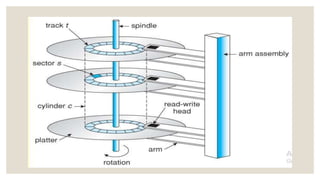
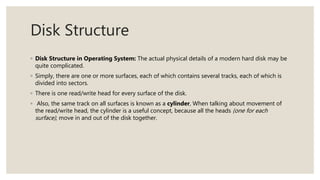
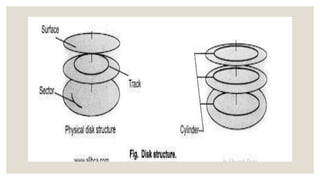
This document discusses storage management and disk structure. It covers mass storage structure including magnetic disks, disk platters, tracks, cylinders, sectors, and read/write heads. It then discusses disk structure in operating systems and concepts like surfaces, tracks, cylinders, and read/write heads. Finally, it covers scheduling and management techniques like long term, short term, and medium term schedulers as well as RAID structures and their benefits like increased reliability and performance.