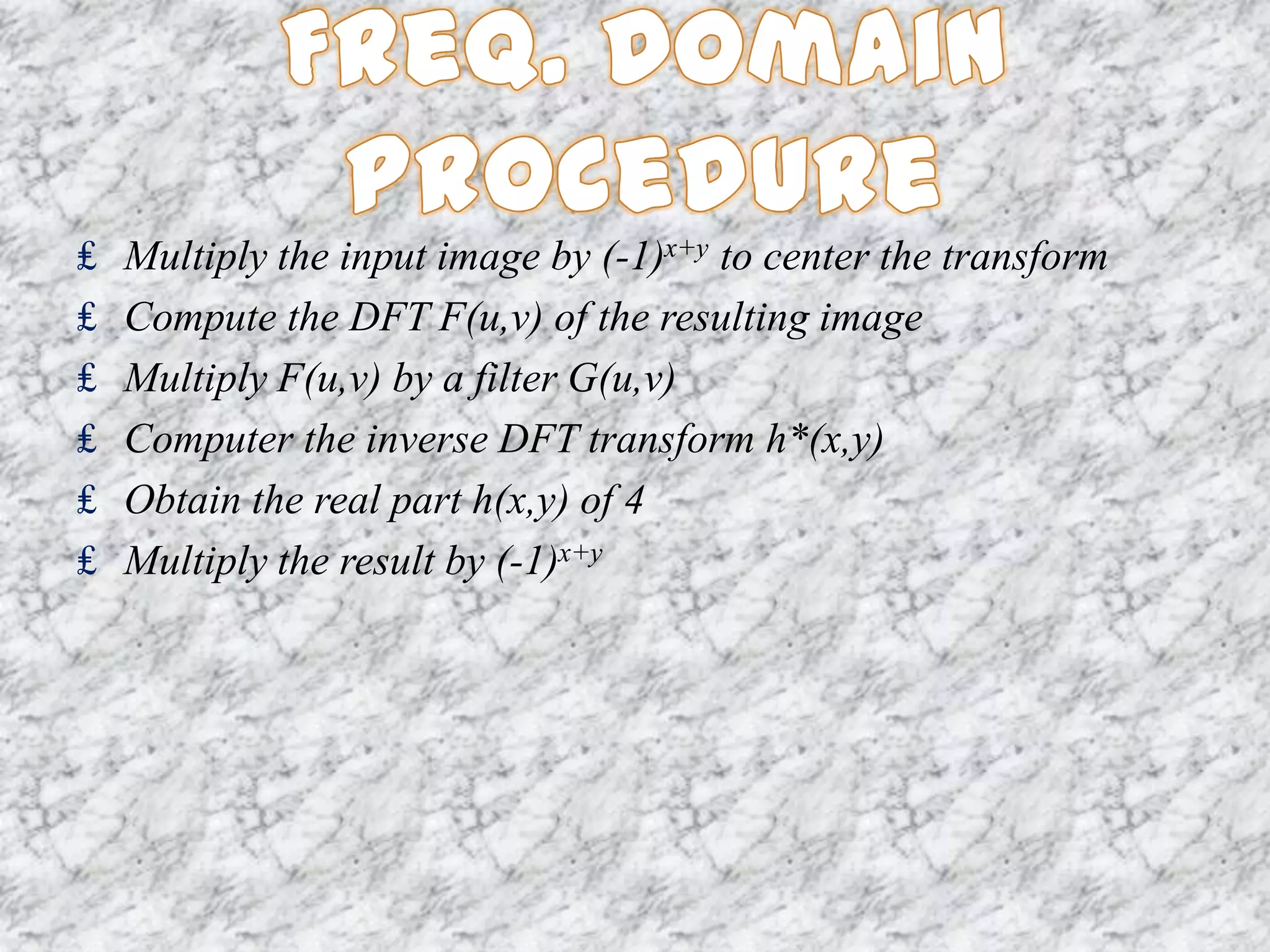
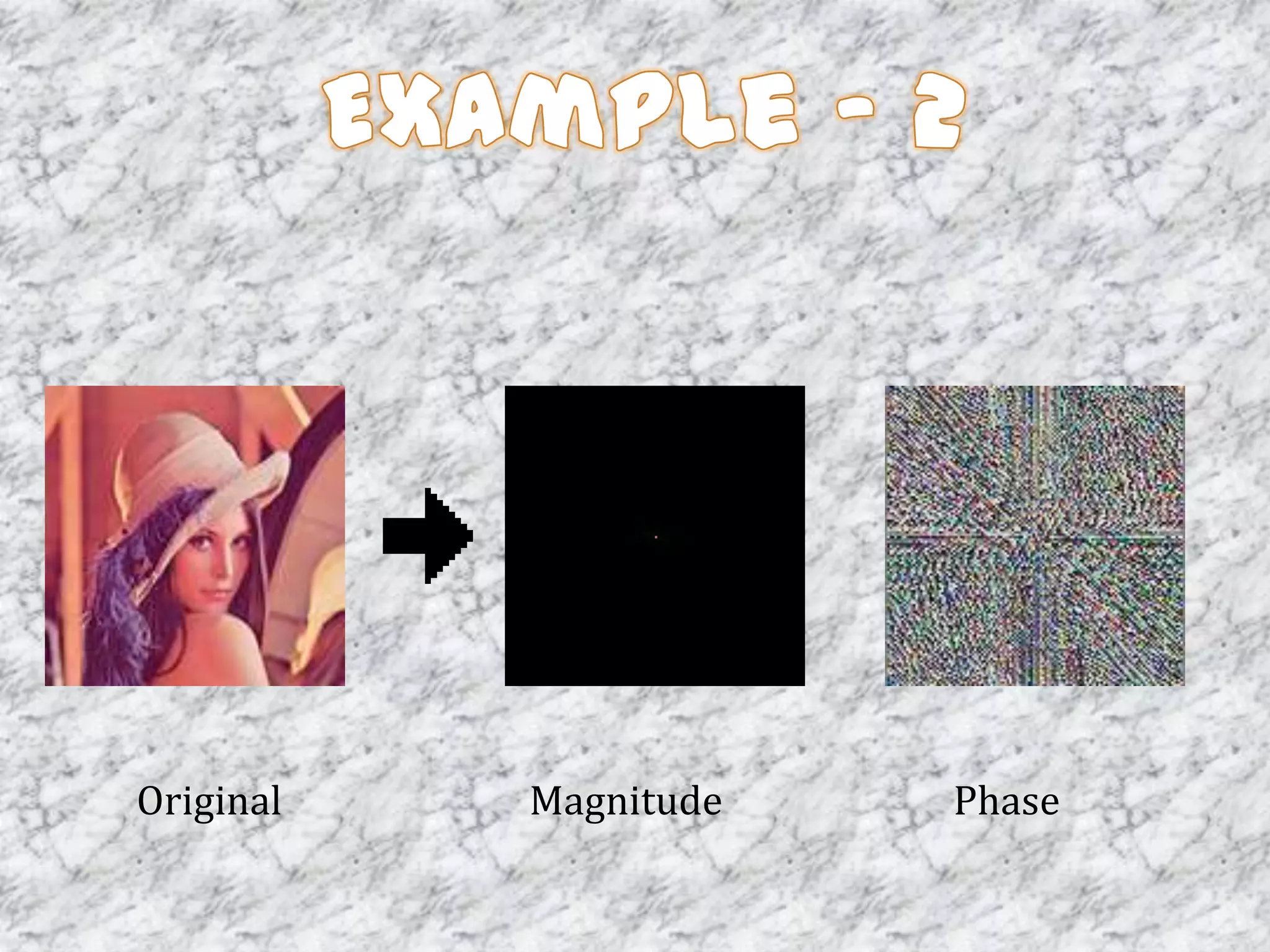
The document discusses the Fourier transform and its applications in image processing. The Fourier transform decomposes an image into its sine and cosine components, representing the spatial frequencies contained in the image. This converts the image from the spatial domain to the frequency domain. Key steps involve transforming the image to the frequency domain, applying image processing techniques, and computing the inverse transform. Applications include image analysis, filtering, reconstruction, and compression.