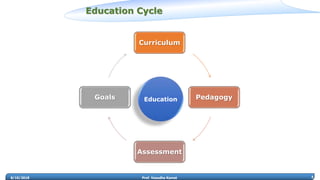
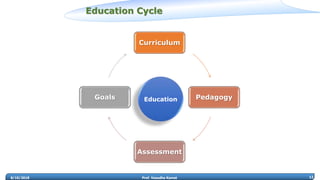
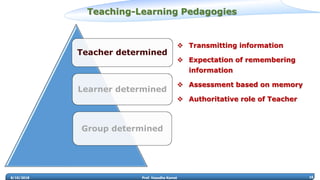
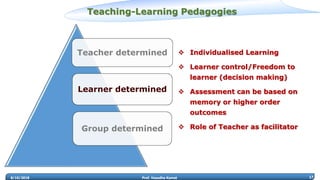
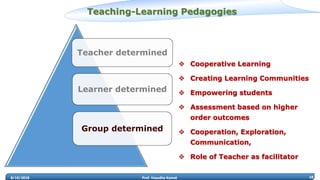
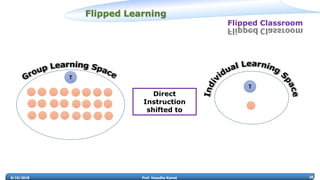
Prof. Vasudha Kamat discusses the need for rejuvenation in undergraduate education in India, emphasizing the integration of 21st-century learning skills such as complex problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity. She highlights the importance of adapting curricula to prepare students for the 4th industrial revolution, advocating for pedagogical methods that foster collaborative and experiential learning environments like makerspaces. The document also addresses frameworks for teaching strategies that encourage student engagement and self-directed learning.